What are the four functions of lymph?
The lymphatic system has three functions:
- The removal of excess fluids from body tissues.
- Absorption of fatty acids and subsequent transport of fat, chyle, to the circulatory system.
- Production of immune cells (such as lymphocytes, monocytes, and antibody producing cells called plasma cells).
What is lymph and what is it composed of?
Lymph is a thin, watery fluid composed of intercellular, or interstitial, fluid, which forms when plasma diffuses into tissue spaces. Lymph is composed of water, digested nutrients, salts, hormones, oxygen, carbon dioxide, lymphocytes, and metabolic wastes such as urea. Know more about it here.
What are the normal components of lymph?
What If the Lymphs Blood Test Results Are Low?
- Medication. People who regularly take corticosteroids will typically have a low white blood cell count of this type.
- Autoimmune disorders. The presence of rheumatoid arthritis or lupus will also cause there to be a reduced number of lymphocytes in the CBC.
- Damage to the bone marrow. ...
What is the most important function of the lymph?
What are functions of lymph?
- It keeps the body cells moist.
- It transports oxygen, hormones and nutrients to different parts of the body and removes metabolic waste from the cells.
- It transports antibodies and lymphocytes to the blood.
- Maintaining the composition of tissue fluid and the volume of blood.

What does lymph consist of quizlet?
Lymph is a thin, watery fluid composed of intercellular, or interstitial, fluid, which forms when plasma diffuses into tissue spaces. Of what is it (lymph) composed? Lymph is composed of water, digested nutrients, salts, hormones, oxygen, carbon dioxide, lymphocytes, and metabolic wastes such as urea.
What are the three components of lymph?
Components of the Lymphatic SystemLymph. Lymph is a fluid similar in composition to blood plasma. ... Lymphatic Vessels. Lymphatic vessels, unlike blood vessels, only carry fluid away from the tissues. ... Lymphatic Organs.
What are lymph nodes made of?
Lymph nodes are made of lymph tissue and different types of cells including: White blood cells (lymphocytes).
What are the four components of lymph nodes?
(1988) 'PANEL DISCUSSION: THE FOUR COMPONENTS OF THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM—LYMPH, LYMPH NODES, LYMPHOCYTES, AND LYMPHATICS', Lymphology.
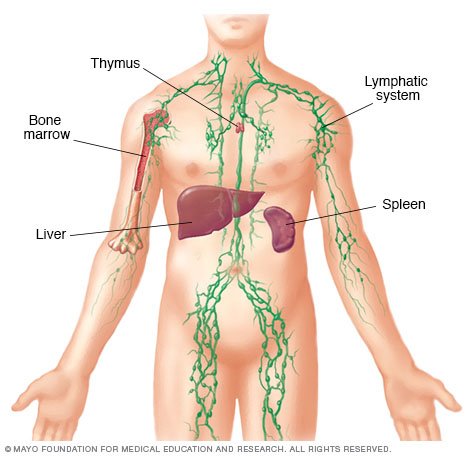
What are the 3 lymphatic organs?
Lymphatic organs include the spleen, thymus and tonsils.
How do you know if your lymphatic system is blocked?
Symptoms of a blocked lymphatic system include swelling, fatigue, bloating, depression and excess weight gain.
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
The function of the lymphatic system is to carry lymph throughout the body that contains infection-fighting white blood cells.
What organs are part of the lymphatic system?
These lymph nodes are connected to lymphatic vessels which circulate the lymph throughout the body. The lymph gets filtered at the lymph nodes. The spleen, tonsils, adenoids and the thymus all forms a part of the lymphatic system.
What are the functions of lymphocytes?
Few major functions of lymph are mentioned below: It keeps the body cells moist. It transports oxygen, hormones and nutrients to different parts of the body and removes metabolic waste from the cells. It transports antibodies and lymphocytes to the blood. Maintaining the composition of tissue fluid and the volume of blood.
What is the role of lymphatic vessels in the small intestine?
Maintaining the composition of tissue fluid and the volume of blood. Absorption of fats from the small intestine through lymphatic vessels. Prevents invasion of microbes and foreign substances inside the lymph nodes.
Where is interstitial fluid collected?
The interstitial fluid is collected by the lymphatic system and the rest is drained out. The drained fluid moves back to the blood vessels and the remaining fluid is collected through the lymph capillaries, which is also known as lymphatic capillaries. Also refer : Difference Between Blood and Lymph.
