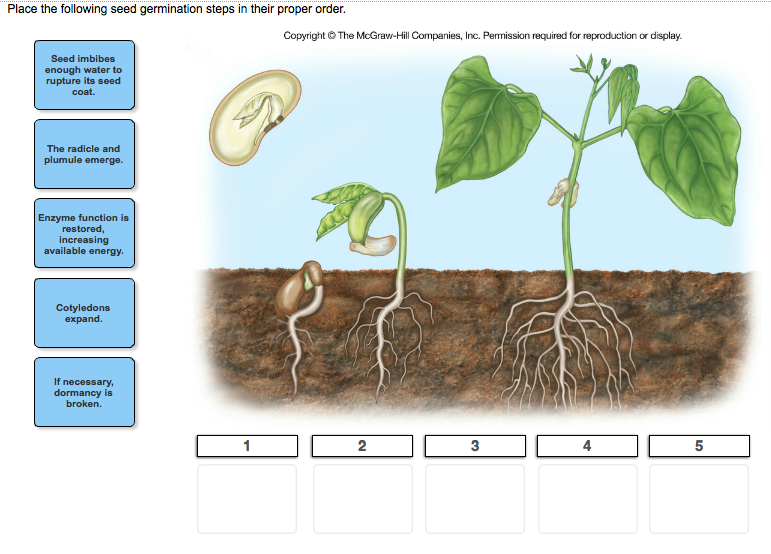
The three stages of seed germination are:
- Imbibition: the seed intakes water, swells, and extends its first root (radicle)
- Dormancy: the seed digests the nutrition inside of it and sprouts.
- Growth: the seed grows exponentially into adulthood.
What are the 3 general stages of seed germination?
There are three major stages in the germination process. These are the imbibition of water, increased metabolic activity, and swelling of cells. Germination begins with the seed's imbibition (absorption) of water. Most dormant seeds have 5 to 10 percent moisture content.
What are the stages of germination?
The process of seed germination includes the following five changes or steps: imbibition, respiration, effect of light on seed germination, mobilization of reserves during seed germination, and role of growth regulators and development of the embryo axis into a seedling.
What are the 3 stages of plant growth?
Become A Better Gardener: Learn the 3 Plant Growth Stages Now!Seed stage (Seed germination)Vegetative stage (Growth)Reproductive, flowering and fruit stage.
What are the 3 stages of a seed?
The Three Stages of Seed GerminationImbibition: the seed intakes water, swells, and extends its first root (radicle)Dormancy: the seed digests the nutrition inside of it and sprouts.Growth: the seed grows exponentially into adulthood.
What is the first stage of germination?
imbibitionThe first stage of germination, called imbibition, occurs when the seed is exposed to water. The seed absorbs water though its seed coat.
What is the second stage of germination?
Stage Two - Digestion of Stored Food and Translocation of Nutrients. In the second stage of germination, the seed breaks down food that had been stored during dormancy.
What stage is after germination?
The germination stage is where the plant grows from the seed. In the right environment (which we'll discuss below), seeds start to produce the familiar parts including roots, stems, and leaves. The vegetative stage occurs after the plant has sprouted and produced its first green tendrils.
What stage comes after germination?
The stages that plants go through are from seed to sprout, then through vegetative, budding, flowering, and ripening stages. Similarly, the nutritional needs of people and plants change as they grow.
What is germination of a plant?
The beginning of the growth of a seed into a seedling is known as germination. All seeds need water, oxygen and the right temperature to germinate. Dormancy is a state of suspended animation in which seeds delay germination until conditions are right for survival and growth.
How do you germinate seeds Fast 3 simple steps?
2:5413:38How To Germinate Seeds Fast | 3 Simple Steps - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFor 12 hours okay so we've dropped our seeds in water we're going to let them soak for 12 hours andMoreFor 12 hours okay so we've dropped our seeds in water we're going to let them soak for 12 hours and we let them soak for 12 hours in darkness.
What are 7 steps of seed germination?
Table of Contents(i) Imbibition:(ii) Respiration:(iii) Effect of Light on Seed Germination:(iv) Mobilization of Reserves during Seed Germination and Role of Growth Regulators:(v) Development of Embryo Axis into Seedling:
What are the 6 stages of germination?
Learn The Six Plant Growth StagesSprout. Each seed contains a small parcel of nutrients that is all they need to germinate and begin growing their first pair of leaves.Seedling. ... Vegetative. ... Budding. ... Flowering. ... Ripening.
What are the 4 processes that happen during seed germination?
Seed germination is vital stage in plant development and can be considered as a determinant for plant productivity. It begins by water imbibition, mobilization of food reserve, protein synthesis and consequence radicle protrusion [1].
What are the four stages of seed germination?
The Seed Germination Process : Imbibition: water fills the seed. The water activates enzymes that begin the plant's growth. The seed grows a root to access water underground. The seed grows shoots that grow towards the sun. The shoots grow leaves and begin photmorphogenesis.
What are the stages of germination?
