- A single mutation can create a gap (very common).
- Unequal crossover in meiosis can lead to insertion or deletion of strings of bases.
- DNA slippage in the replication procedure can result in the repetition of a string.
- Retrovirus insertions.
- Translocations of DNA between chromosomes.
Why are gaps important when aligning sequences?
When aligning sequences, introducing gaps in the sequences can allow an alignment algorithm to match more terms than a gap-less alignment can. However, minimizing gaps in an alignment is important to create a useful alignment.
What are the different types of sequencing gaps?
Sequence-coverage gaps Sequencing gaps occur, under the simplest condition, where no sequence reads have been sampled for a particular portion of the genome. 2. Segmental duplication-associated gaps
What is a gap in the genome?
Essentially, a gap occurs if something happens in our genome that can't be explained by uniformity. Since our genome is highly complicated, you can expect gap is also more than just mis-sequencing. The gap you mention is the sequence-coverage gaps mentioned below. This paper has a section about the types of gaps.
What is the gap information used for?
The gap information is usually used in the form of indel frequency profiles, which is more specific for the sequences to be aligned. ClustalW and MAFFT adopted this kind of gap penalty determination for their multiple sequence alignments.
What does gaps mean in blast?
A space introduced into an alignment to compensate for insertions and deletions in one sequence relative to another. To prevent the accumulation of too many gaps in an alignment, introduction of a gap causes the deduction of a fixed amount (the gap score) from the alignment score.
What are composed of contigs and gaps?
Scaffolds are composed of contigs and gaps. A contig is a contiguous length of genomic sequence in which the order of bases is known to a high confidence level.
How do you remove a gap in a sequence?
0:200:50Premiere Pro CC: Close Gaps (Remove Spaces Between Clips)YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clip2020 all you need to do is drag out a selection over the area where you want to close the gaps. OrMore2020 all you need to do is drag out a selection over the area where you want to close the gaps. Or you can select everything by dragging everything over or using command a come to the sequence menu.
What are affine gaps?
An affine gap penalty is assigned to gaps in an alignment (i.e., indels). In such a penalty, a gap of length is penalized by , where and are constants chosen in advance.
Why there are gaps in in contigs?
Gaps between contigs These gaps occur if the Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) library screened has low complexity, meaning it does not contain a high number of STS or restriction sites, or if certain regions were less stable in cloning hosts and thus underrepresented in the library.
How many contigs are in the human genome?
The data for the public working draft of the human genome contains roughly 400,000 initial sequence contigs in ∼30,000 large insert clones.
What causes gaps in sequence alignment?
A gap in one of the sequences simply means that one or more amino acid residues have been deleted from the sequence, or we could also say that there is an insertion in the second sequence.
Are gaps a bad thing in a sequence alignment?
When aligning sequences, introducing gaps in the sequences can allow an alignment algorithm to match more terms than a gap-less alignment can. However, minimizing gaps in an alignment is important to create a useful alignment. Too many gaps can cause an alignment to become meaningless.
How do you remove gaps from multiple sequence alignment?
Did you know how to delete swiftly columns with gaps from a multiple alignment? To do this open a needed file with a multiple alignment by UGENE. Then select "Edit -> Remove columns of gaps…" in the right-click menu. After that a dialog appears allowing you to specify a number of gaps in columns to be deleted.
What is the difference between constant linear and affine gap penalties?
Therefore, affine gap penalties are length dependent (unlike linear gap penalties which are length independent) and use a gap opening penalty, o, and a gap extension penalty, e. A gap of length l is then given a penalty o + (l-1)e. So that gaps are discouraged, o and e are almost always negative.
What is Blosum in bioinformatics?
In bioinformatics, the BLOSUM (BLOcks SUbstitution Matrix) matrix is a substitution matrix used for sequence alignment of proteins. BLOSUM matrices are used to score alignments between evolutionarily divergent protein sequences. They are based on local alignments.
What is pairwise sequence alignment?
Pairwise Sequence Alignment is used to identify regions of similarity that may indicate functional, structural and/or evolutionary relationships between two biological sequences (protein or nucleic acid).
What is a contig quizlet?
Contig. - a set of two or more overlapping DNA fragments that form a contiguous stretch of DNA.
How are contigs assembled?
The fragments are assembled by identifying overlapping sequence fragments based on local string matching and alignment methods that identify the overlapping ends of the sequence fragments and statistical methods that evaluate the significance of the matched sequence ends.
What information could we use to construct scaffolds from contigs?
When creating a draft genome, individual reads of DNA are second assembled into contigs, which, by the nature of their assembly, have gaps between them. The next step is to then bridge the gaps between these contigs to create a scaffold. This can be done using either optical mapping or mate-pair sequencing.
What is synteny and how do we use it in genomics and genetics?
But what is synteny? In classical genetics, syntenic genes were originally defined as genes that lie on the same chromosome. Today, however, biologists usually refer to synteny as the conservation of blocks of order within two sets of chromosomes that are being compared with each other.
What does gap mean in genetics?
You're not wrong but gap can mean more than that. A good recent reference is this paper: Genetic variation and the de novo assembly of human genomes. Essentially, a gap occurs if something happens in our genome that can't be explained by uniformity. Since our genome is highly complicated, you can expect gap is also more than just mis-sequencing.
What is a sequencing gap?
Sequencing gaps occur, under the simplest condition, where no sequence reads have been sampled for a particular portion of the genome.
What is a biology stack exchange?
Biology Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for biology researchers, academics, and students. It only takes a minute to sign up.
What is a muted gap?
Muted gaps are defined as regions that are inadvertently closed in an assembly but that actually show additional or different sequences in the vast majority of individuals. 5. Allelic variation gaps. Some regions of a genome also show extraordinary patterns of allelic variation, often reflecting deep evolutionary coalescence.
Can the word "gap" be used in genomics?
1. The word ‘gap’ can be used both loosely and in specific genomic contexts, as listed by @Student T. The usage that seems to relate to your question — Sequence Coverage Gaps — is quite nicely illustrated in the Wikipedia entry on ‘Contig’.
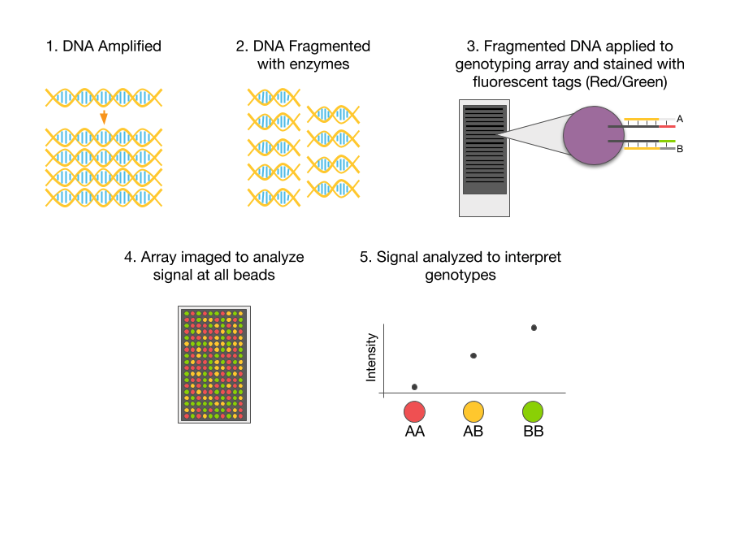
How is DNA sequenced?
DNA sequencing requires breaking up a long DNA strand into numerous short segments, each of which is sequenced individually to determine the arrangement of the four different components, called bases, that make up the complete molecule. The individual segments’ sequences are then pieced together by computer algorithms that identify identical, overlapping sequences on the individual pieces.
How many bases can be in a DNA sequence?
At first, the DNA segments could be no longer than a couple hundred bases, though by the late 2000s technological developments had increased that limit to 700 bases. Unfortunately, segments this short make it extremely difficult to locate the overlapping areas that permit algorithms to stitch together the pieces into a full DNA sequence. Regions of DNA in which the same sequence of bases is repeated dozens or even hundreds of times have particularly bedeviled geneticists, leading to gaps in those parts of the human genome.
Why is long read sequencing important?
Because numerous disorders have been linked to repetitive regions of DNA, such as the neurodegenerative diseases ALS and Huntington’s disease, long-read sequencing has the potential to dramatically expand scientists’ understanding of how such illnesses develop.
What would happen if we didn't have cutting edge genetics?
Without the sort of cutting-edge computational tools being developed in the lab of IRP investigator Adam Phillippy, significant portions of our genetic code would be extremely difficult to sequence efficiently and accurately.
Is long read sequencing error prone?
No technology is perfect, though, and long-read sequencing is actually more error-prone than some older techniques. To prevent mistakes, geneticists sequence the same DNA multiple times. The computational tools developed in Dr. Phillippy’s lab examine the results of all the sequencing attempts in order to determine which base truly occupies each location in a DNA molecule. Moreover, even long-read sequencing techniques require DNA strands to be broken up into shorter segments, albeit much longer segments than older technologies. Consequently, Dr. Phillippy’s algorithms must also look for areas of overlap in the individual pieces in order to put them back together in the right order.
Why are gaps important?
A gap is one or more spaces in a single string of a given alignment and usually corresponds to an insertion or deletion in one or more sequences within the alignment. The insertion or deletion can be an artifact of sequencing chemistry and not indicative of the authentic DNA sequence. According to the European Bioinformatics Institute, there are several other potential explanations for:
How many sequences can I align?
You must have a minimum of 2 sequences to perform an alignment. For comparing 2 sequences you’ll need to perform a “pairwise” alignment. Most programs will align 3 or more sequences at a time and will require a different algorithm e.g. MUSCLE or one of the Clustal algorithms like ClustalW.
What is a “consensus” sequence?
A consensus sequence usually appears at the top of your alignment worktable, and each nucleotide (or amino acid) of the sequence is based on the residue that appears at that position most frequently in your aligned sequence . For instance, if you align 5 sequences, and the nucleotides at position 20 are A, A, T, A, and G, then the consensus sequence will have an A at position 20. The use of consensus sequences can be very useful when examining evolutionary relationships between sequences with high degrees of identity. It is also useful to use the consensus to identify potential gaps in your aligned sequences.
How do I know my sequence data is good?
Regardless of your methods to obtain your sequences, the overall success and accuracy of your sequence alignments and subsequent analyses depend entirely on the quality of your sequence data. Things like solid upstream preparations, primer design and reagent quality can make you a hero….or a zero. So, in scientific terms, the quality of sequence data is directly proportional to the success and robustness of your alignments, you know, ‘garbage in – garbage out’ .
What is the identity of amino acids?
Identity is the degree of correlation between 2 un-gapped sequences, and indicates that the amino acids or nucleotides at a particular position are an exact match. Generally, an identity of 25% or higher suggests the potential for similarity of function; an identity of 18-25% implies similarity of structure or function.
What happens when there is an unequal crossover in meiosis?
Unequal crossover in meiosis can lead to insertion or deletion of strings of bases.
How is raw data scored?
In most cases, your raw data is “scored” and cleaned up by the sequencer software resulting in your finished, exportable sequence. Quality can be scored many different ways, depending on the technology and chemistry used, and utilizes criteria such as signal strength, number of contiguous nucleotides read and the ease with which each nucleotide is determined, e.g. a clean, unobstructed peak in a chromatograph. Other than As, Ts, Cs and Gs, it’s important to understand other codes that may appear in your data (click here for the complete list of IUPAC codes).
