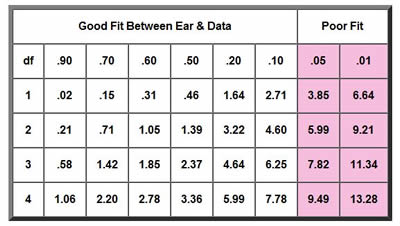
Chi-Square P-Values
- P <= 0.05 (Hypothesis interpretations are rejected)
- P>= 0.05 (Hypothesis interpretations are accepted)
What does a high chi square value mean?
What is a high chi square value? Greater differences between expected and actual data produce a larger Chi-square value. The larger the Chi-square value, the greater the probability that there really is a significant difference. There is no significant difference. The amount of difference between expected and actual data is likely just due to chance.
How do you determine critical value in chi square?
The Chi-Square critical value can be found by using a Chi-Square distribution table or by using statistical software. To find the Chi-Square critical value, you need: A significance level (common choices are 0.01, 0.05, and 0.10) Degrees of freedom; Using these two values, you can determine the Chi-Square value to be compared with the test ...
How do you calculate chi square value?
Quick Steps
- Click on Analyze -> Descriptive Statistics -> Crosstabs
- Drag and drop (at least) one variable into the Row (s) box, and (at least) one into the Column (s) box
- Click on Statistics, and select Chi-square
- Press Continue, and then OK to do the chi square test
- The result will appear in the SPSS output viewer
What is the critical value of chi square?
The Chi-Square critical value for a significance level of 0.05 and degrees of freedom = 11 is 19.67514. Thus, if we’re conducting some type of Chi-Square test then we can compare the Chi-Square test statistic to 19.67514. If the test statistic is greater than 19.67514, then the results of the test are statistically significant.

Is a high or low chi squared value good?
The larger the Chi-square value, the greater the probability that there really is a significant difference. There is a significant difference between the groups we are studying.
What should be the value of chi-square?
In general a p value of 0.05 or greater is considered critical, anything less means the deviations are significant and the hypothesis being tested must be rejected. When conducting a chi-square test, this is the number of individuals anticipated for a particular phenotypic class based upon ratios from a hypothesis.
How do you interpret chi-square result?
For a Chi-square test, a p-value that is less than or equal to your significance level indicates there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the observed distribution is not the same as the expected distribution. You can conclude that a relationship exists between the categorical variables.
Is a low chi-square value good?
A low value for chi-square means there is little difference between what was observed and what would be expected. In theory, if your observed and expected values were equal (“no difference”) then chi-square would be zero. Tip: The Chi-square statistic can only be used on numbers.
What do you do when chi-square expected count is less than 5?
The conventional rule of thumb is that if all of the expected numbers are greater than 5, it's acceptable to use the chi-square or G–test; if an expected number is less than 5, you should use an alternative, such as an exact test of goodness-of-fit or a Fisher's exact test of independence.
How do you know if chi-square is significant in SPSS?
Now look at the “Pearson Chi-Square Asymp. Sig (2 sided)”*. Since Chi-Square is testing the null hypothesis, the Sig value must be . 05 or less for there to be a significant statistical for the relationship between the variables.
What does p 0.05 mean in chi-square?
P > 0.05 is the probability that the null hypothesis is true. 1 minus the P value is the probability that the alternative hypothesis is true. A statistically significant test result (P ≤ 0.05) means that the test hypothesis is false or should be rejected. A P value greater than 0.05 means that no effect was observed.
What would a chi-square significance value of p 0.05 suggest?
A p-value less than 0.05 (typically ≤ 0.05) is statistically significant. It indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, as there is less than a 5% probability the null is correct (and the results are random). Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis, and accept the alternative hypothesis.
How do you use a chi-square to test a hypothesis?
How to perform a Chi-square testDefine your null and alternative hypotheses before collecting your data.Decide on the alpha value. ... Check the data for errors.Check the assumptions for the test. ... Perform the test and draw your conclusion.
What does a high p-value mean in chi-square?
If the p-value is larger than the significance level, you fail to reject the null hypothesis because you do not have enough evidence to conclude that the data do not follow the distribution with specified proportions.
What is the null hypothesis for a chi square test?
The null hypothesis of the Chi-Square test is that no relationship exists on the categorical variables in the population; they are independent.
What does it mean when the chi square value is high?
A very large chi square test statistic means that the sample data (observed values) does not fit the population data (expected values) very well. In other words, there isn't a relationship.
What is likelihood ratio in Chi Square?
