
Full Answer
What is dopamine and how does it relate to addiction?
Dopamine plays an integral part in supporting the formation of self-destructive coping mechanisms. Whether it is food, alcohol, or drugs, dopamine plays the same part. The addictive substances cause an overload of Dopamine inside the brain, which causes the receptors less sensitive to it.
What do drugs cause dopamine?
Regular drug use actually causes the brain to produce, absorb, or transmit less dopamine, resulting in a chemical imbalance in the brain. When the drugs are not active in the brain, dopamine levels can drop, causing uncomfortable withdrawal symptoms and powerful cravings.
How does dopamine agonist drugs work?
Dopamine Agonists. These medications stimulate the parts of the human brain influenced by dopamine. In effect, the brain is tricked into thinking it is receiving the dopamine it needs. In general, dopamine agonists are not as potent as carbidopa/levodopa and may be less likely to cause dyskinesias.
Do dopamine antagonists increase dopamine?
Dopamine antagonists turn down dopamine activity, which may be useful for the treatment of psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, which have been associated with an overactive dopamine system. What are 5 dopamine agonists?
What do dopamine agonists do?
Dopamine agonists stimulate the parts of the brain influenced by dopamine. In effect, dopamine agonists trick the brain into thinking it is receiving the dopamine it needs. In general, dopamine agonists are not as potent as carbidopa-levodopa and may be less likely to cause dyskinesias.
How do dopamine agonists make you feel?
Common side effects include drowsiness, sudden sleep attacks, nausea, and swelling in the limbs. People taking pramipexole may also experience hallucinations, compulsive eating, and impulse control disorder (which may manifest with uncontrolled gambling, online shopping, or other behaviors).
What is an example of a dopamine agonist?
Examples of this type of dopamine agonist are bromocriptine, pergolide, lisuride, and the long acting ergoline, cabergoline.
Do agonists increase dopamine?
Various dopamine agonists can increase dopamine activity in the brain. The majority of dopamine agonists used in Parkinson disease are D2 dopamine receptor agonists.
What is the best drug to increase dopamine?
Medications. Ropinirole, pramipexole, and levodopa can boost dopamine levels. Levodopa is the precursor to dopamine, which means it is something the body needs to produce dopamine.
How do you know if you have low dopamine?
Symptoms of dopamine deficiency (low dopamine levels) may include:You lack motivation, “the drive.”You're tired.You can't concentrate.You're moody or anxious.You don't feel pleasure from previously enjoyable experiences.You're depressed; you feel hopeless.You have a low sex drive.More items...•
How can I raise my dopamine levels fast?
Getting enough sleep, exercising, listening to music, meditating, and spending time in the sun can all boost dopamine levels. Overall, a balanced diet and lifestyle can go a long way in increasing your body's natural production of dopamine and helping your brain function at its best.
What vitamins can increase dopamine?
Along with eating a balanced diet, many possible supplements may help boost dopamine levels, including probiotics, fish oil, vitamin D, magnesium, ginkgo and ginseng. This, in turn, could help improve brain function and mental health.
Why would a neurologist prescribe dopamine agonist?
Dopamine agonists (DA) are therapeutic agents that are commonly used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD). They can reduce undesired motor fluctuations and delay the administration of levodopa therapy.
Are dopamine agonists addictive?
The recent recognition of a range of "behavioural addictions" that are linked to dopamine agonist use has highlighted the role of dopamine in brain reward function and addiction disorders in general. Dopamine agonists have now even been linked occasionally to new substance addictions.
Do dopamine agonists help depression?
Treatment of depressive symptoms not only improves mood but is also associated with improvement of motor symptoms, disability and cognitive symptoms. Currently, dopamine agonists are being suggested as an alternative to antidepressants for the treatment of depression in PD.
What causes low dopamine?
Causes of Low Dopamine A number of factors may be responsible for reduced dopamine in the body. These include sleep deprivation, obesity, drug abuse, saturated fat, and stress.
