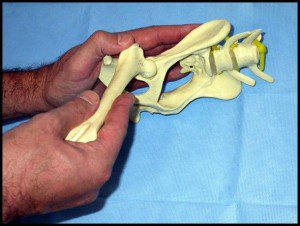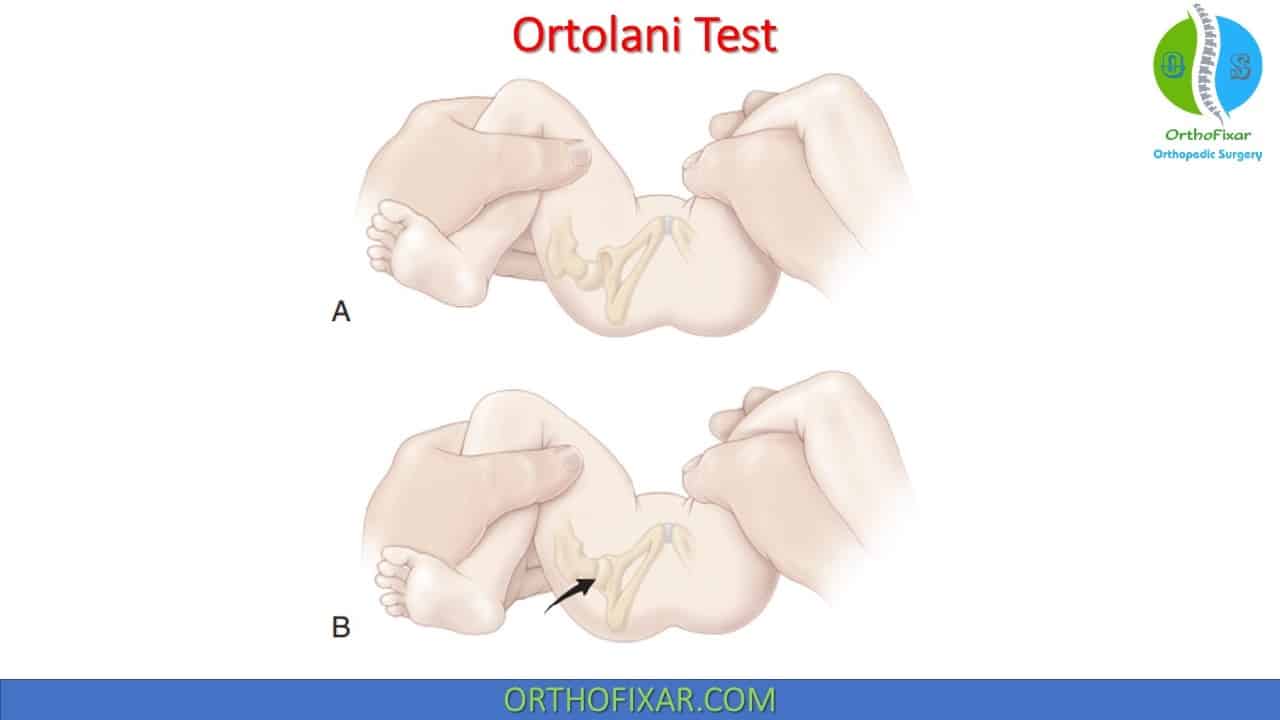
The Ortolani test
Ortolani test
The Ortolani test is part of the physical examination for developmental dysplasia of the hip, along with the Barlow maneuver. Specifically, the Ortolani test is positive when a posterior dislocation of the hip is reducible with this maneuver. This is part of the standard infant exam performed preferably in early infancy.
What does a positive Ortolani test for dislocated hip indicate?
The perception of a palpable clunk indicates a positive Ortolani test and along with this also represents the reduction of a dislocated hip into the acetabulum.
When do Ortolani and Barlow tests stop being positive?
The Ortolani and the Barlow tests are no longer positive from week eight to twelve [13]. It has been recommended that the Barlow test should be done by gently adducting the hip while palpating for the head falling out the back of the acetabulum and that no posterior-directed force be applied.
How do you perform the Ortolani test?
The Ortolani test is performed by an examiner first flexing the hips and knees of a supine infant to 90°, then with the examiner's index fingers placing anterior pressure on the greater trochanters, gently and smoothly abducting the infant's legs using the examiner's thumbs.
How do you test for a positive Barlow test?
A posterior force is applied through the femur as the thigh is gently adducted by 10-20 ° . Mild pressure is then placed on the knee while directing the force posteriorly. The Barlow Test is considered positive if the hip can be popped out of the socket with this maneuver.
