The nucleic acid
Nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three compone…
What does antiparallel mean in DNA?
DNA has to be antiparallel. The antiparallel nature allows two strands to go in opposite direction. Which ultimately facilitate forming daughter DNA into two different directions and preety helpful during polymerase chain reaction that amplify DNA to make multiple copies of it.
Does DNA replication always start at origin of replication?
Replication always starts at specific locations in DNA, which are called origins of replication. In the prokaryotic genome, the single origin of replication has many A-T base pairs, which have weaker hydrogen bonding than G-C base pairs, and make it easier for the DNA strands to separate.
Why are DNA strands antiparallel?
DNA is double stranded, and the strands are antiparallel because they run in opposite directions.Each DNA molecule has two strands of nucleotides. Each strand has sugar phosphate backbone, but the orientation of the sugar molecule is opposite in the two strands.
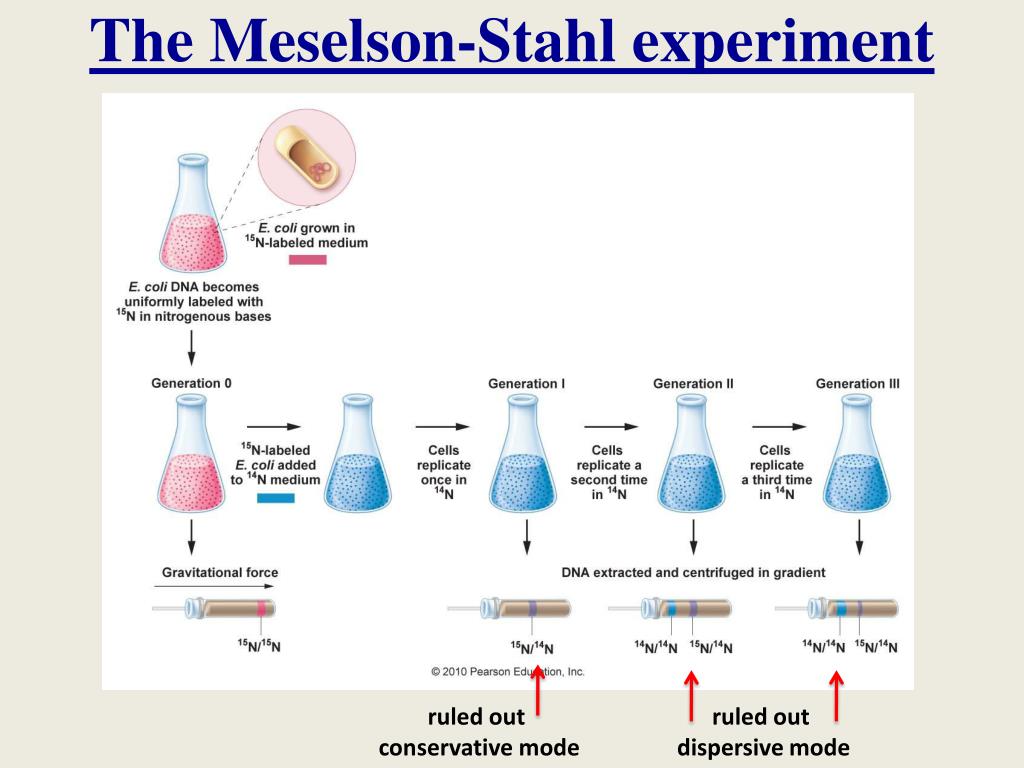
What are the three types of DNA replication?
- Semi-conservative replication. In this model, the two strands of DNA unwind from each other, and each acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. ...
- Conservative replication. ...
- Dispersive replication. ...
What is the role of DNA in the evolution of an organism?
The DNA acts as the hereditary material in almost all living beings. It stores all the information to regulate, differentiation, and reproduction. The genetic information is present in the form of triplets called codes.DNA controls the structural synthesis of the proteins and regulate the metabolism. The replication of the genetic material is almost living organism is semiconservative type. At the time of the replication, the newly generated strand is the leading strand and the old is the lagging strand. The leading strand shows continuous synthesis.