Within the process of germination, it is necessary that the seed has a certain amount of water available so that it can leave the state of dormancy and begin its growth and development, in this case the seed goes through three vital stages: Hydration stage: This stage is carried out through the inhibition process, ...
Which stage of germination is the most important?
Hydration stage: This stage is carried out through the inhibition process, which refers to the absorption of water, this is the most important phase of germination, since without the presence of water, no Germination can occur.
What are the parts of an embryo?
Parts of the embryo 1 Radicular: It is a first rudimentary root that has the embryo. From this root secondary roots and hairs will be developed to improve the absorption of nutrients. 2 Plumule: It is a bud that is on the opposite side to the radicle. 3 Hipocotilo: It is the space between the radicle and the plumule. This part will become a stem 4 Cotyledon: It is the first or two first leaves of the embryo of a flowering plant. According to the number of cotyledons that the seed has, it is divided into monocots, which will have a single leaf, while the dicotyledons develop two cotyledons.
What is the first leaf of a flowering plant?
Cotyledon: It is the first or two first leaves of the embryo of a flowering plant. According to the number of cotyledons that the seed has, it is divided into monocots, which will have a single leaf, while the dicotyledons develop two cotyledons.
What is the process of a seed developing into a new plant?
Germination is a process by which a seed develops into a new plant.
What is the embryo of a plant?
The embryo: It is basically a miniature plant, from the upper part of the embryo the leaves and the stem will emerge, and from the lower part the roots of the future plant will be formed ; the embryo constitutes a small part of the seed, in the seeds of almost all the plants, the embryo stops growing when it is very small and enters a state of “suspended animation” or dormancy, and while the embryo sleeps inside the seed, This can survive long periods of cold, heat or drought.
What happens during the first phase of embryonic development?
In this first phase there is an intense absorption of water that will allow different tissues to hydrate and the embryo will swell until it breaks the shell that covers it and the embryonic root grows towards the ground to extract the nutrients and minerals .
A Seed Is Born: Pre-Germination
Earlier than we are able to leap into the primary stage, we have to have a fast overview of what occurs earlier than the seed even will get to that stage. Understanding the place the seed comes from and what precisely a seedling incorporates will assist us higher perceive and clarify steps that happen later.
First Stage of Seed Germination: Imbibition
The primary stage of seed germination is Imbibition, or water uptake. On this stage, the seedling begins to soak up water and swell in dimension.
Second Stage of Seed Germination: The Dormant Part
This section can also be known as the “Latent Part.” At this level, the seed has swelled with water and prolonged its little child radicle root. As soon as that happens, the seed appears to enter a dormant state, therefore the identify.
Third Seed Germination Part: Development into Maturity
The third and final section of seed germination is each the longest and the broadest. The third section is often outlined by the child leaves (cotyledons) falling off and the grownup, or “true leaves,” proceed rising.
The Surroundings Impacts the Seed
Earlier than planting your backyard, it’s important to take into account that seeds reply to their environment. Relying on the plant selection, all seeds develop to maturity with the right temperature, water consumption, oxygen, and lightweight.
The Three Phases of Seed Germination: Abstract
We coated quite a lot of data as we speak, together with scientific phrases and different issues which will have left your head spinning. Let’s summarize the details:
What happens in the second stage of germination?
In the second stage of germination, the seed breaks down food that had been stored during dormancy. Lipids and carbohydrates (glucose in monocots, starch in dicots) break down into sucrose, and this sucrose and broken-down protein components are shifted to a location in the seed where they can be used for energy and new proteins for the growing plant.
What is the process of a plant growing from a seed to a mature plant?
Germination takes a seed from dormancy to seedling. Germination is the process by which a plant grows from a smaller seed (or "germ") into a larger, mature plant. Germination can be epigeal, above the surface, or hypogeal, below the surface, but the seed undergoes the same process either way. From initial absorption of water to ...
What are the two types of seeds?
Types of Seeds. Seeds of angiosperms (flowering plants) can be divided into two broad categories: monocotyledons and dicotyledons, more commonly referred to as monocots and dicots. The cotyledon is the embryo's first leaf, and a monocot has one of these embryo leaves while a dicot has two.
What is the process of germination?
Germination, the sprouting of a seed, spore, or other reproductive body, usually after a period of dormancy. The absorption of water, the passage of time, chilling, warming, oxygen availability, and light exposure may all operate in initiating the process. In the process of seed germination, water is absorbed by the embryo, ...
Where does germination occur?
Germination sometimes occurs early in the development process; the mangrove ( Rhizophora) embryo develops within the ovule, pushing out a swollen rudimentary root through the still-attached flower. In peas and corn (maize) the cotyledons (seed leaves) remain underground (e.g., hypogeal germination ), while in other species ( beans, sunflowers, etc.) the hypocotyl (embryonic stem) grows several inches above the ground, carrying the cotyledons into the light, in which they become green and often leaflike (e.g., epigeal germination ).
How do environmental factors affect seedlings?
