What is the process of DNA transcription?
DNA transcription is a process that involves transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNA. The transcribed DNA message, or RNA transcript, is used to produce proteins. ... DNA is transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase.
What is the function of DNA to RNA transcription?
DNA transcription is a process that involves transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNA. The transcribed DNA message, or RNA transcript, is used to produce proteins. ... It controls cellular activity by coding for the production of proteins.
Is RNA a finished product of transcription?
In some cases, the RNA molecule itself is a "finished product" that serves some important function within the cell. Often, however, transcription of an RNA molecule is followed by a translation step, which ultimately results in the production of a protein molecule.
Where does transcription occur in prokaryotic cells?
In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm for translation. DNA in prokaryotes is much more accessible to RNA polymerase than DNA in eukaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones to form structures called nucleosomes.
What is the product of DNA transcription?
RNAThe product of transcription is RNA, which can be encountered in the form mRNA, tRNA or rRNA while the product of translation is a polypeptide amino acid chain, which forms a protein. Transcription occurs in the nucleus in eukaryotic organisms, while translation occurs in the cytoplasm and endoplasmic reticulum.
What product is produced from transcription?
In transcription, a portion of the double-stranded DNA template gives rise to a single-stranded RNA molecule. In some cases, the RNA molecule itself is a "finished product" that serves some important function within the cell.
What is the end result of DNA transcription?
The end product of transcription is RNA, a single-stranded molecule made up of RNA nucleotides. The three main types of RNA produced in the transcription are mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA.
What is the product of transcription quizlet?
The products of DNA transcription are strands of RNA. They are complimentary to the DNA strand.
What is the purpose of DNA transcription?
DNA transcription is a process that involves transcribing genetic information from DNA to RNA. The transcribed DNA message, or RNA transcript, is used to produce proteins. DNA is housed within the nucleus of our cells. It controls cellular activity by coding for the production of proteins. The information in DNA is not directly converted into proteins, but must first be copied into RNA. This ensures that the information contained within the DNA does not become tainted.
How does DNA transcription occur in eukaryotes?
In prokaryotes, such as bacteria, the DNA is transcribed by one RNA polymerase molecule without the assistance of transcription factors. In eukaryotic cells, transcription factors are needed for transcription to occur and there are different types of RNA polymerase molecules that transcribe the DNA depending on the type of genes. Genes that code for proteins are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, genes coding for ribosomal RNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase I, and genes that code for transfer RNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase III. In addition, organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own RNA polymerases which transcribe the DNA within these cell structures.
What enzymes unwind the DNA strand and allow RNA polymerase to transcribe only a single?
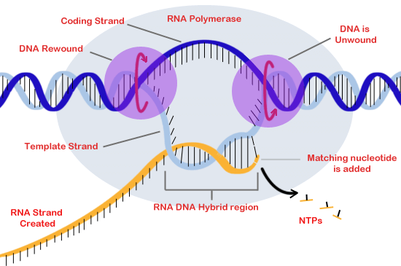
Elongation. Certain enzymes called transcription factors unwind the DNA strand and allow RNA polymerase to transcribe only a single strand of DNA into a single stranded RNA polymer called messenger RNA (mRNA). The strand that serves as the template is called the antisense strand.
How does reverse transcription work?
DNA is transcribed and translated to produce proteins. Reverse transcription converts RNA to DNA. In reverse transcription, RNA is used as a template to produce DNA. The enzyme reverse transcriptase transcribes RNA to generate a single strand of complementary DNA (cDNA).
How do ribosomes and RNA work together?
Once in the cytoplasm, ribosomes and another RNA molecule called transfer RNA work together to translate mRNA into a protein. This process is called translation. Proteins can be manufactured in large quantities because a single DNA sequence can be transcribed by many RNA polymerase molecules at once.
What enzyme transcribes DNA?
DNA is transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. Specific nucleotide sequences tell RNA polymerase where to begin and where to end. RNA polymerase attaches to the DNA at a specific area called the promoter region.
How does mRNA translate into protein?
Once in the cytoplasm, ribosomes and another RNA molecule called transfer RNA work together to translate mRNA into a protein. This process is called translation. Proteins can be manufactured in large quantities because a single DNA sequence can be transcribed by many RNA polymerase molecules at once.
What is the process of transcription?
The process of transcription begins when an enzyme called RNA polymerase (RNA pol) attaches to the template DNA strand and begins to catalyze production of complementary RNA. Polymerases are large enzymes composed of approximately a dozen subunits, and when active on DNA, they are also typically complexed with other factors. In many cases, these factors signal which gene is to be transcribed.
How does transcription end in eukaryotes?
In eukaryotes, termination of transcription occurs by different processes, depending upon the exact polymerase utilized. For pol I genes, transcription is stopped using a termination factor, through a mechanism similar to rho-dependent termination in bacteria. Transcription of pol III genes ends after transcribing a termination sequence that includes a polyuracil stretch, by a mechanism resembling rho-independent prokaryotic termination. Termination of pol II transcripts, however, is more complex.
How many nucleotides can a pol II gene continue to cleave?
Transcription of pol II genes can continue for hundreds or even thousands of nucleotides beyond the end of a noncoding sequence. The RNA strand is then cleaved by a complex that appears to associate with the polymerase. Cleavage seems to be coupled with termination of transcription and occurs at a consensus sequence. Mature pol II mRNAs are polyadenylated at the 3′-end, resulting in a poly (A) tail; this process follows cleavage and is also coordinated with termination.
What is the consensus sequence of a gene?
