Mendel Gregor Johann Mendel was a scientist, Augustinian friar and abbot of St. Thomas' Abbey in Brno, Margraviate of Moravia. Mendel was born in a German-speaking family in the Silesian part of the Austrian Empire and gained posthumous recognition as the founder of the modern scienc…Gregor Mendel
How many laws does Mendel have?
The 3 laws of Mendel they are the most important statements of biological inheritance. Gregorio Mendel, a monk and Austrian naturalist, is considered the father of Genetics. Through his experiments with plants, Mendel discovered that certain traits were inherited following specific patterns.
What is the fourth law of Mendel?
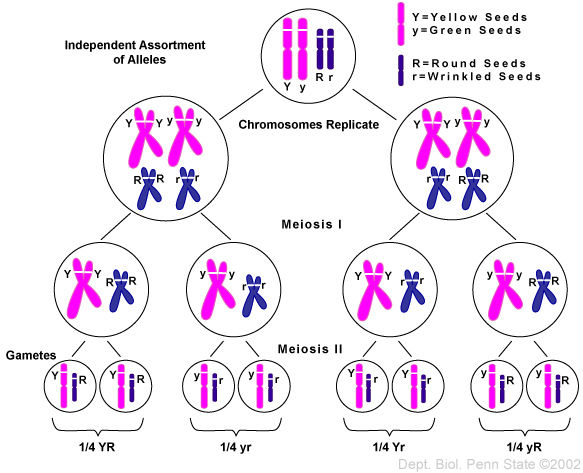
What is Mendel’s 4th Law? Mendel’s fourth postulate is called the principle of independent assortment.It states that “when more than one pair of characters are involved in a cross , factor pairs assort independent of each other.”
What are Mendels basic laws of herdity?
Mendel's principle of dominance is realized in the heredity of a considerable number of characters among both animals and plants. In accordance with this principle, hybrid offspring have visibly the character of only one parent or the other, though they transmit those of both parents. 3. In other cases the hybrid has a distinctive character of ...
How do Mendels laws relate to probability?
How do Mendel's laws relate to probability? The laws of segregation and probability are based on random events. The chance that two particular events will occur together during meiosis is determined as any other random event (roll of dice, coin toss, etc.)
See more
What were Mendel's laws?
Mendel's Laws of Heredity are usually stated as: The Law of Segregation: Each inherited trait is defined by a gene pair. ... The Law of Independent Assortment: Genes for different traits are sorted separately from one another so that the inheritance of one trait is not dependent on the inheritance of another.More items...
What is Mendel 1st law?
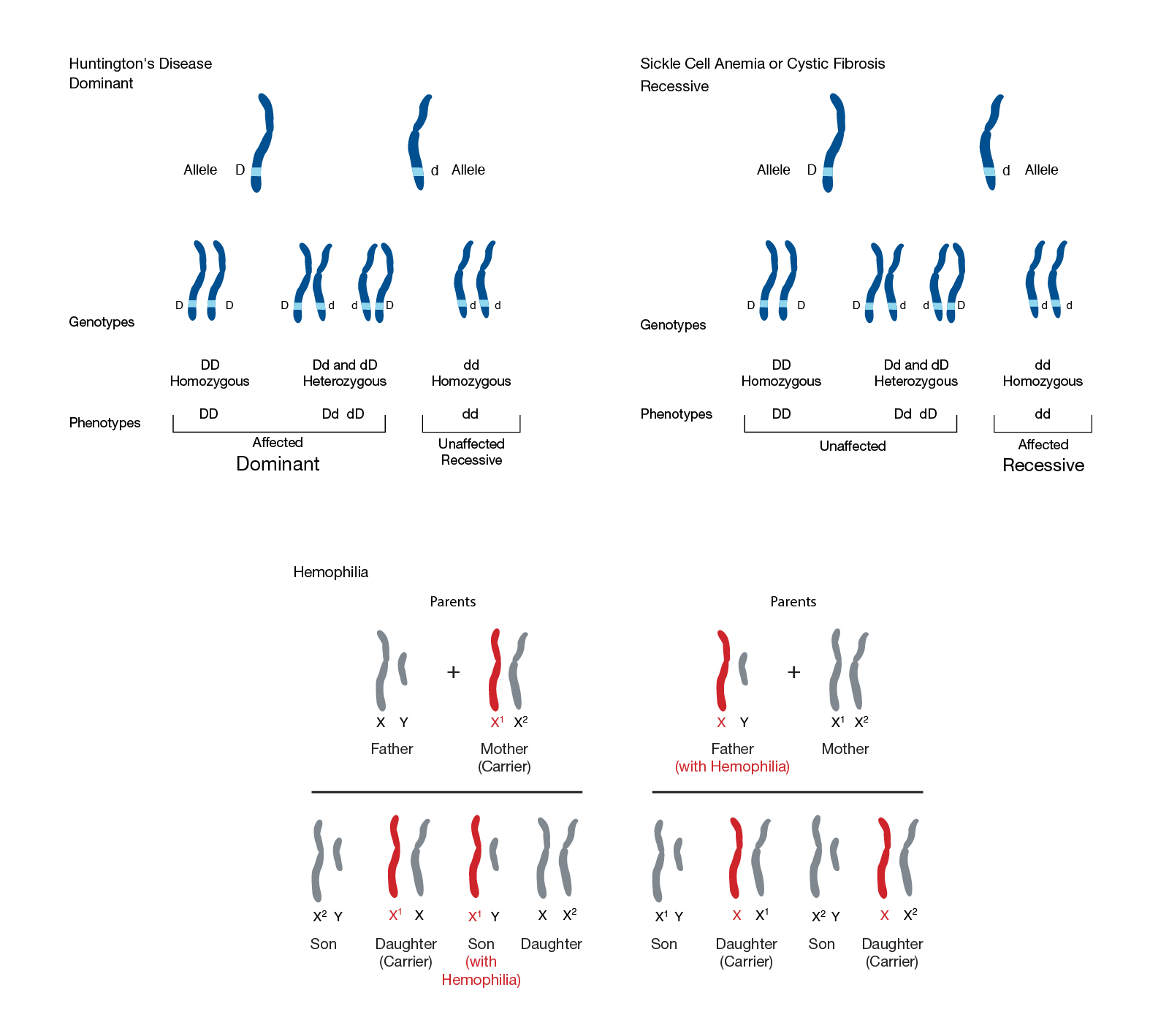
Mendel's First Law - the law of segregation; during gamete formation each member of the allelic pair separates from the other member to form the genetic constitution of the gamete.
What is Mendel's 1st and 2nd law?