Do dopamine agonists cause euphoria?
Conversely, excessive dopaminergic stimulation also causes abnormal emotion and behavior, including euphoria, disinhibition, or repetitive stereotyped movements (7–10).
Does dopamine make you happy?
Dopamine: Often called the "happy hormone," dopamine results in feelings of well-being. A primary driver of the brain's reward system, it spikes when we experience something pleasurable. Praised on the job? You'll get a dopamine hit.
Does dopamine give you energy?
When dopamine is released in the brain, it creates feelings of alertness and wakefulness. Animal studies indicate that dopamine is released in large amounts in the morning when it's time to wake up and that levels naturally fall in the evening when it's time to go to sleep.
Are dopamine agonists addictive?
The recent recognition of a range of "behavioural addictions" that are linked to dopamine agonist use has highlighted the role of dopamine in brain reward function and addiction disorders in general. Dopamine agonists have now even been linked occasionally to new substance addictions.
What is a dopamine agonist?
Dopamine agonists are a form of drug that treats conditions such as Parkinson’s disease. Dopamine agonists imitate dopamine, which is a chemical that is important for various physical and mental functions.
What receptors do dopamine agonists bind to?
Dopamine agonists bind to the D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptors. By doing so, they activate the dopamine receptors in the same way that dopamine does. This means that dopamine agonists can help to relieve symptoms that occur due to low dopamine levels.
What are the two types of dopamine receptors?
The two types of dopamine receptors are D1-like dopamine receptors and D2-like dopamine receptors. The D1-like dopamine receptor group contains the subtypes D1 and D5. The D2-like dopamine receptor group contains D2, D3, and D4 subtypes.
What is neuroleptic malignant syndrome?
neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a rare side effect of antipsychotic medication
How long does it take for Parkinson's to develop impulse control?
Research from 2018 found that approximately 46% of people taking dopamine agonists for Parkinson’s disease developed impulse control disorders over 5 years.
What is the function of dopamine?
Dopamine helps with functions such as movement, memory, mood, learning, and cognition.
What are the effects of low levels of dopamine?
Low levels of dopamine are linked to depression, schizophrenia, and Parkinson’s disease.
What is dopamine partial agonism?
In this article, you will learn about dopamine partial agonism. This effect is best illustrated by Abilify (aripiprazole) and and Rexulti (brexipiprazole). These second-generation antipsychotic/atypical neuroleptics stand apart from all the other atypical antipsychotics due to a different mechanism of action.
What is a partial agonist?
Dopamine Partial Agonists. A dopamine partial agonist is a molecule that binds to the receptor and partially activates it. Think about it as a key that sorts of fit in the lock so that the door can be wriggled about but not completely open.
What does it mean when there is too much dopamine around aripiprazole?
This partial effect means that when there is too much dopamine around aripiprazole (a dopamine partial agonist) by taking the dopamine space on the receptors and activating them only partially will actually take down the effect of the excess dopamine.
What is partial effect dopamine?
The effect of a dopamine partial agonist is less than the full effect of dopamine but more than a complete lack of effect, which is what happens when a receptor is completely blocked. In other words, a partial effect. This partial effect means that when there is too much dopamine around aripiprazole (a dopamine partial agonist) ...
Which antipsychotics block dopamine?
The second-generation antipsychotics such as risperidone, ziprasidone, and paliperidone are all potent antagonists of dopamine D2 receptors while clozapine ...
