Examples of aminoglycosides include:
- Gentamicin (generic version is IV only)
- Amikacin (IV only)
- Tobramycin
- Gentak and Genoptic (eye drops)
- Kanamycin
- Streptomycin
- Neo-Fradin (oral)
- Neomycin (generic version is IV only)
What are examples of aminoglycosides?
What are examples of aminoglycosides?
- Gentamicin (generic version is IV only)
- Amikacin (IV only)
- Tobramycin.
- Gentak and Genoptic (eye drops)
- Kanamycin.
- Streptomycin.
- Neo-Fradin (oral)
- Neomycin (generic version is IV only)
What are aminoglycosides used for?
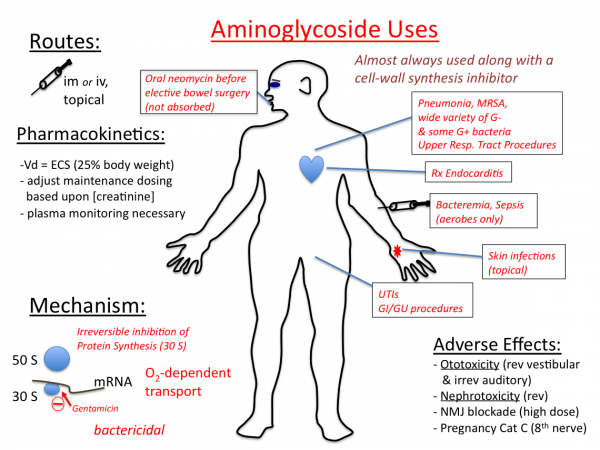
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics used to treat serious infections caused by bacteria that either multiply very quickly or are difficult to treat. Examples of aminoglycosides include: Gentamicin (generic version is IV only) Amikacin (IV only) Tobramycin.
What are aminoglycosides used to treat?
They are also effective in treating other bacterial infections, including:
- Complicated urinary tract infections
- Pneumonia and upper respiratory tract infections
- Endocarditis ( inflammation of the heart valves)
- Bacteremia, sepsis (life-threatening illness caused by your body's response to an infection)
- Skin infections and soft tissue infections
- Severe pelvic inflammatory disease
- Severe infections of the abdomen
- Tuberculosis
What are the classes of antibiotics?
Top 10 List of Generic Antibiotics
- amoxicillin
- doxycycline
- cephalexin
- ciprofloxacin
- clindamycin
- metronidazole
- azithromycin
- sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim
- amoxicillin and clavulanate
- levofloxacin
What are the 3 aminoglycosides?
In general, gentamicin, tobramycin and amikacin are used in similar circumstances, often interchangeably. Tobramycin may be the aminoglycoside of choice for use against P.
What is another name for aminoglycoside?
Kanamycin. Streptomycin. Neo-Fradin (oral)
Which are the aminoglycoside antibiotics?
A substance that works against many types of bacteria and includes streptomycin, gentamicin, and neomycin.
Is doxycycline a aminoglycosides?
Aminoglycosides are bactericidal against these organisms and the use of bacteriostatic agents, such as doxycycline or chloramphenicol has led to treatment failures (Dennis et al. 2001; Snowden and Stovall 2011). Inhaled tobramycin therapy in CF patients with chronic lung infection caused by P.
What are the two major side effects of aminoglycosides?
The major side effects of aminoglycosides are kidney injury, hearing impairment and vestibular toxicity.
Are there oral aminoglycosides?
Aminoglycosides in current use in the United States include streptomycin, gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, plazomicin and neomycin. The aminoglycosides are poorly absorbed orally and typically are given parenterally, either by intravenous or intramuscular injection.
Is Ciprofloxacin an aminoglycoside antibiotics?
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent structurally related to nalidixic acid. It has a broad antibac- terial spectrum that includesactivity against many aerobic gram-negative rods, including those resistant to aminoglyco- side and cephalosporin agents (6, 33).
Is vancomycin an aminoglycoside?
Another useful attribute of aminoglycosides is their synergism with antibiotics that inhibit bacterial cell wall biosynthesis, such as β-lactams and vancomycin. Finally, aminoglycosides have relatively predictable pharmacokinetic characteristics that allow them to be dosed to minimize their inherent toxicities.
What drug class is azithromycin?