Mendel's first law describes the segregation of the two copies of alleles of a particular gene into the gametes. Mendel's second law describes the independent assortment of alleles of different genes from each other during the formation of gametes.
What are the laws of Mendel Class 10?
Mendel's law of inheritance are as follows: Law of segregation: During gamete formation, the alleles for each gene segregate from each other so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene. Law of independent assortment: Genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes.
What is Mendel's 2nd law?
Mendel's Second Law - the law of independent assortment; during gamete formation the segregation of the alleles of one allelic pair is independent of the segregation of the alleles of another allelic pair.
What is second law of inheritance?
Solution : Mendel's second law of inheritance (law of segrega- tion) :
(1) Mendel's law of segregation is second law of inheritance. It states that when a pair of contrasting characters occur together in a hybrid, they remain together without mixing with each other and segregate during the formation of gametes.
What are the 3 principles of Mendelian genetics?
The key principles of Mendelian inheritance are summed up by Mendel's three laws: the Law of Independent Assortment, Law of Dominance, and Law of Segregation.
What does Mendel's third law of inheritance say?
Mendel's Third Law: The law of dominance Mendel concluded that different traits are inherited independently of each other, there is no relationship between them. This means that the inheritance pattern of one trait will not affect the inheritance pattern of another (as long as the genes are not linked).
What is Mendel's law PDF?
The set of three laws, proposed by Gregor J. Mendel in the mid-1860s, to explain the biological inheritance or heredity is known as Mendel's laws. These laws are the law of segregation, law of independent assortment, and law of dominance, and they form the core of classical genetics to date.
What law did Mendel not give?
So, the correct option is 'Law of incomplete dominance'.
What are the 2 components to the law of segregation?
First, it defines an allele. Second, it states that organisms inherit one allele from each parent. Third, it states that gametes only carry one allele for each trait.
What is law of segregation in simple words?