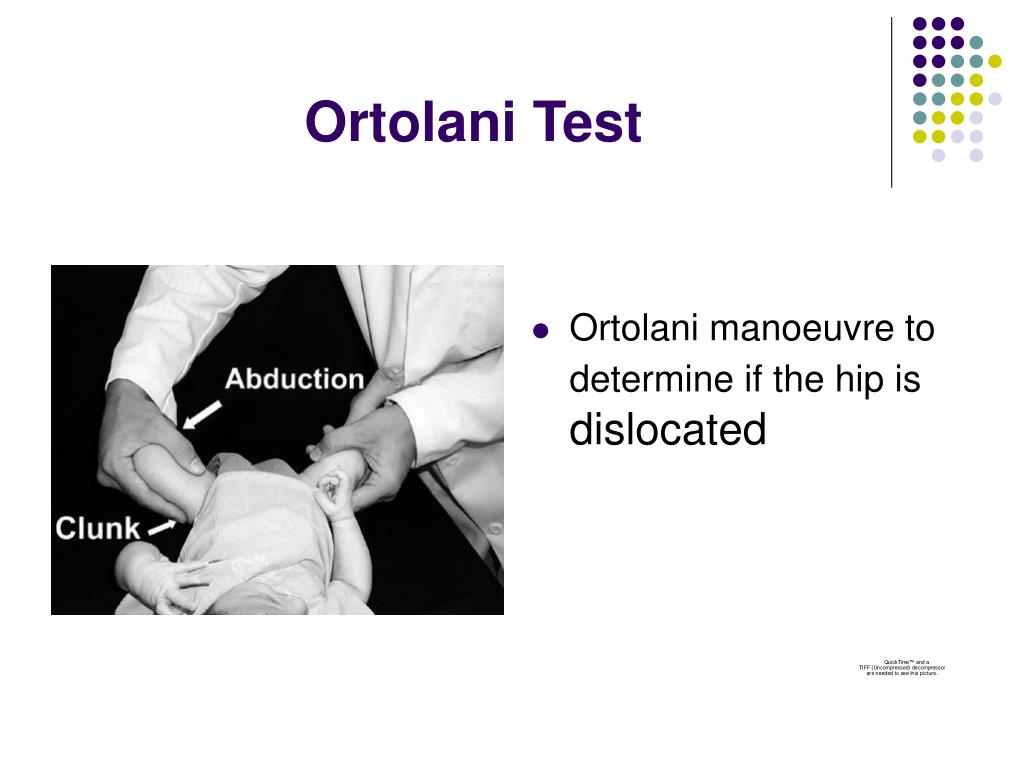
Should Ortolani be positive or negative?
Each hip should be examined separately. An infant with a positive examination result, defined as either a positive Ortolani or Barlow sign, should be referred to an orthopedist.
What is the purpose of Ortolani maneuver?
The Ortolani maneuver identifies a dislocated hip that can be reduced. The infant is positioned in the same manner as for the Barlow maneuver, in a supine position with the hip flexed to 90º. From an adducted position, the hip is gently abducted while lifting or pushing the femoral trochanter anteriorly.
What is Ortolani's click?
The Ortolani Test: The examiner's hands are placed over the child's knees with his/her thumbs on the medial thigh and the fingers placing a gentle upward stress on the lateral thigh and greater trochanter area. With slow abduction, a dislocated and reducible hip will reduce with a described palpable “clunk.”
What is the difference between Ortolani and Barlow test?
Barlow provocative manoeuvres attempt to identify a dislocatable hip adduction of the flexed hip with gentle posterior force while Ortolani manoeuvres attempt to relocate a dislocated hip by abduction of the flexed hip with gentle anterior force 1,2.
Which diagnosis does a positive Ortolani test confirm?
- Ortolani test identifies dislocated hip that can reduced in early weeks of life; - a positive test requires active treatment (see treatment in newborns); - if hip remains dislocated (for weeks), limitation of abduction becomes more consistent clinical finding.
What age does Ortolani and Barlow stop?
The Barlow and Ortolani screening tests are recommended up to 6 months of age, although they begin to lose their sensitivity and usefulness around 3 months of age due to increased musculature. Thereafter, limited and/or asymmetric hip abduction suggests the diagnosis.
How is congenital hip dysplasia diagnosed?
Serial physical examination remains the primary method for diagnosing developmental dysplasia of the hip in infants. In many U.S. institutions, ultrasound examination is used to evaluate newborns and young infants who have an abnormal hip on physical examination.
How is hip dysplasia diagnosed?