What are the two strands of DNA?
Nucleotides are the important structures that are the polymeric units of the DNA molecule. The bases in the DNA are adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine. The ratio of the purines in genetic material is equal to the pyrimidine. This rule was proposed by Chargaff. This is usually used in calculating the number of bases in the genetic material. The nucleotides found in the genetic material are linked with bonds. The name of this kind of bond is phosphodiester. The different bases of nitrogen are joined by the hydrogen bonds, these either have a double bond or triple bond. Deoxyribose sugar is present in the DNA, in this sugar, the oxygen molecule is lacking at the second carbon position. The acknowledgment that DNA’s structure is that of a two-fold helix explained the component of base matching by which hereditary data is stored and replicated in living beings and is broadly viewed as one of the most significant logical discoveries of the twentieth century. Cramp, Wilkins, and Watson each got 33% of the 1962 Nobel Prize for their commitments to the discovery.
What are the different types of DNA?
There are various forms of DNA, this may be found in A-DNA, B-DNA, C-DNA, and D-DNA . A-DNA is consist of 11 base pairs that are sufficiently tilted from the axis of the helix. It is found at seventy-five relative humidity in the presence of sodium ions, potassium ions, and calcium ions. B-DNA includes ten base pairs this is usually found in the ninety-two degrees of relative humidity and low ionic concentration. DNA is the genetic material as well as the macromolecule. It is composed of the three vital components, namely the heterocyclic nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and the phosphate group. A polynucleotide chain is developed with the help of interlinking of several nucleotides by the 5’ to 3’ phosphodiester. The bond link the 5’ carbon of a pentose of nucleotide with the 3’-carbon of a pentose of the adjoining nucleotide. The bond formed between the sugar and the phosphate molecule is called an ester end. One groove, the significant notch, is 22 Å wide, and the other, the minor groove which is 12 Å wide. The direction of the strand is opposite because one strands 5; carbon faces to other carbon of another strand at 3’ carbon. This antiparallel sequence of the nucleotides helps in DNA replication. This genetic material is present in the nucleus of every living organism except them. In viruses, the genetic material is either DNA or ribonucleic acid (RNA). These nucleotides are formed with the help of the C, H, O, N, and P. the strands of the DNA run opposite to each other. One runs in the 3’ to 5’ direction while the other one moves in the opposite direction. The slenderness of the minor groove implies that the edges of the bases are more available in the significant groove. Thus, proteins like transcription factors that can tie to explicit arrangements in double-stranded DNA often make contact to the sides of the bases uncovered in the major groove.
Is DNA a macromolecule?
The DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid and these are considered as the macromolecules of utmost importance. These are known as polymeric compounds of the nucleotides; therefore, these are referred to as a polynucleotide.
Why is the double helix anti-parallel?
Because the double helix is anti-parallel and DNA polymerase only synthesizes new DNA from 5′-3′, the template strand reading 3′-5′ results in a continuous, leading strand, while the template strand reading 5′-3′ results in a discontinuous, lagging strand. Being a highly regulated process, multiple proteins are required both during ...
How is DNA replicated?
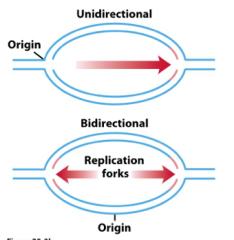
When DNA begins to replicate, a replication bubble is formed that can be detected visually by electron microscopy. A specific sequence of bases- known as the origin of replication – determines where this replication bubble begins. Inside of the bubble, two Y-shaped replication forks result where DNA is actively replicated on either side of the region. The replication forks are formed as the double strands of DNA are separated by helicase in both directions away from the origin of replication. It is at the replication fork that DNA replication proteins attach to fulfill their functions.
Why is DNA polymerase 3 important?