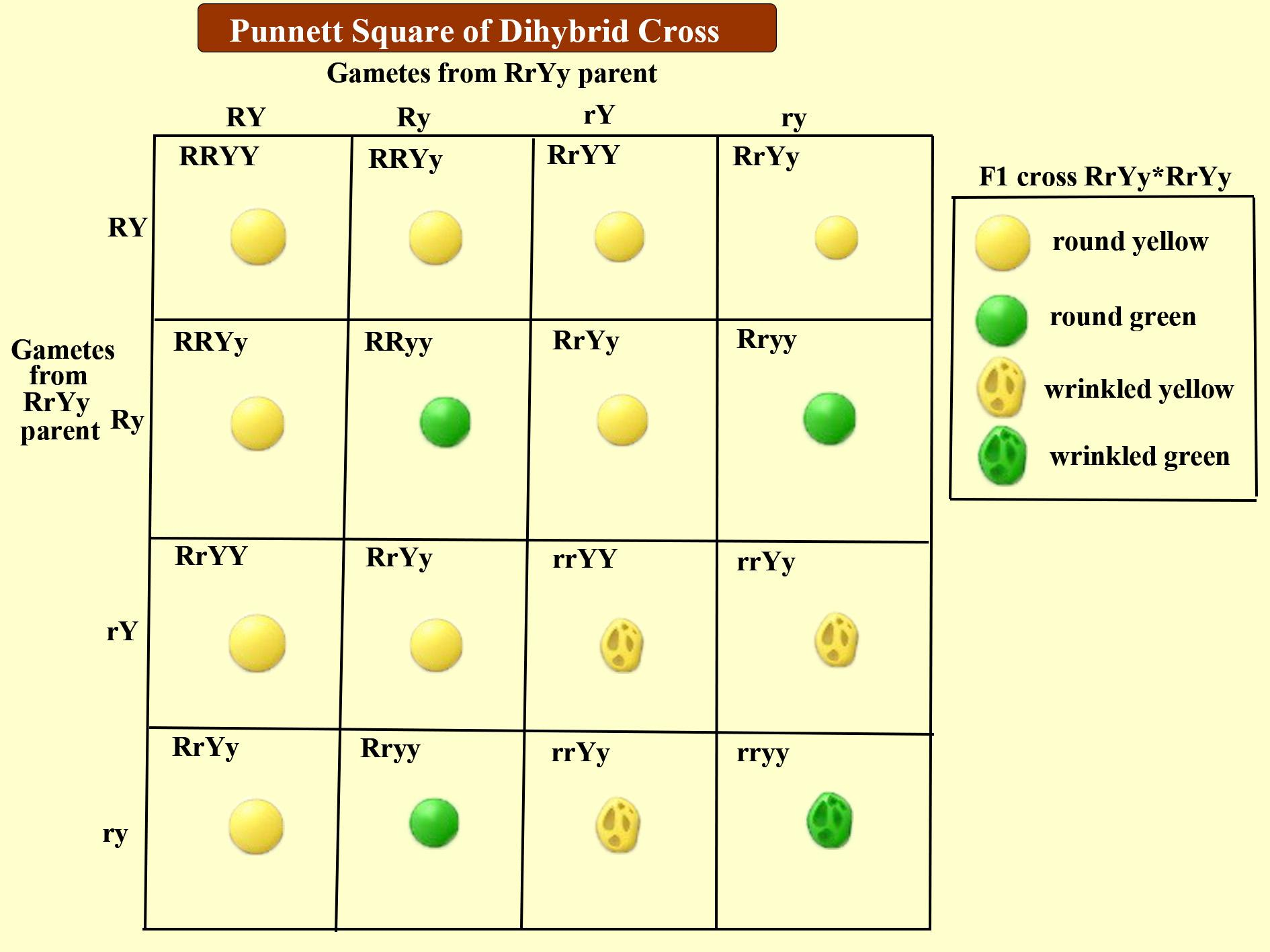
When an organism makes gametes, each gamete receives just one gene copy, which is selected randomly. This is known as the law of segregation. A Punnett square can be used to predict genotypes (allele combinations) and phenotypes (observable traits) of offspring from genetic crosses.
What is the difference between law of segregation and law of Independent Assortment?
The law of segregation describes how alleles of a gene are segregated into two gametes and reunite after fertilization. The law of independent assortment describes how alleles of different genes independently segregate from each other during the formation of gametes.
Which law of Mendel is shown in F1 generation?
Correct Option - A law of dominance Explanation - The character which is expressed in F1 generation is dominant and the recessive character is suppressed in F1 generation.
What are the three laws of inheritance proposed by Mendel?
The three laws of inheritance proposed by Mendel include: Law of Dominance Law of Segregation Law of Independent Assortment
Which is the universally accepted law of inheritance?
Law of segregation is the universally accepted law of inheritance. It is the only law without any exceptions. It states that each trait consists of...
Why is the law of segregation known as the law of purity of gametes?
The law of segregation is known as the law of purity of gametes because a gamete carries only a recessive or a dominant allele but not both the all...
Why was the pea plant used in Mendel’s experiments?
