
See more

What does Micrococcus look like?
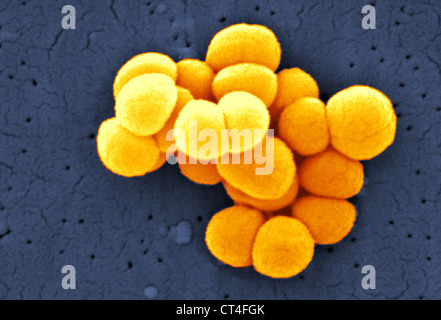
Micrococci have Gram-positive spherical cells ranging from about 0.5 to 3 micrometers in diameter and typically appear in tetrads. They are catalase positive, oxidase positive, indole negative and citrate negative. Micrococcus has a substantial cell wall, which may comprise as much as 50% of the cell mass.
What shape are Micrococcus luteus?
spherical shapeM. luteus was first known as Micrococcus lysodeikticus and was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. Its name stands for: microscopic (micro), of spherical shape (coccus), and yellow (luteus).
How do you identify Micrococcus luteus?
Other distinguishing identification features are that M. luteus is urease & catalase positive but coagulase negative. Some Micrococcus species are now identified, particularly on newer identification techniques such as MALDI-TOF, as Kocuria sp. This is due to reclassification of some species of Micrococcus.
What color is M. luteus?
Micrococcus luteus is coagulase negative, bacitracin susceptible, and forms bright yellow colonies on nutrient agar.
What is the color of Micrococcus?
They are catalase positive and often oxidase positive although this reaction may be weak (see Table 23.3). They form pigmented red or yellow colonies and have an optimum growth temperature of 25 to 37 °C. Micrococcus are halotolerant and grow in 5% salt.
What is the size of Micrococcus luteus?
0.5 to 3.5 μmMicrococcus luteus was first described by [1], [6]. Micrococcus lutues are Gram positive cocci that are 0.5 to 3.5 μm in diameter and arranged in tetrads or irregular clusters.
How can you distinguish between Micrococcus luteus and Staphylococcus epidermidis?
MANNITOL SALT AGARTESTStaphylococcus aureusStaphylococcus epidermidisCatalasePositivePositiveGlucose FermentationPositivePositiveCoagulasePositiveNegativeSalt Tolerance on Mannitol Salt TolerancePositivePositive3 more rows
What stain is used for Micrococcus luteus?
Positive Gram-stainGram-staining remains the fundamental method for determinative bacteriology, dividing bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms.
What color is Gram-positive?
A Gram stain is colored purple. When the stain combines with bacteria in a sample, the bacteria will either stay purple or turn pink or red. If the bacteria stays purple, they are Gram-positive. If the bacteria turns pink or red, they are Gram-negative.
What color is Micrococcus luteus after Gram staining?
Since M. luteus was not on slide 3 and was on the other two slides that presented the distinguishable purple color, it is concluded M. luteus is the gram positive bacteria.
Is Micrococcus luteus translucent?
Micrococcus luteus Several uncommon strains produce raised colonies with translucent, depressed centers. Colony pigmentation varies considerably but is usually different shades of yellow or cream-white.
Is Micrococcus luteus methyl red positive?
(2000) investigated that Micrococcus luteus was positive to urease and methyl red, while negative to indole formation, nitrate reduction and Voges Proskauer.
What is the colony morphology of M. luteus?
The colony morphology of being yellow, shiny and smooth line up perfectly with M. luteus (Public Health England). The antibiotic resistance test showed only minor resistance to the antibiotic Oxacillin, which is likely due to a chance inheritance in the population or complete chance because of the weak strength.
Where can micrococcus be found?
The Micrococcus genus is known to be found on dust particles, in water, on skin and skin glands in vertebrates, and some species can be found in milk. They are fairly ubiquitous in the environment, and are small (0.5 to 3.5 micrometers in diameter) and non-motile.
How big are Korona cells?
They are fairly small as well, usually about a millimeter in diameter and of a normal height. Under the microscope they are round cells. When looking at the genetic tests, most of the identified strains in the Korona test are Micrococcus luteus.