The Likelihood-Ratio test (sometimes called the likelihood-ratio chi-squared test) is a hypothesis test that helps you choose the “best” model between two nested models. “Nested models” means that one is a special case of the other.
How to find the p value of a chi squared statistic?
Look up the p value associated with your chi-square test statistic using the chi-square distribution table. To do this, look along the row corresponding to your calculated degrees of freedom. Find the value in this row closest to your test statistic. Follow the column that contains that value upwards to the top row and read off the p value. If your test statistic is in between two values in the initial row, you can read off an approximate p value intermediate between two p values in the top row.
What is chi squared test?
Chi-squared, more properly known as Pearson's chi-square test, is a means of statistically evaluating data. It is used when categorical data from a sampling are being compared to expected or "true" results. For example, if we believe 50 percent of all jelly beans in a bin are red, a sample of 100 beans from that bin should contain approximately 50 that are red. If our number differs from 50, Pearson's test tells us if our 50 percent assumption is suspect, or if we can attribute the difference we saw to normal random variation.
How to find the degrees of freedom of chi squared?
Determine the degrees of freedom of your chi-square value. If you are comparing results for a single sample with multiple categories, the degrees of freedom is the number of categories minus 1. For example, if you were evaluating the distribution of colors in a jar of jellybeans and there were four colors, the degrees of freedom would be 3. If you are comparing tabular data the degrees of freedom equals the number of rows minus 1 multiplied by the number of columns minus 1.
What is critical p value?
Determine the critical p value that you will use to evaluate your data. This is the percent probability (divided by 100) that a specific chi-square value was obtained by chance alone. Another way of thinking about p is that it is the probability that your observed results deviated from the expected results by the amount that they did solely due to random variation in the sampling process.
How many values should be in a sample to be valid?
The value obtained for each category in the sample should be at least 5 for results to be valid.
What is chi squared test?
The Chi-squared test allows you to assess your trained regression model's goodness of fit on the training, validation, and test data sets.
Who Uses Chi-Square Analysis?
Chi-square is most commonly used by researchers who are studying survey response data because it applies to categorical variables. Demography, consumer and marketing research, political science, and economics are all examples of this type of research.
Can a chi square determine causality?
Be mindful that the chi-square can only determine whether two variables are related. It does not necessarily follow that one variable has a causal relationship with the other. It would require a more detailed analysis to establish causality.
Is chi squared statistically significant?
The chi-square test, for starters, is extremely sensitive to sample size. Even insignificant relationships can appear statistically significant when a large enough sample is used. Keep in mind that "statistically significant" does not always imply "meaningful" when using the chi-square test.
What is a chi squared test?
A Chi-Square goodness of fit test is used to determine whether or not a categorical variable follows a hypothesized distribution.
What is the p-value of X2?
According to the Chi-Square Score to P Value Calculator, the p-value associated with X2 = 4.36 and n-1 = 5-1 = 4 degrees of freedom is 0.359472.
How many counts are needed for chi square?
This test is not valid for small samples, and if some of the counts are less than five (may be at the tails). The reason is Central Limit Theorem, chis-square distribution approaches standard normal distribution for large degrees of freedom.
What is the degree of freedom in chi square?
In chi-square goodness of fit test, the degrees of freedom is (k-1) where k is the number of categories you are comparing. you need to see critical value of chi-square at the desired level of significance for the calculated degrees of freedom and compare it with the value of chi-square you got. Now, the real issue is you much significance level you want. Best regards. P.Ganguly
Why are p-values different?
One of the reasons, why the p-values are different, may be because of choice of bins. Chi -square goodness of test is sensitive to the choice of bins. There is no optimal choice for the bin width (since the optimal bin width depends on the distribution). Most reasonable choices should produce similar, but not identical, results. If the distributional assumption is not justified, a non-parametric or robust technique may be required.
Is chi squared a parametric test?
Chi-square goodness of fit is a non-parametric test. It does not require normality assumptions .It is rather used for categorical variable. The test criteria (Q) suggested by Pearson (1900) is the sum of squares deviations of expected and observed frequencies normalized by the expected frequency.
Does the chi square test require normality?
I am sorry but the chi-square test does not require any assumption of Normality; it is based on the chi-square distribution and has its own applicability criteria. However, it is possible to use exact methods instead.
Is a p value of 0.03 enough for chi square test?
A p value = 0.03 would be considered enough if your distribution fulfils the chi-square test applicability criteria. Since p < 0.05 is enough to reject the null hypothesis (no association), p = 0.002 reinforce that rejection only.
Is 0.03 good for Nyquist?
Yes. 0.03 is good enough for Nyquist plot.