Which organ is the largest lymphatic organ?
The spleen , tonsils, adenoids and the thymus all forms a part of the lymphatic system. The spleen is considered as the largest lymphatic organ in the system, which is located under the ribcage, above the stomach, and exactly in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen.
Is plasma the same as interstitial fluid?
It consists of small water-soluble substances which flow in between the tissue cells. Both plasma and interstitial fluid are the same due to the continuous exchange of small solutes, water and ions across the capillary walls of the tissues.
What is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system?
Note how the tissue fluid is entering the blind ends of lymph capillaries (shown as deep green arrows) Lymph (from Latin, lympha meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, ...
What is the function of lymph nodes?
Anatomical terminology. Lymph (from Latin, lympha meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to the central circulation.
How does lymph transport fat?
Lymph also transports fats from the digestive system (beginning in the lacteals) to the blood via chylomicrons . Bacteria may enter the lymph channels and be transported to lymph nodes, where the bacteria are destroyed. Metastatic cancer cells can also be transported via lymph.
Why does lymph not flow backwards?
Lymph that enters the lymph vessels from the interstitial spaces usually does not flow backwards along the vessels because of the presence of valves. If excessive hydrostatic pressure develops within the lymph vessels, though, some fluid can leak back into the interstitial spaces and contribute to formation of edema .
Why does lymphoma move?
Despite low pressure, lymph movement occurs due to peristalsis (propulsion of the lymph due to alternate contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle tissue), valves, and compression during contraction of adjacent skeletal muscle and arterial pulsation.
Which lymph node is richer in lipids?
Lymph that leaves a lymph node is richer in lymphocytes than blood plasma is. The lymph formed in the human digestive system called chyle is rich in triglycerides (fat), and looks milky white because of its lipid content.
Where does interstitial fluid form?
Interstitial fluid forms at the arterial (coming from the heart) end of capillaries because of the higher pressure of blood compared to veins, and most of it returns to its venous ends and venules; the rest (up to 10%) enters the lymph capillaries as lymph.
What is the liquid in the lymphatic system?
lymph. [ limf] a transparent, usually slightly yellow, often opalescent liquid found within the lymphatic vessels, and collected from tissues in all parts of the body and returned to the blood via the lymphatic system. It is about 95 per cent water; the remainder consists of plasma proteins and other chemical substances contained in ...
What is a lymph node?
lymph node any of the accumulations of lymphoid tissue organized as definite lymphoid organs along the course of lymphatic vessels (see accompanying illustration); they consist of an outer cortical and an inner medullary part.
What is the term for fluid that is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system?
When this fluid is drained from the tissues and collected by the lymphatic system, it is called lymph . The lymphatic system eventually returns the lymph to the blood, where it again becomes plasma. This movement of fluid through the body is described under circulatory system.
Why do lymph nodes swell?
Infection: An infection in the body can lead to an increase in white blood cells concentration and cause swelling in lymph nodes of the neck. Lymph, aside from carrying waste, also contains white blood cells that are known to protect the body from infection and disease.
What is the function of lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes are the main source of lymphocytes of the peripheral blood and, as part of the reticuloendothelial system, serve as a defense mechanism by removing noxious agents such as bacteria and toxins, and probably play a role in antibody formation. Sometimes called, incorrectly, lymph gland. Called also lymph or lymphatic follicle ...
Why is my lymph milky?
Lymph from the intestines is milky, especially after a meal, because of the large number of fat globules which it contains. Fat-laden lymph is called CHYLE. Collins Dictionary of Medicine © Robert M. Youngson 2004, 2005.
What is the fluid that is collected from the tissues throughout the body?
lymph. A clear, transparent, sometimes faintly yellow and slightly opalescent fluid that is collected from the tissues throughout the body, flows in the lymphatic vessels (through the lymph nodes), and is eventually added to the venous blood circulation. Lymph consists of a clear liquid portion, varying numbers of white blood cells ...
What Is Lymph?
Lymph is short for lymphatic fluid, and is defined as the fluid in the body that plays a large role in the immune system.
Functions of Lymph
The lymph produced from tissues in the small intestine contains a significant amount of fat and fat-soluble vitamins. Fat serves as a high-yield source of energy, storing vitamins like A, D, E, and K which keep the body healthy and working properly.