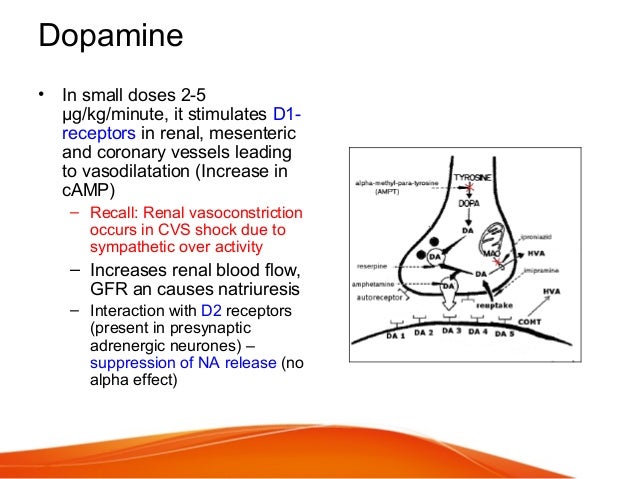
Where is dopamine released?
Dopamine is released in the synaptic space from vesicles house d in the pre-synaptic neuron, then binds to dopamine receptors at the level of the postsynaptic neuron.
Does aripiprazole increase dopamine?
To summarize, aripiprazole, as a dopamine partial agonist, acts as a modulator of dopamine effects. When present, it diminishes the effects of both dopamine excess (by decreasing dopamine action when there is too much of it) and deficit (by increasing dopamine action when there is too little of it).
What is dopamine agonist?
Dopamine agonists are mainly used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The cause of Parkinson's is not fully known but genetic factors, for example specific genetic mutations, and environmental triggers have been linked to the disease. In Parkinson's disease dopaminergic neurons that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain slowly break down and can eventually die. With decreasing levels of dopamine the brain can't function properly and causes abnormal brain activity, which ultimately leads to the symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
How is dopamine synthesized?
In the second stage Levodopa (L-dopa) is formed by adding a phenol group to the benzene ring of L-Tyrosine . The formation of L-dopa from L-tyrosine is catalyzed by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase. The third stage is the formation of dopamine by removing the carboxylic acid group from L-dopa, catalysed by the enzyme dopa decarboxylase.
Why are agonists dirtier than non-ergoline agonists?
Ergoline derived agonists are said to be dirtier drugs because of their interaction with other receptors than dopamine receptors, therefore they cause more side effects.
What happens when dopamine levels decrease?
With decreasing levels of dopamine the brain can't function properly and causes abnormal brain activity, which ultimately leads to the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. There are two fundamental ways of treating Parkinson's disease, either by replacing dopamine or mimicking its effect.
How many subtypes of dopamine are there?
Dopamine receptors have five subtypes, D 1 through D 5, the subtypes can be divided into two subclasses due to their mechanism of action on adenylate cyclase enzyme, D 1 -like receptors (D 1 and D 5) and D 2 -like receptors (D 2, D 3 and D 4 ).
Why can't dopamine cross the BBB?
If compounds do not possess these qualities they must have a specific transporter that can transport them over the BBB. Dopamine cannot diffuse across the BBB because of the catechol group, it is too polar and therefore unable to enter the brain. The catechol group is a dihydroxy benzene ring.
What is DA in chemistry?
D010300. In Wikidata. A dopamine agonist (DA) is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D 2 -like and D 1 -like, and they are all G protein-coupled receptors. D 1 - and D 5 -receptors belong to the D 1 -like family and the D 2 -like family includes D 2, D 3 and D 4 receptors.
What is the purpose of dopamine agonists?
Dopamine agonistsare medications that activate signaling pathways between brain cells using the cells' own dopamine receptors when there is an absence or reduction of dopamine in the brain.
What is the drug that stimulates dopamine receptors in the brain?
A drug that stimulates dopamine receptors in the brain. Some of these agents, such as ropinirole and pramipexole , are used to treat Parkinson disease.
Is safinamide an add on?
The company has also received feedback about the findings of the studies showing statistically significant efficacy of safinamide as add-on therapy in patients receiving a stable dose of a single dopamine a gonistin early PD patients and on motor fluctuations in patients with advanced PD on levodopa and other PD treatments.
Does dopamine make RLS worse?