Environmental factors play an important part not only in determining the orientation of the seedling during its establishment as a rooted plant but also in controlling some aspects of its development. The response of the seedling to gravity is important. The radicle, which normally grows downward into the soil, is said to be positively geotropic. The young shoot, or plumule, is said to be negatively geotropic because it moves away from the soil; it rises by the extension of either the hypocotyl, the region between the radicle and the cotyledons, or the epicotyl, the segment above the level of the cotyledons. If the hypocotyl is extended, the cotyledons are carried out of the soil. If the epicotyl elongates, the cotyledons remain in the soil.
Why do seeds not germinate?
The seeds of many plants that endure cold winters will not germinate unless they experience a period of low temperature, usually somewhat above freezing. Otherwise, germination fails or is much delayed, with the early growth of the seedling often abnormal. (This response of seeds to chilling has a parallel in the temperature control of dormancy in buds .) In some species, germination is promoted by exposure to light of appropriate wavelengths. In others, light inhibits germination. For the seeds of certain plants, germination is promoted by red light and inhibited by light of longer wavelength, in the “far red” range of the spectrum. The precise significance of this response is as yet unknown, but it may be a means of adjusting germination time to the season of the year or of detecting the depth of the seed in the soil. Light sensitivity and temperature requirements often interact, the light requirement being entirely lost at certain temperatures.
How does light affect seedlings?
Light affects both the orientation of the seedling and its form. When a seed germinates below the soil surface, the plumule may emerge bent over, thus protecting its delicate tip, only to straighten out when exposed to light (the curvature is retained if the shoot emerges into darkness).
What is the dormancy of a seed?
Dormancy is brief for some seeds—for example, those of certain short-lived annual plants. After dispersal and under appropriate environmental conditions, such as suitable temperature and access to water and oxygen, the seed germinates, and the embryo resumes growth.
How does water affect the growth of seed cells?
In the process of seed germination, water is absorbed by the embryo, which results in the rehydration and expansion of the cells. Shortly after the beginning of water uptake, or imbibition, the rate of respiration increases, and various metabolic processes, suspended or much reduced during dormancy, resume.
What is the process of seed germination?
Germination is when a seed begins to grow into a seedling. All seeds require water, oxygen, and a temperature that is right for Germination. In a state of suspended animation, dormancy occurs when seeds wait until the right conditions are met for sprouting.
What are the factors that affect germination?
For example, several external factors affect seed germination, including light, water, temperature, and oxygen. Similarly, the viability of seeds, dormancy, and maturity of seeds are also internal factors.
What is the light that is needed for seed germination?
Seeds of plants like lettuce and tobacco, for instance, require light for Germination and are known as positive photoblastic seeds. Conversely, onion seeds and lily seeds germinate when they are dark since they are negatively photoblastic.
What is hypogeal germination?
Hypogeal Germination: In this type of Germination, seeds remain beneath the soil as the epicotyl elongates rapidly. It occurs in many monocotyledonous seeds as well as dicotyledonous seeds. An epicotyl that is elongated and uncurved evolves during this phase of Germination. These leaves extend above the soil surface. During this phase, the cotyledons remain beneath the soil surface. When planted monocotyledonous seeds, such as maize, the coleoptile (plumule covering) grow straight down into the soil. During the coleoptile, plumbers elongate and emerge from the soil. When they grow further, they rupture the coleoptile. As a result, the coleorhiza (covering of the radicle) and the radicle grow downward. Coleorhiza ruptures after a certain amount of time due to the continued growth of the radicle. As soon as the primary root is formed, a fibrous foot is attached.
How do seeds grow?
Introduction to steps of seed germination, types, and stages: Once the seed has been moved to a new location and covered with dirt, it can germinate. It is through Germination that seeds grow into new plants. However, environmental conditions must be present for the seed to germinate. It is usually determined by water availability, depth of planting, and temperature. In a process known as imbibition, seeds fill with water when there is plenty of water available. As a result of the water activating particular proteins, called enzymes, seed growth occurs. Firstly, the seed grows roots below the soil to get water under the earth. Once the roots appear, the seed starts to grow shoots above ground. Next, a seed sends a shoot to the surface and grows leaves to absorb sunlight. In a process known as photomorphogenesis, the leaves grow toward the light source. The Germination of seeds and growth of embryos from seed to seedling under favorable conditions is known as seed germination. The process by which different plant species emerge from a single seed into plants is also known as seed germination.
What is the process of transforming a seed into a plant?
Germination refers to the process of transforming a seed into a plant.
When do dicotyledons germinate?
By rapid growth of the hypocotyl, these plants germinate when the cotyledons emerge above ground. Epigeal Germination occurs in the seeds of many dicotyledonous plants, including beans, castor, sunflowers, gourds, and cucumbers. Germination occurs during which the hypocotyl overgrows and becomes curved. A seed emerges from the ground during this stage. Straightening occurs once the hypocotyl rises above the soil surface. The seed coat falls off the cotyledon, and it becomes green. It is now time for the epicotyl to grow and the plumule to produce green leaves. The cotyledons fall ultimately.