In prokaryotes, most genes have a sequence called the Pribnow box, with the consensus sequence TATAAT positioned about ten base pairs away from the site that serves as the location of transcription initiation. Not all Pribnow boxes have this exact nucleotide sequence; these nucleotides are simply the most common ones found at each site. Although substitutions do occur, each box nonetheless resembles this consensus fairly closely. Many genes also have the consensus sequence TTGCCA at a position 35 bases upstream of the start site, and some have what is called an upstream element, which is an A-T rich region 40 to 60 nucleotides upstream that enhances the rate of transcription (Figure 3). In any case, upon binding, the RNA pol " core enzyme " binds to another subunit called the sigma subunit to form a holoezyme capable of unwinding the DNA double helix in order to facilitate access to the gene. The sigma subunit conveys promoter specificity to RNA polymerase; that is, it is responsible for telling RNA polymerase where to bind. There are a number of different sigma subunits that bind to different promoters and therefore assist in turning genes on and off as conditions change.
Why are eukaryotic promoters more complex than prokaryotic promoters?
Eukaryotic promoters are more complex than their prokaryotic counterparts, in part because eukaryotes have the aforementioned three classes of RNA polymerase that transcribe different sets of genes. Many eukaryotic genes also possess enhancer sequences, which can be found at considerable distances from the genes they affect. Enhancer sequences control gene activation by binding with activator proteins and altering the 3-D structure of the DNA to help "attract" RNA pol II, thus regulating transcription. Because eukaryotic DNA is tightly packaged as chromatin, transcription also requires a number of specialized proteins that help make the template strand accessible.
What is the core promoter in eukaryotes?
A core promoter consists of a transcription start site, a TATA box (at the -25 region), and a TFIIB recognition element (at the -35 region).
Which type of RNA polymerase is used in eukaryotic cells?
Three different types of RNA polymerase exist in eukaryotic cells, whereas bacteria have only one. In eukaryotes, RNA pol I transcribes the genes that encode most of the ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), and RNA pol III transcribes the genes for one small rRNA, plus the transfer RNAs that play a key role in the translation process, as well as other small regulatory RNA molecules. Thus, it is RNA pol II that transcribes the messenger RNAs, which serve as the templates for production of protein molecules.
What is the process of turning DNA into RNA?
Transcription is one of the fundamental processes that happens to our genome. It's the process of turning DNA into RNA. And you may have heard about the central dogma, which is DNA, to RNA, to protein. Well, transcription refers to that first part of going from DNA to RNA.
What is the process of making a copy of a gene?
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. This copy, called a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes.
Overview of transcription
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a DNA segment. This copy is called a messenger RNA ( mRNA) molecule. This mRNA will be transported from the cell nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where the mRNA directs the synthesis of the protein.
Gene expression
Genes contain the information to build proteins that cells need. Our genes are written as the nucleotide base pairs (A, T, G, C) in the DNA. For a gene to exert its function, the genetic information must read out to build a protein.
What kinds of RNA can be transcribed (produce)?
When talking about RNA and transcription, we usually refer to messenger RNA (mRNA). An mRNA is transcribed from a protein-encoding gene and subsequently is translated to a protein. But there is a whole set of other RNAs that get transcribed, like transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomal RNA (rRNA), that do different functions in the cells.
Stages of transcription
Transcription of a gene takes place in three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Here, we will briefly see how these steps happen.
Eukaryotic RNA modifications after transcription
In prokaryotic cells, the RNA transcripts can act as messenger RNAs (mRNAs) right away. However, in eukaryotic cells, the RNA transcripts produced by transcription are only pre-mRNAs. These pre-mRNAs must go through extra processing before they can be used in translation.
The regulation of Individual genes
Not all genes are transcribed all the time. Instead, transcription is controlled spatially (in different cells) and temporarily (in different timing) for each gene. For example, some growth hormones express only when we are young. Some proteins which can wake our immune system up will only be produced when our bodies sense pathogen invasion.
Transcription in bacteria
In this article, we mainly discuss the transcription in eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes produce RNA in a very similar way. However, there are some differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic gene expression. In bacteria, all transcription is performed by a single type of RNA polymerase.
What is the process of transcription in bacteria?
The initiation of transcription in bacteria begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter in DNA. Transcription initiation is more complex in eukaryotes, where a group of proteins called transcription factors mediates the binding of RNA polymerase and the initiation of transcription.
What are the steps of transcription?
Key Takeaways: Steps of Transcription 1 The two main steps in gene expression are transcription and translation. 2 Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. 3 The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
What is the promoter of DNA?
The promoter is a DNA sequence that signals which DNA strand is transcribed and the direction transcription proceeds. Approximately 23 nucleotides must be synthesized before RNA polymerase loses its tendency to slip away and prematurely release the RNA transcript. 04. of 05.
What is the role of DNA in RNA synthesis?
One strand of DNA serves as the template for RNA synthesis, but multiple rounds of transcription may occur so that many copies of a gene can be produced.
What are the steps of gene expression?
The two main steps in gene expression are transcription and translation . Transcription is the name given to the process in which DNA is copied to make a complementary strand of RNA. RNA then undergoes translation to make proteins. The major steps of transcription are initiation, promoter clearance, elongation, and termination.
Why is RNA called messenger RNA?
The RNA is called messenger RNA because it carries the "message," or genetic information, from the DNA to the ribosomes, where the information is used to make proteins. RNA and DNA use complementary coding where base pairs match up, similar to how the strands of DNA bind to form a double helix. One difference between DNA and RNA is ...
Where does mRNA translation occur?
Translation of the mRNA into proteins also occurs in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, transcription occurs in the cell's nucleus. mRNA then moves to the cytoplasm for translation. DNA in prokaryotes is much more accessible to RNA polymerase than DNA in eukaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones to form structures called ...