However a problem with the above theory is that in some people with RLS, dopamine agonistsactually make their symptoms worse.
Do you need dopamine agonists for microprolactinomas?
Asymptomatic patients harboring microprolactinomas do not need to be prescribed dopamine agonists.3 Symptomatic prolactin-secreting microadenomas may be treated with bromocriptine or cabergoline before pregnancy, to lower prolactin levels, decrease tumour size, and restore gonadal function.
Is bromocriptine a dopamine agonist?
Bromocriptine is the next dopamine agonist after caberg oline which evokes interest in recent years, owing to its advantages in patients at risk of OHSS, including its shorter half-life and greater experience with this drug in pregnancy, the lack of teratogenicity, despite side effects such as nausea, headaches and orthostatic dysregulation.
How do dopamine agonists work?
How Dopamine Agonist Drugs Help. Dopamine agonist drugs increase your brain's ability to make and use dopamine. They turn on the dopamine receptors so the dopamine in your brain can do its work. After all, it doesn't help to the amount of dopamine in your brain if your receptors can't receive it. When enough dopamine is present ...
What is the function of dopamine?
It acts as a messenger to carry the messages of pleasure or motivation to other parts of the brain that can interpret the message and respond accordingly. If the dopaminergic system is functioning properly, the message is sent and received.
Why do we need to increase dopamine?
So, why would you need to increase your dopamine? The main reason is if you have a dopamine deficiency. Parkinson's disease, restless leg syndrome, narcolepsy, depression, and ADHD are examples of conditions related to dopamine deficiency. A dopamine agonist drug increases dopamine transmissions to allow your brain to function better.
What are dopamine receptors?
Dopamine receptors are parts of the brain cells in dopamine-sensitive areas of the brain. They are the parts of the neurons that receive the message. A single dopamine receptor is composed of a protein containing 400 amino acids.
What happens when the dopamine system isn't working?
When the dopamine system in the brain isn't working the right way, serious physical and mental problems can happen. For some people, dopamine agonist drugs provide a solution.
When do dopamine deficiency symptoms go away?
When enough dopamine is present and is being used effectively , symptoms of dopamine deficiency may go away or at least diminish.
What is dopamine in the brain?
Dopamine is a major player in brain chemistry, influencing our moods, motivation, and movement.
What are the side effects of dopamine agonists?
Those taking dopamine agonists could be at risk of side-effects that include binge eating, gambling, frequent shopping and compulsive sexual behaviour.
What are some examples of drugs that have the effect of some of the actions of dopamine?
Examples are bromocriptine, cabergoline (Cabaser), pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate (Mirapexin), quinagolide (Norprolac), ropinirole (Requip), lysuride, and apomorphine (Apo-go, Uprima).
Can dopamine agonists cause impulse control?
Researchers warn that dopamine agonists, which control tremors and other symptoms, can also result in impulse control disorders.
Can DDM be treated with dopamine?
DDM can be successfully treated with dopamine agonists.
Can dantrolene be taken with benzodiazepines?
Dantrolene can be combined with benzodiazepines or dopamine agonists, but it should not be co-administered with calcium channel blockers, as cardiovascular collapse can occur.
Do you need dopamine agonists for microprolactinomas?
Asymptomatic patients harboring microprolactinomas do not need to be prescribed dopamine agonists .3 Symptomatic prolactin-secreting microadenomas may be treated with bromocriptine or cabergoline before pregnancy, to lower prolactin levels, decrease tumour size, and restore gonadal function.
What is dopamine?
Dopamine is a type of monoamine neurotransmitter. It’s made in your brain and acts as a chemical messenger, communicating messages between nerve cells in your brain and your brain and the rest of your body.
How does dopamine make someone feel happy?
Dopamine is known as the “feel-good” hormone. It gives you a sense of pleasure. It also gives you the motivation to do something when you’re feeling pleasure.
What health conditions are associated with high or low dopamine levels?
