Common Causes
This squeezing can change how the spinal cord functions and cause stiffness, pain and numbness in the neck, arms and legs. In severe cases, cervical stenosis can cause major body weakness or even paralysis if the spinal cord is damaged.
Related Conditions
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease include: Guillain-Barré syndrome This disease is characterized by ascending paralysis. Charcot Marie Tooth disorder This disease is characterized by ascending muscle weakness and atrophy. Myasthenia gravis This disease is characterized by progressive fluctuating muscle weakness starting in the facial or eye muscles.
Does cervical stenosis always lead to paralysis?
The shortness of breath is due to the affect on lung function. Rarely does adult scoliosis alone cause paralysis or other severe neurologic problems, but it can be associated with lumbar stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal or tube where the nerves lay), which can result in nerve irritation, leg pain and possibly weakness.
What is the disease is characterized by ascending paralysis?
Some of the main causes of paralysis are:
- sudden weakness on one side of the face, with arm weakness or slurred speech – a stroke or transient ischaemic attack (TIA or "mini-stroke")
- sudden weakness on one side of the face, with earache or face pain – Bell's palsy
- temporary paralysis when waking up or falling asleep – sleep paralysis
Can scoliosis eventually cause paralysis?
What are some causes of paralysis?

Which are the disease of descending paralysis?
Miller Fisher syndrome (MFS) is a rare variant of Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) which usually presents with descending paralysis. Common symptoms are ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and areflexia.
What is descending flaccid paralysis?
A descending flaccid paralysis develops. Bulbar palsies present first as paralysis of the motor functions of the cranial nerves. 3 Eventually, the larger muscles of the arms and legs are affected, proximally to distally.
Is Guillain-Barre ascending or descending?
GBS is characterized by the rapid onset of numbness, weakness, and often paralysis of the legs, arms, breathing muscles, and face. Paralysis is ascending, meaning that it travels up the limbs from fingers and toes towards the torso.
What can cause ascending paralysis?
The list of differential diagnoses for ascending flaccid paralysis and acute ataxia is extensive: 1) neuropathies such as Guillain-Barre syndrome, diptheric polyneuropathy, porphyrias and meningoradiculopathies, 2) neuromuscular junction disorders such as botulism and myasthenia gravis, 3) myopathies due to electrolyte ...
Can you walk with flaccid paralysis?
When a person has flaccid paralysis, they cannot initiate any voluntary movement on their affected side. If flaccidity lasts too long without treatment, the muscles can begin to atrophy. Flaccidity is also often associated with low muscle tone (hypotonia) after stroke.
What is the most common cause of acute flaccid paralysis?
The most common etiology of acute flaccid paralysis in this entire population was neuroparalytic snake envenomation, which was responsible for 51.9% of the cases, followed by the Guillain Barre syndrome (33.1%). These two etiologies accounted for 85% of all patients.
What mimics Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Other neurological conditions, which commonly mimic these GBS variants include: brainstem stroke, myasthenia gravis, botulism, infective or inflammatory rhombencephalitis and bacterial, carcinomatous or lymphomatous meningitis.
Is myasthenia gravis a descending paralysis?
Abstract. Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder characterized by weakness in specific muscle groups, especially the ocular and bulbar muscles. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) presents with ascending paralysis and areflexia, often secondary to an infection.
What does descending and ascending mean?
Descending can also be thought of as climbing down the stairs of numbers starting from the highest value. Moving down the slide is descending. The opposite of descending order is known as ascending order, in which the numbers are arranged from lower value to higher value.
What causes sudden temporary paralysis?
temporary paralysis when waking up or falling asleep – sleep paralysis. paralysis after a serious accident or injury – a severe head injury or spinal cord (back) injury. weakness in the face, arms or legs that comes and goes – multiple sclerosis or, less commonly, myasthenia gravis or hypokalaemia periodic paralysis.