Diagnosis and Tests The doctor will perform a physical exam to check for hip dysplasia in the first few days of a baby's life and again after about two months. Signs of the condition may not show up until a child is older. X-rays, ultrasound and CT scans can confirm a diagnosis in children who are older than 6 months.
How do you perform Ortolani and Barlow?
0:311:00"How to Test for Newborn Hip Dysplasia" by Nina Gold ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe hips one at a time using two maneuvers in the Barlow maneuver first adduct the hip by bringingMoreThe hips one at a time using two maneuvers in the Barlow maneuver first adduct the hip by bringing the thigh toward the midline.
How would you determine if the infant has congenital hip dysplasia?
Diagnosing DDH Your baby's hips will be checked as part of the newborn physical screening examination within 72 hours of being born. The examination involves gently moving your baby's hip joints to check if there are any problems. It should not cause them any discomfort.
How is hip dysplasia diagnosed in babies?
Ultrasound (sonogram): Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures of the femoral head (ball) and the acetabulum (socket). It is the preferred way to diagnose hip dysplasia in babies up to 6 months of age.
How do you know if your baby has hip dysplasia?
Two tests help doctors check for DDH:An ultrasound uses sound waves to make pictures of the baby's hip joint. This works best with babies under 6 months of age. ... An X-ray works best in babies older than 4–6 months. At that age, their bones have formed enough to see them on an X-ray.
How do you assess hip dysplasia in infants?
During well-baby visits, doctors typically check for hip dysplasia by moving an infant's legs into a variety of positions that help indicate whether the hip joint fits together well. Mild cases of hip dysplasia can be difficult to diagnose and might not start causing problems until you're a young adult.
How is hip dysplasia diagnosed in babies?
Ultrasound (sonogram): Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures of the femoral head (ball) and the acetabulum (socket). It is the preferred way to diagnose hip dysplasia in babies up to 6 months of age.
How is hip dysplasia measured?
The diagnosis of hip dysplasia can be made with a center-edge angle of Wiberg of less than 20° measured on a well-centered antero- posterior radiograph of the pelvis (Table 1 and Fig. 2). A center-edge angle value greater than 25° is normal [5].
Why do they check baby's hips?
Why does the doctor check my baby's hips? A few babies have hip problems that can lead to dislocation of the hip bones. This means that the long bone in the upper leg comes out of the hip socket. If your baby has this problem, it's important to find out early so it can be fixed (see Picture 1).
What does a negative result mean on a Barlow and Ortolani maneuver?
This means that a negative result effectively rules out hip dislocation or subluxation. Nevertheless, a high number of infants will require rescreening because of false positives with this technique. When both the Barlow and Ortolani maneuvers are combined, the specificity of the test increases from 0.98 to 0.99 .
Where was the Ortolani test first performed?
It was clinically tested during 1957–1962 at Hope Hospital, Salford, Lancashire . The Ortolani Test was first described in 1936 by an Italian pediatrician Marino Ortolani; an outstanding pioneer in the early diagnosis and treatment of hip dysplasia.
What is Barlow and Ortolani?
The Barlow and Ortolani tests are used to assess for hip instability. Each hip should be examined separately . For proper Ortolani and Barlow technique, there should also be a proper positioning of the infant to be tested and a proper maneuver must be used. The examiner must have the ability to differentiate ‘click’ or ‘clunk’ .
What is the Barlow test?
The Barlow Test is considered positive if the hip can be popped out of the socket with this maneuver. The dislocation will be palpable . 2. Ortolani Test. In this test, the baby is placed in a supine position with flexed hips at 90 degrees.
When is the Barlow test positive?
The Ortolani and the Barlow tests are no longer positive from week eight to twelve . It has been recommended that the Barlow test should be done by gently adducting the hip while palpating for the head falling out the back of the acetabulum and that no posterior-directed force be applied.
Is the Barlow test safe?
The significance and safety of the Barlow test are still questioned even though widely used in the literature and in practice, Barlow stated in his original description that the test is for the laxity of the hip joint rather than for an existing dislocation.
What is the Ortolani test?
The Ortolani test is part of the physical examination for developmental dysplasia of the hip, along with the Barlow maneuver. Specifically, the Ortolani test is positive when a posterior dislocation of the hip is reducible with this maneuver.
How is the Ortolani test performed?
The Ortolani test is performed by an examiner first flexing the hips and knees of a supine infant to 90°, then with the examiner's index fingers placing anterior pressure on the greater trochanters, gently and smoothly abducting the infant's legs using the examiner's thumbs.