Many diseases are associated with high or low levels of dopamine. There’s still much to be learned.
What are dopamine agonists?
Dopamine agonists are drugs that mimic the natural neurotransmitter dopamine. Dopamine agonists bind to and activate the dopamine receptors on nerve cells in your brain, causing nerve cells to react in the same way as they would to natural dopamine.
What are dopamine antagonists?
Dopamine antagonists are drugs that bind to and block dopamine receptors (on the receiving nerve cell) in your brain. This means they block or stop dopamine from being received by the next nerve cell. Many antipsychotic drugs are dopamine antagonists.
What are dopamine reuptake inhibitors?
Dopamine reuptake inhibitors are drugs that prevent dopamine from re-entering and being reabsorbed by the nerve cell that released it. This makes more dopamine available to more neurons in your brain.
What is levodopa?
Levodopa is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. Loss of dopamine is responsible for the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinson’s disease. To help levodopa reach your brain (as opposed to other parts of your body), levodopa is combined with carbidopa. Once it reaches your brain, it’s converted into dopamine.
What Is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a type of neurotransmitter. Your body makes it, and your nervous system uses it to send messages between nerve cells. That's why it's sometimes called a chemical messenger.
What is dopamine? What is its function?
Dopamine: What It Is & What It Does. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in pleasure, motivation, and learning. It’s also linked to some major diseases. Here’s what you should know. Skip to main content .
What is the cause of Parkinson's disease?
Parkinson’s disease. Dopamine enables neurons in your brain to communicate and control movement. In Parkinson’s, one type of neuron steadily degenerates. It doesn’t have a signal to send anymore, so your body makes less dopamine. The chemical imbalance causes physical symptoms. These include tremor, stiffness, slowness of spontaneous movement, poor balance, and poor coordination. Doctors treat these symptoms with medications that raise levels of this chemical.
What is the drug that helps with ADHD?
Some research shows it may be due to a shortage of dopamine. This problem may be due to your genes. The ADHD drug methylphenidate (Ritalin) works by boosting dopamine.
How does Ritalin help with ADHD?
The ADHD drug methylphenidate(Ritalin) works by boosting dopamine. Drug misuse and addiction. Drugs such as cocainecan cause a big, fast increase of dopamine in your brain. That satisfies your natural reward system in a big way.
What is the role of dopamine in our lives?
Dopamine plays a role in how we feel pleasure. It's a big part of our unique human ability to think and plan. It helps us strive, focus, and find things interesting.
Why is dopamine a chemical messenger?
Your body makes it, and your nervous systemuses it to send messages between nerve cells. That's why it's sometimes called a chemical messenger. Dopamine plays a role in how we feel pleasure. It's a big part of our unique human ability to think and plan. It helps us strive, focus, and find things interesting.

What Is A Dopamine Agonist?