What percentage of Gram positive bacteria are gram negative?
Most of the bacterium in the gram stains were gram negative, but a significant amount, about twenty percent , showed up as gram positive. The colonies are a pale, translucent yellow, and are shiny when looked at in the light. They are fairly small as well, usually about a millimeter in diameter and of a normal height.
Is M. luteus an aerobe?
Many of the tests did line up with M. luteus though, such as the fluid thyoglycate test, which showed that it was an obligate aerobe. M. luteus is an obligate aerobe (Medical Laboratories). The positive catalase result lines up with M. luteus (Public Health England).
Is micrococcus luteus gram positive?
The Gram stain, while it was gram variable, does not ideally match with the genetic test that resulted in Micrococcus luteus, which can be gram variable but is usually gram positive (Bonjar). On top of that, most of the bacterium that were stained were gram negative, which conflicts with this result.
What is the name of the strain of Micrococcus luteus?
In 2003, it was proposed that one strain of Micrococcus luteus, ATCC 9341, be reclassified as Kocuria rhizophila.
How long has Micrococcus luteus been in oligotrophic environments?
Recent work by Greenblatt et al. demonstrate that Micrococcus luteus has survived for at least 34,000 to 170,000 years on the basis of 16S rRNA analysis, and possibly much longer. It was sequenced in 2010 and has one of the smallest genomes of free-living actinobacteria sequenced to date, comprising a single circular chromosome of 2,501,097 bp.
What is the wavelength of light that luteus absorbs?
Norwegian researchers in 2013 found a M. luteus strain that synthesizes a pigment that absorbs wavelengths of light from 350 to 475 nano-meters. Exposure to these wavelengths of ultraviolet light has been correlated with an increased incidence of skin cancer, and scientists believe this pigment can be used to make a sunscreen that can protect against ultraviolet light.
Is M. luteus a bacterium?
luteus is considered a contaminant in sick patients and is resistant by slowing of major metabolic processes and induction of unique genes. It is a high G + C ratio bacterium. M. luteus is coagulase negative, bacitracin susceptible, and forms bright yellow colonies on nutrient agar.
Is Micrococcus luteus a Gram positive bacterium?
Micrococcus luteus is a Gram-positive, to Gram-variable, nonmotile, coccus, tetrad-arranging, pigmented, saprotrophic bacterium that belongs to the family Micrococcaceae. It is urease and catalase positive. An obligate aerobe, M. luteus is found in soil, dust, water and air, and as part of the normal microbiota of the mammalian skin.
Habitat
Results
Genetics
Example
- Table 1: Graph from Korona showing the percent reads of each organism, and to which taxonomic level.
Taxonomy
- Table 2: Graph of the genomic reads by taxonomic level using Korona. M. luteus is the majority of reads on the species level.
Chemistry
- When looking at the antibiotic test results, the isolate is resistant to none of the applied antibiotics, and is only lightly to intermediately resistant to oxacillin. The Gentamicin, Cefoperazone, Vancomycin, Tobramycin, Amikacin, Trimethoprim, and Cefazdin antibiotics showed obvious susceptibility, with most of them having enormous rings of 50 to 52 millimeter…
Diagnosis
- Many of the tests did line up with M. luteus though, such as the fluid thyoglycate test, which showed that it was an obligate aerobe. M. luteus is an obligate aerobe (Medical Laboratories). The positive catalase result lines up with M. luteus (Public Health England). The colony morphology of being yellow, shiny and smooth line up perfectly with M. luteus (Public Health En…
Environment
- The Micrococcus genus is known to be found on dust particles, in water, on skin and skin glands in vertebrates, and some species can be found in milk. They are fairly ubiquitous in the environment, and are small (0.5 to 3.5 micrometers in diameter) and non-motile. This fits well with where I sampled my bacterium from, as a shower drain is a place w...
Research
- If I were to continue researching this isolate, I would redo the API 20 E test strip with a fresh, active culture to ensure that it can reduce nitrate, and also the oxidase test to ensure that it does have cytochrome c oxidase present, which it should according to Public Health England. Further tests that I would do would be testing how much heat resistance it has, the density of a broth su…