Azithromycin belongs to the class of drugs known as macrolide antibiotics. It works by killing bacteria or preventing their growth. However, this medicine will not work for colds, flu, or other virus infections. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription.
Is clindamycin an aminoglycosides?
Clindamycin is a macrolide antibiotic, which, when used as an antiprotozoan agent, is always combined with other therapies for the treatment of falciparum malaria, toxoplasmosis, and babesiosis.
What drug class is Clindamycin?
Clindamycin is in a class of medications called lincomycin antibiotics.
Is Bactrim an aminoglycoside?
Aminoglycosides, like amikacin; Genoptic and Gentak (gentamicin); Aktob, Bethkis, Kitabis Pak, Tobi, Tobi Podhaler, Tobradex, and Tobrex (tobramycin); and Neo-Fradin (neomycin) Sulfonamides (sulfa drugs), such as Septra and Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim)
Are aminoglycosides the same as macrolides?
For example, aminoglycosides prevent protein translation, macrolides inhibit protein synthesis, and fluoroquinolones target DNA replication [3]. Aminoglycoside antibiotics are used to treat a wide variety of infections, and mainly target Gram-negative bacteria [4].
Are aminoglycosides beta lactams?
The beta lactam antibiotics (e.g. penicillins, cephalosporins) and the aminoglycosides (e.g. gentamicin) kill bacteria by different means. Combining a beta lactam with an aminoglycoside could, therefore, result in more effective treatment of patients with severe infection but with the side effects of both antibiotics.
What is the generic name of kanamycin?
What Is Kantrex? Kantrex (kanamycin) Injection is an aminoglycoside antibiotic used to treat serious infections caused by bacteria.
Is ampicillin an aminoglycoside?
The ampicillin-aminoglycoside combination had been given as initial treatment in 189 cases of septicaemia or meningitis. Treatment failed in 36 infections (20%), although all organisms were sensitive to one or both antibiotics.
What Is an Aminoglycoside?
An aminoglycoside is a type of very powerful antibiotic used to treat serious bacterial infections. Aminoglycosides are especially useful in treating infections caused by certain gram-negative bacteria that are responsible for infections such as meningitis, tuberculosis, and plague. The very first aminoglycoside, streptomycin, was discovered in 1944. Today there are several other aminoglycosides: amikacin, gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin, and tobramycin.
Why do people take aminoglycoside antibiotics?
Many patients receive aminoglycoside antibiotics to treat infections . In this lesson, learn the names of the different aminoglycoside antibiotics and some of the problems a patient may experience when taking one of these antibiotics. Create an account.
How do you know if Jack's kidneys are damaged?
Our kidneys are important in maintaining fluid and chemical balance, so we can tell if Jack's kidneys are being damaged if we see any changes in Jack's urine or blood. Some things we'll look at include:
Why do you need to watch for aminoglycosides?
And, patients who receive aminoglycosides must be watched carefully to prevent ototoxicity (problems with hearing and balance) and nephrotoxicity (problems with kidney function). To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account.
Why are aminoglycosides used in antibiotics?
Aminoglycosides are very useful antibiotics that help fight serious infections. But because they can hurt the patient as well as the bacteria, they are only used for certain serious infections.
What is Jack's goal with the antibiotic?
Preventing Toxicity. Jack is receiving an antibiotic that is potentially nephrotoxic and ototoxic, so our goal for Jack is that the infection will be treated without him suffering any toxicity.
Is gentamicin Jack ototoxic?
Because aminoglycosides can damage this nerve, the gentamicin Jack is receiving is considered a potentially ototoxic antibiotic.
What is the role of mRNA in genetic diseases?
The interference with mRNA proofreading has been exploited to treat genetic diseases that result from premature stop codons (leading to early termination of protein synthesis and truncated proteins). Aminoglycosides can cause the cell to overcome the stop codons, insert a random amino acid, and express a full-length protein. The aminoglycoside gentamicin has been used to treat cystic fibrosis (CF) cells in the laboratory to induce them to grow full-length proteins. CF is caused by a mutation in the gene coding for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator ( CFTR) protein. In approximately 10% of CF cases, the mutation in this gene causes its early termination during translation, leading to the formation of a truncated and non-functional CFTR protein. It is believed that gentamicin distorts the structure of the ribosome-RNA complex, leading to a mis-reading of the termination codon, causing the ribosome to "skip" over the stop sequence and to continue with the normal elongation and production of the CFTR protein.
What is the first class of antibiotic?
Streptomycin is the first-in-class aminoglycoside antibiotic. It is derived from Streptomyces griseus and is the earliest modern agent used against tuberculosis. Streptomycin lacks the common 2-deoxystreptamine moiety (image right, below) present in most other members of this class. Other examples of aminoglycosides include the deoxystreptamine-containing agents kanamycin, tobramycin, gentamicin, and neomycin (see below).
What is gentamicin used for?
The aminoglycoside gentamicin has been used to treat cystic fibrosis (CF) cells in the laboratory to induce them to grow full-length proteins. CF is caused by a mutation in the gene coding for the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator ( CFTR) protein.
How do aminoglycosides inhibit protein synthesis?
The inhibition of protein synthesis is mediated through aminoglycosides' energy-dependent, sometimes irreversible binding, to the cytosolic, membrane-associated bacterial ribosome (image at right). (Aminoglycosides first cross bacterial cell walls— lipopolysaccharide in gram-negative bacteria—and cell membranes, where they are actively transported.) While specific steps in protein synthesis affected may vary somewhat between specific aminoglycoside agents, as can their affinity and degree of binding, aminoglycoside presence in the cytosol generally disturbs peptide elongation at the 30S ribosomal subunit, giving rise to inaccurate mRNA translation and therefore biosynthesis of proteins that are truncated, or bear altered amino acid compositions at particular points. Specifically, binding impairs translational proofreading leading to misreading of the RNA message, premature termination, or both, and so to inaccuracy of the translated protein product. The subset of aberrant proteins that are incorporated into the bacterial cell membrane may then lead to changes in its permeability and then to "further stimulation of aminoglycoside transport". The amino sugar portion of this class of molecules (e.g., the 2-deoxystreptamine in kanamycins, gentamicins, and tobramycin, see above) are implicated in the association of the small molecule with ribosomal structures that lead to the infidelities in translation (ibid.). Inhibition of ribosomal translocation —i.e., movement of the peptidyl-tRNA from the A- to the P-site—has also been suggested. Recent single-molecule tracking experiments in live E. coli showed an ongoing but slower protein synthesis upon treatment with different aminoglycoside drugs. ( Spectinomycin, a related but distinct chemical structure class often discussed with aminoglycosides, does not induce mRNA misreading and is generally not bactericidal.)
What is the suffix for aminoglycosides?
Nomenclature. Aminoglycosides that are derived from bacteria of the Streptomyces genus are named with the suffix -mycin , whereas those that are derived from Micromonospora are named with the suffix -micin.
How much toxicity does an antibiotic have on the inner ear?
The incidence of inner ear toxicity varies from 7 to 90%, depending on the types of antibiotics used, susceptibility of the patient to such antibiotics, and the duration of antibiotic administration. Another serious and disabling side effect of aminoglycoside use is vestibular ototoxicity.
What is the name of the molecule that inhibits protein synthesis?
Aminoglycoside. Streptomycin. 2D line-angle representation. Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside ( sugar ).
Sar of Aminoglycosides
Streptomycin, neomycin, gentamicin, paromomycin, sisomicin, ribostamycin, tobramycin, nebramycin, dibekacin, amikacin, and kanamycin are all aminocyclitol-containing antibiotics. Streptomyces and Micromonospora species produce them.
Mechanism of Action
They only need a brief contact period and are most successful against rapidly multiplying susceptible bacterial populations.
Types of Aminoglycosides
There are several different antibiotics in the aminoglycoside class. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, plazomicin, streptomycin, neomycin, and paromomycin for clinical use in the United States.
Clinical Use
The recent appearance of infections caused by Gram-negative bacterial strains with advanced antimicrobial resistance trends has led doctors to reconsider their use of these antibiotics.
Common Side Effects
Aminoglycosides are extremely powerful antibiotics with serious side effects, particularly when taken orally or intravenously.
Warnings and Precautions
If you're allergic to aminoglycosides or any of the inactive ingredients in these products, stay away from them.
Why are aminoglycosides used in antibiotics?
Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics used to treat serious infections caused by bacteria that either multiply very quickly or are difficult to treat. Aminoglycosides are called bactericidal antibiotics because they kill bacteria directly. They accomplish this by stopping bacteria from producing proteins needed for their survival.
What are the health problems associated with sulfites?
Are allergic to sulfites (often found in certain wines and dried fruits) Have kidney or hearing problems, including problems with balance and uncontrollable eye movements. Have a disorder affecting the nerves and muscles, like multiple sclerosis or myasthenia gravis. Are 65 years of age or older.
What causes hearing loss?
Damage to the hearing structures in the ear, resulting in hearing loss. Damage to the inner ear, resulting in trouble maintaining balance. Kidney damage (noted by protein in the urine, dehydration, and low levels of magnesium) Paralysis of skeletal muscles.
What is the drug that prevents patients from moving during surgery called?
Certain drugs called neuromuscular blocking agents, often used to prevent patients from moving during surgery, enhance some of the side effects of aminoglycosides.
Where are aminoglycosides administered?
Because aminoglycosides are normally used to treat serious infections, they are typically administered into the veins of the body (intravenously, or IV). However, some aminoglycosides can be taken orally, or as ear or eye drops. Examples of aminoglycosides include:
Can aminoglycosides be taken by mouth?
Aminoglycosides are very powerful antibiotics, and their side effects can be severe — especially when taken by mouth or IV.
Can aminoglycoside cause paralysis?
Although side effects and their severity may vary from person to person, the higher the dose of an aminoglycoside you receive, or the longer the duration of use, the greater your risk of side effects.
Why is neomycin used in small amounts?
It is used to treat tularemia and plague and, with other antibiotics, to treat tuberculosis . Because of toxicity, neomycin and kanamycin are limited to topical use in small amounts. Neomycin is available for eye, ear, oral, and rectal use and as a bladder irrigant.
How long does it take for aminoglycosides to cause renal failure?
Patients receiving aminoglycosides for > 2 weeks and those at risk of vestibular and auditory toxicity should be monitored with serial audiography.
How long does aminoglycoside stay in the body?
Aminoglycosides are excreted by glomerular filtration and have a serum half-life of 2 to 3 hours; the half-life increases exponentially as the glomerular filtration rate falls (eg, in renal insufficiency, in older people).
What are the adverse effects of aminoglycosides?
Adverse Effects of Aminoglycosides. All aminoglycosides cause. Renal toxicity (often reversible) Vestibular and auditory toxicity (often irreversible) Prolongation of effects of neuromuscular blockers. Symptoms and signs of vestibular damage are vertigo and ataxia. Risk factors for renal, vestibular, and auditory toxicity are.
Which antibiotics inhibit protein synthesis?
Aminoglycosides (see table Aminoglycosides) have concentration-dependent bactericidal activity. These antibiotics bind to the 30S ribosome, thereby inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Spectinomycin is a bacteriostatic antibiotic chemically related to the aminoglycosides.
How often should serum creatinine be measured?
Serum creatinine is measured every 2 to 3 days, and if it is stable, serum aminoglycoside levels do not need to be measured again. Peak concentration is the level 60 minutes after an IM injection or 30 minutes after the end of a 30-minute IV infusion. Trough levels are measured during the 30 minutes before the next dose.
Is amikacin a beta-lactam?
Aminoglycosides are infrequently used alone, except when used for plague and tularemia . They are usually used with a broad-spectrum beta-lactam for severe infection suspected to be due to a gram-negative bacillary species.
What is an aminoglycoside antibiotic?
Chemically, the aminoglycoside antibiotics are characterized by an aminocyclitol group, with aminosugars attached to the aminocyclitol ring in glycosidic linkage. Because of minor differences in the position of substitutions on the molecules, there may be several forms of a single aminoglycoside. For example, gentamicin is a complex ...
What are the aminoglycosides of Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin (synthesized from kanamycin ), sisomicin, and netilmicin are aminoglycosides with extended spectra that include Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Why is glomerular filtration less in neonates?
Glomerular filtration rates differ between species and are often less in neonates, which may explain the greater sensitivity to aminoglycosides in newborn foals and puppies. Elimination varies with glomerular filtration changes associated with cardiovascular and renal function, age, fever, and several other factors.
How long does the effect of aminoglycosides last?
The effect generally lasts 2–8 hr after exposure and allows for dosing intervals longer than the half-lives of the drugs.
How do aminoglycosides kill bacteria?
They need only a short contact with bacteria to kill them and, as such, are concentration dependent in their actions. Their main site of action is the membrane-associated bacterial ribosome through which they interfere with protein synthesis. To reach the ribosome, they must first cross the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) covering (gram-negative organisms), the bacterial cell wall, and finally the cell membrane. Because of the polarity of these compounds, a specialized active transport process is required.
Why are mutants resistant to antibiotics?
2) Anaerobic bacteria and induced mutants are generally resistant, because they lack appropriate transport systems.
What happens if you get a vestibular injury?
Vestibular injury leads to nystagmus, incoordination, and loss of the righting reflex. The lesion is often irreversible, although physiologic adaptation can occur. Ototoxicity is not unusual in people, but relevance to veterinary patients is not clear.
Why do we combine aminoglycosides with beta lactam?
We sometimes combine aminoglycosides with a cell wall-active agent (like a beta lactam) in order to add synergistic action against Gram positive bacteria. Think of this strategy as the beta lactam opening the cell wall door for the aminoglycoside to go in and fulfill its death mission from within the bacteria itself.
What is the peak concentration of aminoglycoside?
For example, when using gentamicin or tobramycin, target peaks for serious or life threatening infections can range from 6-10 mcg/mL. A UTI may only require peaks of 4-6 mcg/mL. And we only shoot for 3 - 5 mcg/mL with Gram positive syner gy.
What does PAE mean in antibiotics?
In a nutshell, PAE means that the antibiotic's inhibitory action extends beyond the period of exposure. So even AFTER the aminoglycoside concentration falls below the MIC, the bacteria are not able to grow. Many antibiotics show some degree of PAE.
What is aminoglycoside used for?
Aminoglycosides can be used for a wide range of infections. From double covering for Pseudomonas aeruginosa in hospital-acquired pneumonias, to treating urinary tract infections, to synergistic coverage for endocarditis. But their use can come with a price…. Part II: Aminoglycosides and Concentrations.
Which aminoglycosides are the most popular?
For the remainder of this post, let’s focus on gentamicin and tobramycin since those are the most popular aminoglycosides.
What drugs fall under aminoglycosides?
That way we’re all on the same page. When we talk about aminoglycosides, we’re referring to gentamicin, tobramycin, and amikacin .
Why do we need to reach a certain concentration of aminoglycosides?
Remember, they're concentration-dependent drugs, so we need to reach a certain concentration in the serum in order to stop those nasty bacteria.

Overview
Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside (sugar). The term can also refer more generally to any organic molecule that contains amino sugar substructures. Aminoglycoside antibiotics display bactericidal activity against …
Mechanisms of action
Aminoglycosides display concentration-dependent bactericidal activity against "most gram-negative aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacilli" but not against gram-negative anaerobes and most gram-positive bacteria. They require only short contact time, and are most effective against susceptible bacterial populations that are rapidly multiplying. These activities are attributed to a pri…
Routes of administration
Since they are not absorbed from the gut, they are administered intravenously and intramuscularly. Some are used in topical preparations for wounds. Oral administration can be used for gut decontamination (e.g., in hepatic encephalopathy). Tobramycin may be administered in a nebulized form.
Clinical use
The recent emergence of infections due to Gram-negative bacterial strains with advanced patterns of antimicrobial resistance has prompted physicians to reevaluate the use of these antibacterial agents. This revived interest in the use of aminoglycosides has brought back to light the debate on the two major issues related to these compounds, namely the spectrum of antimicrobial susceptibility and toxicity. Current evidence shows that aminoglycosides do retain …
Adverse effects
Aminoglycosides can cause inner ear toxicity which can result in sensorineural hearing loss. The incidence of inner ear toxicity varies from 7 to 90%, depending on the types of antibiotics used, susceptibility of the patient to such antibiotics, and the duration of antibiotic administration.
Another serious and disabling side effect of aminoglycoside use is vestibular ototoxicity. This leads to oscillopsia (gaze instability) and balance impairments that impact all aspects of an indivi…
Contraindication for specific diseases
Aminoglycosides can exacerbate weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis, and use is therefore avoided in these patients.
Aminoglycosides are contraindicated in patients with mitochondrial diseases as they may result in impaired mtDNA translation, which can lead to irreversible hearing loss, tinnitus, cardiac toxicity, and renal toxicity. However, hearing loss and tinnitus have also been observed in some …
External links
• MedlinePlus drug information - Aminoglycosides (Systemic)
• Science Daily Bacterial 'Battle for Survival' - Rhodostreptomycin