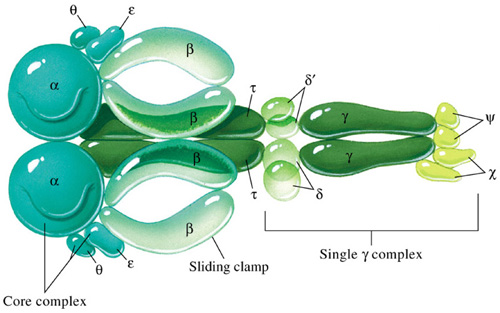
Because eukaryotic DNA is linear, they have ends that create a challenge. For the leading strand, DNA polymerase III can continue down the entire length of DNA. However, in the lagging strand, a primer must be added in front of the Okazaki fragment being synthesized before DNA polymerase III can attach and synthesize the new DNA strand opposite of the replication fork. Once the last Okazaki fragment is synthesized, a small DNA segment is leftover at the tip of the strand. This segment cannot be left unattended. If this DNA isn’t replicated, then genetic material will be lost each time replication occurs. After several replication cycles, this can result in lost information that could be critical for the individual to survive.
What is the process of DNA replication?
Definition. DNA replication is a process that occurs during cellular division where two identical molecules of DNA are created from a single molecule of DNA. As a semiconservative process, a single molecule containing two strands of DNA in double helix formation is separated, where each strand serves as a template for the new DNA molecules.
What direction does DNA run?
DNA has directionality that can run either 3′-5′ or 5′-3′ based off of the carbons in the sugar group. The two strands of DNA in the double helix must run opposite to each other in an anti-parallel fashion. Therefore, if the first strand starts at the 3′ end and finishes at the 5′ end, then the second strand must run opposite, starting at the 5′ end and finishing at the 3′ end.
Where does DNA polymerase III move?
DNA polymerase III moves down the leading strand towards the replication fork, adding bases to the new strand from the 5’ end to the 3’ end.
Which enzyme relieves tension by making cuts in the DNA and rejoining them before the replication fork arrives?
Topoisomerase: Because unwinding of the DNA by helicase creates tension further down the strand, this enzyme relieves tension by making cuts in the DNA and rejoining them before the replication fork arrives.
What are anti-parallel strands?
Anti-parallel strands. The DNA molecule is composed of two strands held together by hydrogen bonds. ... The names come from the notation for the two sugar carbon atoms which participate in the phosphodiester bonds. The different strands in the helix run in opposite (anti-parallel) directions. 1.3K views.
Why is antiparallel orientation important?
The antiparallel orientation allows for the base pairs to compliment one another. Antiparallel DNA is also more structurally stable than parallel DNA.The antiparallel orientation of DNA has important implications for DNA replication, as at the replication fork one strand allows steady replication, thereby known as leading strand while the other becomes lagging strand.
Why would life not exist if DNA strands were not antiparallel?
And NO LIFE would exist because of lacking mechanism to carry out replication ("copying"), and transcription ("translation") of genetic information.
How does RNA polymerase work?
For RNA transcription, RNA polymerase unwinds the two strands during replication so that pre-mRNA molecule will sneak through the space and copy the genetic info. If the DNA strands were to be parallel, this wouldn't make sense for the info to be read from DNA .
Which direction does DNA grow in?
Each strand has sugar phosphate backbone, but the orientation of the sugar molecule is opposite in the two strands. Both of the strands of DNA double helix can grow in 5' to 3' direction, but they grow in opposite directions due to opposite orientation of the sugar molecule in them.
When did Watson and Crick discover the double helix of DNA?
When Watson and Crick discovered the double helix of DNA in the early 1950's, they did not KNOW that the 2 strands of DNA were anti-parallel, but they (probably Crick) DEDUCED that they should be and they probably were and wrote in their paper that they were.
Who discovered that DNA is a double stranded DNA?
Though DNA was known to be the genetic material since 1944 when Avery demonstrated it alone as the transfoming principle, how it replicated was a mystery until Watson and Crick put together the evidence obtained by other investigators and reasoned that DNA was an anti-parallel double stranded DNA. Akash Arora.