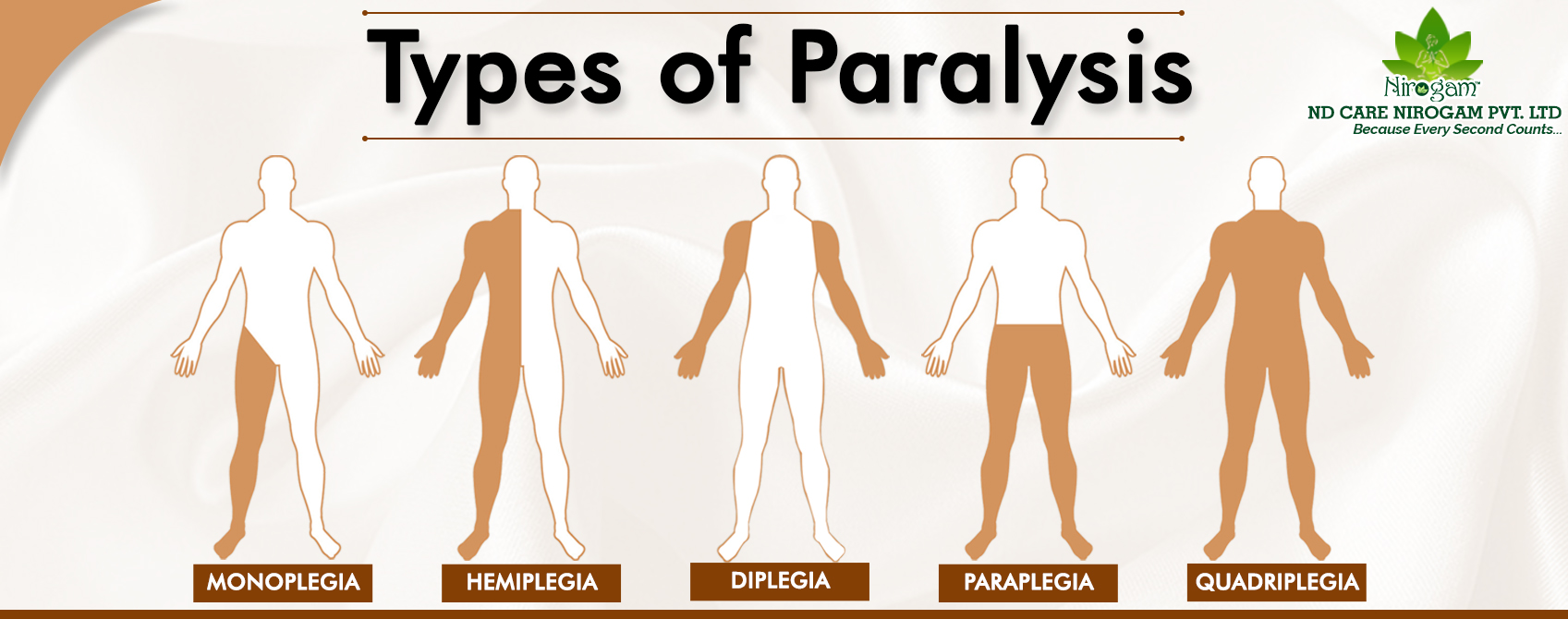
What are the four types of paralysis?
What Are the Four Types of Paralysis?Monoplegia.Hemiplegia.Paraplegia.Quadriplegia/tetraplegia.
How do you test for Guillain-Barré syndrome?
The clinical diagnosis of GBS needs to be confirmed by cerebrospinal fluid analysis and nerve conduction studies. Lumbar puncture is indicated in every case of suspected GBS.
What are the symptoms of flaccid paralysis?
SymptomsSudden muscle weakness in the arms or legs.Neck weakness.Some other symptoms that patients may have include drooping eyelids or a facial droop, and difficulty swallowing or slurred speech.
What does flaccid mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of flaccid : not firm or stiff also : lacking normal or youthful firmness flaccid muscles.
Where does flaccid paralysis affect the body?
Flaccid paralysis may affect one or more limbs but more commonly affects the lower limbs. Because it is a lower motor neurone disease the reflexes are also absent and the muscles involved waste. These muscles may be very tender with muscle spasm in the early stages.
What is the difference between flaccid and spastic paralysis?
Flaccid paralysis causes your muscles to shrink and become flabby. It results in muscle weakness. Spastic paralysis involves tight and hard muscles. It can cause your muscles to twitch uncontrollably, or spasm.
What causes paralysis in the brain?
Paralysis Caused by Conditions. Paralysis is most often caused by strokes, usually from a blocked artery in your neck or brain. It also can be caused by damage to your brain or spinal cord, like what can happen in a car accident or sports injury.
What is localized paralysis?
Localized paralysis affects just one specific area, like your face, hands, feet, or vocal cords.
What is the difference between monoplegia and diplegia?
Monoplegia is a kind of generalized paralysis that affects just one limb. Diplegia affects the same area on both sides, like both arms, both legs, or both sides of your face . Hemiplegia affects just one side of your body and is usually caused by a stroke, which damages one side of your brain. Quadriplegia (or tetraplegia) is when all four limbs are ...
What is the most common demyelinating disease?
There are several demyelinating diseases, but the most common is multiple sclerosis. Motor neuron diseases (MNDs). Motor neurons are the nerve cells that control the muscles you use to walk, breathe, speak, and move your limbs.
What happens when your nerve cells are damaged?
Demyelinating diseases. These happen when the protective coating around your nerve cells, called the myelin sheath, is damaged over time. That makes it harder for your neurons to send signals throughout your body. It weakens your muscles and eventually causes paralysis.
What is it called when you can't move your muscles?
Types of Paralysis . Complete paralysis is when you can’t move or control your paralyzed muscles at all. You also may not be able to feel anything in those muscles. Partial or incomplete paralysis is when you still have some feeling in, and possibly control over, your paralyzed muscles. This is sometimes called paresis.
What does it mean when you can't move?
In this Article. Paralysis is when you can’t move certain parts of your body after something goes wrong with their connection to your brain. It comes in many different forms and can be temporary or permanent or even come and go. Someone who is paralyzed because of a birth defect or sudden injury often can’t feel or move anything at all in their ...