Composition of Lymph: What does Lymph Contain?
The composition of lymph is essential to bodily function and varies based on the part of the body from which it originates. For example, lymph produced from the gastrointestinal tract will contain high amounts of fat because tissues in the gut metabolize fat consumed from the diet.
Diseases of the Lymph
In this research activity students will be researching a disease that affects the lymph. Students will do academic research using credible sources, such as Mayo Clinic, Web MD, NHS or others that are written by medical professionals, news outlets or universities. For example, students might research lymphoma, a cancer of the lymphatic cells.
Structure
The composition of Lymph is exceptionally close to that of blood plasma but not identical. Blood plasma has more concentrated lymphocytes than Lymph that exits a lymph node. Because of its lipid content, the Lymph produced in the human digestive system is known as chyle, high in triglycerides (fat) and has a milky white texture.
Composition of Lymph
Lymph plasma, lymph corpuscles, and lymphoid organs comprise Lymph. The following is a list of all the components of Lymph:
Important functions of Lymph
Lymph serves several essential functions. The following are a few of Lymph's most significant parts:
What is the lymphatic system?
Overview. The lymphatic system is a network of tissues, vessels and organs that work together to move lymph back into your your bloodstream. The lymphatic system is part of your immune system.
What is the function of lymphocytes?
It produces and releases lymphocytes (white blood cells) and other immune cells that monitor and then destroy the foreign invaders — such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi — that may enter your body. Transports and removes waste products and abnormal cells from the lymph. ###.
What system collects excess fluid?
Maintains fluid levels in your body: As just described, the lymphatic system collects excess fluid that drains from cells and tissue throughout your body and returns it to your bloodstream, which is then recirculated through your body. Absorbs fats from the digestive tract: Lymph includes fluids from your intestines that contain fats ...
What system moves blood into the circulatory system?
The lymphatic system is a network of tissues, vessels and organs that work together to move a colorless, watery fluid called lymph back into your circulatory system (your bloodstream). Some 20 liters of plasma flow through your body’s arteries and smaller arteriole blood vessels and capillaries every day.
How to keep lymphatic system strong?
To keep your lymphatic system strong and healthy, you should: Avoid exposure to toxic chemicals like those in pesticides or cleaning products. These chemicals can build up in your system and make it harder for your body to filter waste. Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated so lymph can easily move throughout your body.
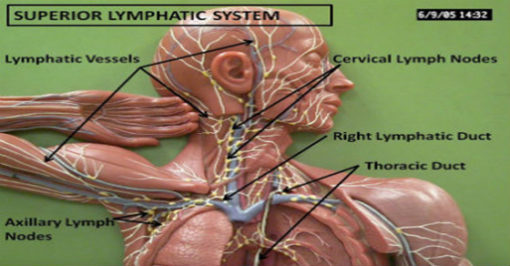
Which ducts are used to collect lymph?
Collecting ducts: Lymphatic vessels empty the lymph into the right lymphatic duct and left lymphatic duct (also called the thoracic duct). These ducts connect to the subclavian vein, which returns lymph to your bloodstream. The subclavian vein runs below your collarbone.
How many liters of fluid are returned to the circulation?
After delivering nutrients to the body’s cells and tissues and receiving their waste products, about 17 liters are returned to the circulation by way of veins. The remaining three liters seep through the capillaries and into your body’s tissues. The lymphatic system collects this excess fluid, now called lymph, ...
What is the lymphatic system?
News. The lymphatic system is part of the immune system. It also maintains fluid balance and plays a role in absorbing fats and fat-soluble nutrients. The lymphatic or lymph system involves an extensive network of vessels that passes through almost all our tissues to allow for the movement of a fluid called lymph.
How do lymph vessels work?
They work in a similar way to the blood vessels. The lymph vessels work with the veins to return fluid from the tissues. Unlike blood, the lymphatic fluid is not pumped but squeezed through the vessels when we use our muscles.
How does lymphatic fluid work?
The properties of the lymph vessel walls and the valves help control the movement of lymph. However, like veins, lymphatic vessels have valves inside them to stop fluid from flowing back in the wrong direction.
Why do lymph nodes swell?
These nodes swell in response to infection, due to a build-up of lymph fluid, bacteria, or other organisms and immune system cells. A person with a throat infection, for example, may feel that their “glands” are swollen.