Dopamine Agonists vs. Antagonists
- Dopamine is one of the neurotransmitters found in the synaptic space, which is the space between neurons (nerve cells). Dopamine is released into the synaptic space from vesicles housed in the pre-synaptic neuron. These chemicals then bind to dopamine receptors in the postsynaptic neuron. Think of this as a key and lock type of effect: Dopamine receptors are lock…
Types of Dopamine Agonists
- Antipsychotic medications that act as dopamine agonists are: 1. Abilify (aripiprazole) 2. Rexulti (brexipiprazole) The majority of second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics block the D-2 (dopamine-2) receptors but also block serotoninreceptors. Serotonin is another neurotransmitter involved in mood. Second-generation antipsychotics such as Risperdal (risperidone), Geodon (zi…
Uses of Dopamine Agonists
- Because these medications modulate dopamine activity, they can be useful in the treatment of psychiatric conditions including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. These conditions are associated with too much dopamine activity. Excessive dopamine action can cause certain areas of the brain to become overactive, which is believed to play a role in symptoms such as delusion…
Impact of Dopamine Agonists
- Dopamine agonists may help relieve common symptoms of schizophrenia including hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. Research suggests that aripiprazole is as effective as other antipsychotic medications in the treatment of schizophrenia.3 A benefit of this medication is that it is less likely to produce extrapyramidal side effects than typical antipsychot…
Potential Pitfalls
- Dopamine agonists can still have side effects and other adverse reactions. Some potential side effects include:4 1. Constipation 2. Drowsiness 3. Extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) include akathisia, dystonia, parkinsonism, and tardive dyskinesia5 4. Headaches 5. Increased glucose With aripiprazole, the risk for certain neurological adverse effects such as episodes of acute mu…
Summary
- Dopamine agonists such as Abilify and Rexulti can be an effective option in the treatment of schizophrenia. These medications work by affecting dopamine receptors to help modulate dopamine levels in the body. This may help relieve some psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking. These medications are also less likely to ca…
Overview
A dopamine agonist (DA) is a compound that activates dopamine receptors. There are two families of dopamine receptors, D2-like and D1-like, and they are all G protein-coupled receptors. D1- and D5-receptors belong to the D1-like family and the D2-like family includes D2, D3 and D4 receptors. Dopamine agonists are used to treat Parkinson's disease and, to a lesser extent, hyperprolactinemia and restless …
Medical uses
Dopamine agonists are mainly used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The cause of Parkinson's is not fully known but genetic factors, for example specific genetic mutations, and environmental triggers have been linked to the disease. In Parkinson's disease dopaminergic neurons that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain slowly break down and can eventually die. With decreasing levels of dopamine the brain can't function properly and causes …
Adverse effects
Dopamine agonists are mainly used to treat Parkinson’s disease but are also used to treat hyperprolactinemia and restless legs syndrome. The side effects are mainly recorded in treatment for Parkinson’s disease where dopamine agonists are commonly used, especially as first-line treatment with levodopa.
Dopamine agonists are divided into two subgroups or drug classes, first-generation and newer a…
Pharmacology
The absorption of the oral dose is approximately 28% however, only 6% reaches the systemic circulation unchanged, due to a substantial first-pass effect. Bromocriptine reaches mean peak plasma levels in about 1–1.5 hours after a single oral dose. The drug has high protein binding, ranging from 90-96% bound to serum albumin. Bromocriptine is metabolized by CYP3A4 and excreted primarily in the feces via biliary secretion. Metabolites and parent drugs are mostly excre…
Mechanism of action
The dopamine receptors are 7-transmembrane domains and are members of the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) superfamily. Dopamine receptors have five subtypes, D1 through D5, the subtypes can be divided into two subclasses due to their mechanism of action on adenylate cyclase enzyme, D1-like receptors (D1 and D5) and D2-like receptors (D2, D3 and D4). D1-like receptors are primarily coupled to Gαs/olf proteins and activates adenylate cyclase which increa…
Structure–activity relationship
When dealing with agonists it can be extremely complex to confirm relationships between structure and biological activity. Agonists generate responses from living tissues. Therefore, their activity depends both on their efficacy to activate receptors and their affinity to bind to receptors.
Many molecules are unable to cross the blood brain barrier (BBB). Molecules m…
Members
Examples of dopamine agonists include:
• Aripiprazole (Partial agonist of the D2 family receptors - Trade name "Abilify" in the United States; atypical antipsychotic)
• Phencyclidine (a.k.a. PCP; partial agonist. Psychoactivity mainly due to NMDA antagonism)
History
Since the late 1960 Levodopa (L-DOPA) has been used to treat Parkinson’s disease but there has always been a debate whether the treatment is worth the side effects. Around 1970 clinicians started using the dopamine agonist apomorphine alongside L-DOPA to minimize the side effects caused by L-DOPA, the dopamine agonists bind to the dopamine receptor in the absence of dopamine. Apomorphine had limited use since it had considerable side effects and difficulty wit…