How many people have ascending paralysis?
The total annual statistics for ascending paralysis is one case for 55-91 thousand people. In Western countries, the number of new episodes per year is from 0.89 to 1.89 cases per 100,000 people. The risk of developing an ascending paralysis is increased by 20% for each decade of life (data from the European journal of physical and rehabilitation medicine).
Where is ascending paralysis treated?
Treatment of ascending paralysis is carried out in a neurological hospital. If the ascending paralysis of Landry progresses rapidly, emergency medical care is required in the intensive care unit, where there are conditions for using (if necessary) an artificial lung ventilation device.
What is the name of the ascending paralysis of Guillain-Barre syndrome?
Other names of this pathology are ascending Landry paralysis or Landry syndrome, ascending paralysis of Guillain-Barre (Guillain-Barre-Strohl syndrome, GBS). There is also the name of the Landry-Guillain-Barre syndrome.
What is the cause of campylobacteriosis?
Campylobacteriosis is caused by the bacterium Campylobacter jejuni, which, penetrating the digestive tract, begins to multiply with the release of toxins. As a result, inflammation, swelling and even ulceration of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract develops, as well as general intoxication of the body (through blood and lymph). In this case, the body produces lipo-oligosaccharides of campylobacterial membranes of IgA and IgG antibodies, which cause inflammation and degeneration of the human myelin sheaths and nerve cells.
What are the complications of chronic paralysis?
Complications of chronic paralysis are accompanied by muscle tissue atrophy and complete disability. Vegetative disorders - sudden fluctuations in blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmias, swelling, increased sweating - are noted in at least 40% of patients with ascending paralysis. Often, cardiac complications reach the urgent need for stimulation of myocardial contraction or the installation of a pacemaker driver.
What vitamins are needed for ascending paralysis?
In addition, in the treatment of ascending paralysis, it is necessary to take B vitamins.
What are the diseases of the lungs, bronchi and pleura?
Diseases of the lungs, bronchi and pleura (pulmonology) Diseases of the ear, throat and nose (otolaryngology) Diseases of the endocrine system and metabolic disorders (endocrinology) Sexually transmitted infections (sexually transmitted diseases) Gynecological diseases (gynecology)
SECTION 1
A 38-year-old construction worker with no medical history presented with back pain, urinary retention, and flaccid lower extremity paralysis. Three weeks prior to presentation, he fell from a ladder with no immediate injury. Two weeks after the fall, he presented to another hospital for back pain and urinary retention.
SECTION 2
Flaccid paralysis of the lower extremities localizes to the spinal cord, anterior horn cells, nerve roots, peripheral nerves, or muscle. The addition of sensory loss suggests a spinal cord, nerve root, or peripheral nerve injury. The combination of back pain with ascending motor and sensory loss raises concern for Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS).
SECTION 3
The CSF pleocytosis argues against GBS, though a lymphocytic pleocytosis can be seen with GBS in the setting of HIV infection. 2 The patient’s presentation continued to raise concern for a spinal cord process, thus empiric acyclovir, vancomycin, and ceftriaxone were started to cover for an epidural abscess or an infectious myelitis.
SECTION 4
The differential diagnosis for longitudinal extensive myelitis (LEM) includes both infectious and noninfectious etiologies. Viruses, such as enterovirus D68, A71, D70, VZV, HSV 1 and 2, West Nile, HIV, and cytomegalovirus, should be considered.
SECTION 5
Despite the negative AQP4 serology, the patient met criteria for NMOSD in that he fulfilled 2 major clinical criteria: ON and LEM with characteristic MRI findings and exclusion of an alternative diagnosis. The lack of cord enhancement may be explained by the prior methylprednisolone treatment.
DISCUSSION
NMOSDs are a group of inflammatory disorders of the CNS characterized by demyelination and axonal damage predominately affecting the spinal cord and optic nerves. The diagnosis is made in part through serum autoantibodies against the water aquaporin-4 channel (AQP4).
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Jon Rosenberg: conception and drafting of the original manuscript, preparation of the images, and critical revisions to the manuscript. Stephen Aradi: drafting of the manuscript and critical revisions to the intellectual content. Amy Pruitt: drafting of the manuscript and critical revisions to the intellectual content.
Consultation, Treatment, and Testing Steps
If you suspect your patient has botulism, call immediately. Do not wait for laboratory confirmation.
What Is Infant Botulism?
Infant botulism is an intestinal toxemia. The disease results after spores of the bacterium Clostridium botulinum or related species are swallowed, temporarily colonize an infant’s large intestine, and produce botulinum neurotoxin.
Treatment
If clinical consultation supports botulism, request treatment immediately and administer it as soon as it’s available. Do not wait for laboratory confirmation.
Diagnostic Testing
A stool or enema specimen is required for definitive diagnosis of infant botulism. Enemas should be performed with sterile, non-bacteriostatic water. Stool specimens can be collected before or after antitoxin administration.