Mendel picked pea plants in his experiments because the pea plant has different observable traits. It can be grown easily in large numbers and its...
What was the main aim of Mendel’s experiments?
The main aim of Mendel’s experiments was: To determine whether the traits would always be recessive. Whether traits affect each other as they are i...
What are Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance?
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance are certain laws or statements which describe the mechanism of transmission of certain characteristics from one genera...
What is the importance of Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance?
1. It helps us to determine the new combinations in the progeny of hybrids and to predict their frequency. 2. The law of independent assortment hel...
Why did Mendel select pea plant for his experiments?
Mendel had selected pea plant for his experiments because of the following reasons: 1. Pure varieties of pea were available. 2. Pea plants showed a...
Which law of Mendel is most important and why?
Out of the three laws proposed by Mendel, the Law of Segregation is the most important and acceptable law as it has no exceptions. This law states...
What are Mendel’s three important conclusions?
By analysing the results of his experiments, Mendel proposed the following three laws: 1. Law of Dominance 2. Law of Segregation 3. Law of Independ...
Which two laws did Mendel propose?
So, from the results of monohybrid cross, Mendel proposed two laws of inheritance, i.e., Law of Dominance and Law of Segregation.
Which law of inheritance did Mendel propose?
So, from the results of dihybrid cross, Mendel had proposed the third law of inheritance, i.e., Law of Independent Assortment.
What are Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance?
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance are certain laws or statements which describe the mechanism of transmission of certain characteristics from one generation to another in an organism.
Why did Mendel study peas?
Gregor Mendel carried out his experiments on the garden pea plant, i.e., Pisum sativum L.because of the following reasons: 1. The plants are primarily self-pollinated. But cross pollination is also easily possible . 2. Pure varieties of pea were available.
How many pairs of contrasting characters did Mendel study?
Intermediate characters are not formed easily. Mendel selected seven pairs of contrasting traits which always appear in two opposing conditions, one dominant and the other recessive, which are as follows: Fig: Table containing the seven pairs of contrasting characters in pea plant studied by Mendel.
What are the steps of Mendel's experiment?
First he produced the parent generation as a true-breeding generation. Continuous self pollination (also called selfing) resulted into homozygous generation or true-breeding generation. 2. He followed standard hybridisation techniques ...
Why is Mendel's law of inheritance important?
Following are the importance of Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance: 1. It helps us to determine the new combinations in the progeny of hybrids and to predict their frequency. 2. The law of independent assortment helps to confirm the concept of genes. 3.
What are Mendel's laws?
Mendel's laws, also known as Mendelian genetics, are the set of basic rules about genetic inheritance. In other words, how the different possibilities (alleles) that they exist for a specific position (locus) of a gene is inherited. These laws were postulated by an Austrian Augustinian monk called Gregor Mendel .
Why are Mendel's laws important?
Nevertheless, Mendel's laws are very important for genetics and still applying . If we go to the field of health, Mendel's laws are fulfilled in what we know as monogenic or Mendelian diseases - cystic fibrosis, color blindness.
What is codominance in a heterozygous state?
2. Codominance : in the heterozygous state there is no recessive allele, but both behave as dominant, such as in intermediate inheritance, but unlike the latter, both features are manifested without mixing . An example of codominance is the color of begonias (Illustration 3) or the ABO system. People with blood group AB present antigens A and B simultaneously. Both alleles are being expressed in the heterozygote individual.
What is Mendel's second law?
Mendel's Second Law or principle of segregation : defends that alleles of the same locus segregate (separate) giving rise to two classes of gametes in equal proportion, half of the gametes with the dominant allele (A) and half with recessive allele (a). This conclusion was obtained by selfing the F1 (heterozygous) from the crossing of two parents of pure lines that differ in one feature (Figure 1) and obtaining a second generation of descendants (F2) of which ¾ of the phenotypes were equal to the phenotype of the dominant homozygous parent (yellow) and ¼ was equal to the phenotype of the recessive homozygous parent (green). The segregation of alleles in the production of gametes ensures genetic variation in the offspring. In figure 5 we can see the explanation represented visually.
What are Mendelian inheritance patterns?
Mendelian inheritance patterns explain how a character is inherited and what determines individuals phenotype (what is shown). As we will see in the section on “exceptions to Mendel's laws”, these patterns are not applicable for all loci in the genome.
How long did Mendel's peas self grow?
Mendel, to ensure that he was working with pure lines , subjected all his pea varieties to selfing for two years (two successive generations). The different plant varieties differed in the following features (Illustration 1):
What is intermediate dominance?