How long does it take for lymph nodes to swell?
However, medical advice should be sought if: 1 lymph nodes stay swollen for longer than 1 to 2 weeks 2 a swollen lymph node feels hard or fixed in place 3 swelling is accompanied by fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss
What happens if the lymphatic system drains too much fluid?
Without the lymphatic system draining excess fluid, our tissues would swell, blood volume would be lost and pressure would increase.
How much fluid is leaking from the cardiovascular system into the body?
Around 2 liters of fluid leak from the cardiovascular system into body tissues every day. The lymphatic system is a network of vessels that collect these fluids, or lymph. Lymph is a clear fluid that is derived from blood plasma. The lymph vessels form a network of branches that reach most of the body’s tissues.
What is lymph used for?
There is one exception, however. Lymph is also useful for transporting fatty acids throughout the body.
What is the fluid that makes up the lymphatic system?
Instead, a great deal of the soft tissue in your body is comprised of cells floating in a suspension of liquid known as interstitial fluid. Lymph is the result of this interstitial fluid making its way to the lymphatic system, a whole collection of vessels and organs dedicated to maintaining balance and providing immune cells.
Why is interstitial fluid sent through lymph nodes?
At is most basic level, it is interstitial fluid that has been sent through lymph nodes in order to carry certain cellular wastes away. This is especially true of proteins and dead cells. However, it also permits a more efficient method of transport for fatty acids throughout the body.
What does a syringe look like?
Throughout most of the body, it looks sort of like a weak milky fluid, somewhere between white and a pale yellow. It gets that pale color from the protein waste products and immune cells that it carries. It takes these cells and proteins away from the cells in question and onward to be processed out of your body.
How does water enter the body?
You drink water, and it enters your digestive tract. It's then absorbed by the small intestine and enters the blood stream. The pumping action of the heart pushes some of this water out of the blood vessels and into the space between cells. This is where it becomes interstitial fluid.
How much water is lymph?
What Is Lymph? Think about something for a moment. Your body is around 75% water. So, where do you think all that water is? Of course, around four to six liters of fluid in your body is blood, which does have water in it. Also, your stomach acid is diluted to some degree by water, lest it eat through your entire body.
Is lymph important for cancer?
In this lesson, we looked at the importance of lymph to the human body. Lymph is one of the most important fluids in the human body and fulfills many requirements.
Overview
Lymph (from Latin, lympha, meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to the central circulation. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues —enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vess…
Etymology
The word lymph is derived from the name of the ancient Roman deity of fresh water, Lympha.
Structure
Lymph has a composition similar but not identical to that of blood plasma. Lymph that leaves a lymph node is richer in lymphocytes than blood plasma is. The lymph formed in the human digestive system called chyle is rich in triglycerides (fat), and looks milky white because of its lipid content.
Development
Blood supplies nutrients and important metabolites to the cells of a tissue and collects back the waste products they produce, which requires exchange of respective constituents between the blood and tissue cells. This exchange is not direct, but instead occurs through an intermediary called interstitial fluid, which occupies the spaces between cells. As the blood and the surrounding cells continually add and remove substances from the interstitial fluid, its composition continual…
Functions
Lymph returns proteins and excess interstitial fluid to the bloodstream. Lymph may pick up bacteria and transport them to lymph nodes, where the bacteria are destroyed. Metastatic cancer cells can also be transported via lymph. Lymph also transports fats from the digestive system (beginning in the lacteals) to the blood via chylomicrons.
Tubular vessels transport lymph back to the blood, ultimately replacing the volume lost during th…
Clinical significance
Histopathological examination of the lymph system is used as a screening tool for immune system analysis in conjunction with pathological changes in other organ systems and clinical pathology to assess disease status. Although histological assessment of the lymph system does not directly measure immune function, it can be combined with identification of chemical biomarkers to determine underlying changes in the diseased immune system.
As a growth medium
In 1907 the zoologist Ross Granville Harrison demonstrated the growth of frog nerve cell processes in a medium of clotted lymph. It is made up of lymph nodes and vessels.
In 1913, E. Steinhardt, C. Israeli, and R. A. Lambert grew vaccinia virus in fragments of tissue culture from guinea pig cornea grown in lymph.
External links
• Media related to Lymph fluid at Wikimedia Commons