Why are gaps important in DNA sequencing?
Genetic sequence alignment - In bioinformatics, gaps are used to account for genetic mutations occurring from insertions or deletions in the sequence, sometimes referred to as indels. Insertions or deletions can occur due to single mutations, unbalanced crossover in meiosis, slipped strand mispairing, and chromosomal translocation. The notion of a gap in an alignment is important in many biological applications, since the insertions or deletions comprise an entire sub-sequence and often occur from a single mutational event. Furthermore, single mutational events can create gaps of different sizes. Therefore, when scoring, the gaps need to be scored as a whole when aligning two sequences of DNA. Considering multiple gaps in a sequence as a larger single gap will reduce the assignment of a high cost to the mutations. For instance, two protein sequences may be relatively similar but differ at certain intervals as one protein may have a different subunit compared to the other. Representing these differing sub-sequences as gaps will allow us to treat these cases as “good matches” even though there are long consecutive runs with indel operations in the sequence. Therefore, using a good gap penalty model will avoid low scores in alignments and improve the chances of finding a true alignment. In genetic sequence alignments, gaps are represented as dashes (-) on a protein/DNA sequence alignment.
What happens if the end gaps are penalized in one sequence 1 but not in sequence 2?
If the end gaps are penalized in one sequence 1 but not in sequence 2, it produces an alignment that contains sequence 2 within sequence 1.
What is a gap penalty?
A Gap penalty is a method of scoring alignments of two or more sequences. When aligning sequences, introducing gaps in the sequences can allow an alignment algorithm to match more terms than a gap-less alignment can. However, minimizing gaps in an alignment is important to create a useful alignment. Too many gaps can cause an alignment ...
What are the two types of errors that occur during DNA replication?
These two replication errors are insertions and deletions of single DNA bases from the DNA strand (indels). Indels can have severe biological consequences by causing mutations in the DNA strand that could result in the inactivation or over activation of the target protein. For example, if a one or two nucleotide indel occurs in a coding sequence the result will be a shift in the reading frame, or a frameshift mutation that may render the protein inactive. The biological consequences of indels are often deleterious and are frequently associated with human pathologies such as cancer. However, not all indels are frameshift mutations. If indels occur in trinucleotides, the result is an extension of the protein sequence that may also have implications on protein function.
Why is gap important in alignment?
The notion of a gap in an alignment is important in many biological applications, since the insertions or deletions comprise an entire sub-sequence and often occur from a single mutational event. Furthermore, single mutational events can create gaps of different sizes.
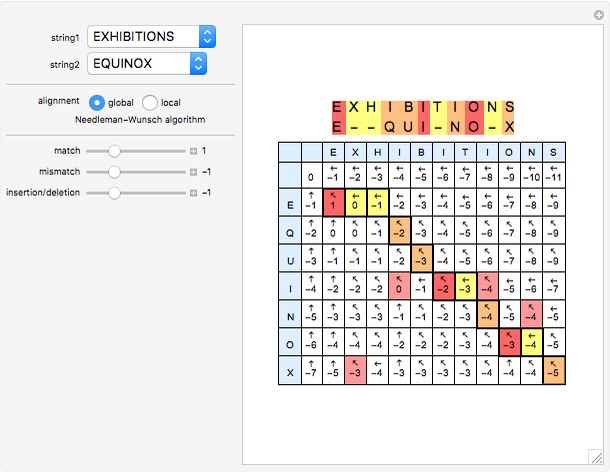
What is the score of a DNA match if each match was worth 1 point?
Aligning two short DNA sequences, with '-' depicting a gap of one base pair. If each match was worth 1 point and the whole gap -1, the total score: 7 − 1 = 6.
What is the simplest type of gap penalty?
This is the simplest type of gap penalty: a fixed negative score is given to every gap, regardless of its length. This encourages the algorithm to make fewer, larger, gaps leaving larger contiguous sections.