Intermediate dominance : there is no dominant allele or recessive allele. In heterozygous individuals the features corresponding to the two alleles are mixed. An example of intermediate dominance is carnation color. When we cross a red carnation (C R ) with a white carnation (C W ) (Illustration 2).
What did Mendel study?
Mendel studied the genetics of pea plants, and he traced the inheritance of a variety of characteristics, including flower color, flower position, seed color, and seed shape. To do so, he started by crossing pure-breeding parent plants with different forms of a characteristic, such as violet and white flowers. Pure-breeding just means that the plant will always make more offspring like itself, when self-fertilized over many generations.
How did Mendel find his model of inheritance?
One thing I find pretty amazing is that Mendel was able to figure out his entire model of inheritance simply from his observations of pea plants. This wasn't because he was some kind of crazy super genius, but rather, because he was very careful, persistent, and curious, and also because he thought about his results mathematically (for instance, the ratio). These are some of the qualities of a great scientist—ones that anyone, anywhere, can develop!
What is the dominant allele in Mendel's model?
In Mendel's model, parents pass along “heritable factors," which we now call genes, that determine the traits of the offspring. Each individual has two copies of a given gene, such as the gene for seed color ( Y gene) shown below. If these copies represent different versions, or alleles, of the gene, one allele—the dominant one—may hide the other allele—the recessive one. For seed color, the dominant yellow allele Y hides the recessive green allele y.
What trait did Mendel call the trait that was visible in the generation?
Conventional wisdom at that time would have predicted that the hybrid flowers should be pale violet—that is, that the parents' traits should blend in the offspring. Instead, Mendel’s results showed that the white flower trait had completely disappeared. He called the trait that was visible in the generation (violet flowers) the dominant trait, and the trait that was hidden or lost (white flowers) the recessive trait.
What clue did Mendel use to crack the puzzle of inheritance?
As it turned out, the ratio was a crucial clue that let Mendel crack the puzzle of inheritance. Let's take a closer look at what Mendel figured out.
What results did Mendel find in his crosses for flower color?
When he gathered and planted the seeds produced in this cross, Mendel found that percent of the plants in the next generation, or generation, had violet flowers.
What are the characteristics of Mendel's peas?
Seven characteristics of Mendel’s pea plants are illustrated. The flowers can be purple or white. The peas can be yellow or green, or smooth or wrinkled. The pea pods can be inflated or constricted, or yellow or green. The flower position can be axial or terminal. The stem length can be tall or dwarf.
What was Mendel's third law based on?
When proposing this Third Law, Mendel based it on the results obtained in his second theory (remember that DNA still hadn’t been discovered).
What did Mendel do with his peas?
Mendel prepared a simple experiment. In his orchard, there were two varieties of peas: purple and white. Subsequently, he made several crosses between purple lines: As a result, he obtained an entire first generation of plants with 100% purple flowers (Aa) You’ll be wondering what the letters in brackets are.
What earned Mendel his nickname of the “father of genetics”?
What earned Mendel his nickname of the “father of genetics” was his brilliant (and correct) interpretation of the results that he observed.
What is the law of dominance?
It states the following – If one parent has two copies of allele X – the dominant allele, and the other parent has two copies of allele x – the recessive allele, in that case, the child inherits Xx genotype exhibiting the dominant phenotype .
Which law states that the segregation of alleles into two daughter cells during the second stage of meio?
The third law stated by Mendel is as follows – The segregation of the allele pair into two daughter cells during the second stage of meiosis division does not affect the way in which the other allele pair gets separated or segregated.
What Were Mendel's Experiments?
- Mendel's experiments were a series of experiments carried out by Mendel on 33 varieties of pea plant. They involved lots of laborious work, but ultimately helped Mendel form his laws of inheritance. An inbred line (of anything, including peas) is one that is homozygous for all of its traits .For the same gene we have two possibilities (alleles). If these alleles are the same in the s…
Mendel's Patterns of Inheritance
- Mendelian inheritance patterns explain how character is inheritedand what determines the phenotype they acquire. As we will see in the section on “exceptions to Mendel's laws”, these patterns do not apply to all loci in the genome.
Mendel's Laws
- Thanks to all the information he obtained from his experiments, Mendel postulated three important laws that help us understand genetics. However, this recognition was obtained long after he published his work in 1858. This is despite the fact that he made handwritten copies for all the recognized scientists in the area. Unfortunately, nobody unders...
6 Exceptions to Mendel's Laws
- The first exceptions to Mendel's Laws were described in the early 20th century. Today many phenomena are known that are not governed by Mendel's laws. Among them we want to highlight: