Credit Risk Concentration
- Definition. Credit Risk Concentration refers to disproportionally large risk exposure to specific credit risks (as opposed to a diversified risk profile).
- Data Requirements. Measuring credit risk concentration requires detailed information about Exposure (loan level data, accurate sector assignement etc.)
- Calculation. ...
- Mitigation
What is a concentration risk in banking?
Concentration risk is a banking term describing the level of risk in a bank's portfolio arising from concentration to a single counterparty, sector or country. The risk arises from the observation that more concentrated portfolios are less diverse and therefore the returns on the underlying assets are more correlated.
What are the specific concentrations of credit risk?
Regulatory frameworks generally recognize the following specific concentrations risks : Measuring credit risk concentration requires detailed information about Exposure (loan level data, accurate sector assignement etc.) There is a large variety of approaches for measuring Concentration Risk.
What is the difference between Fourth Party concentration risk and credit concentration?
Fourth-party concentration risk results from using multiple vendors’ inventory who all outsource services and production to the same fourth parties. Credit concentration risk occurs when loans are susceptible to a specific sector of the economy or business group that has slowed down, which is particularly risky for banks and financial institutions.
What is sector concentration in portfolio risk?
Sector concentration emerges when the portfolio is not perfectly diversified across sectoral factors, corresponding to systematic components of risk. According to Joseph (2013: 258), Portfolio credit risk is influenced by credit portfolio concentration.
What is credit concentration?
A concentration of credit consists of direct, indirect, or contingent obligations exceeding 25 percent of a bank's capital structure. In general concentrations may involve one borrower, an affiliated group of borrowers, or borrowers engaged in or dependent on one industry.
What is meant by concentration risk?
Concentration risk is the potential for a loss in value of an investment portfolio or a financial institution when an individual or group of exposures move together in an unfavorable direction. The implication of concentration risk is that it generates such a significant loss that recovery is unlikely.
How can credit concentration risk be reduced?
The following tips can help manage concentration risk:1 Diversify across, and within, the major asset classes and fund managers/issuers. ... 2 Review regularly and rebalance when needed. ... 3 Look "under the hood" of each investment you own. ... 4 Know how easily you can sell your investments.More items...
Is concentration risk part of credit risk?
Definition. Credit Risk Concentration refers to disproportionally large risk exposure to specific credit risks (as opposed to a diversified risk profile). Regulatory frameworks generally recognize the following specific concentrations risks: Name Concentration.
How is credit concentration risk measured?
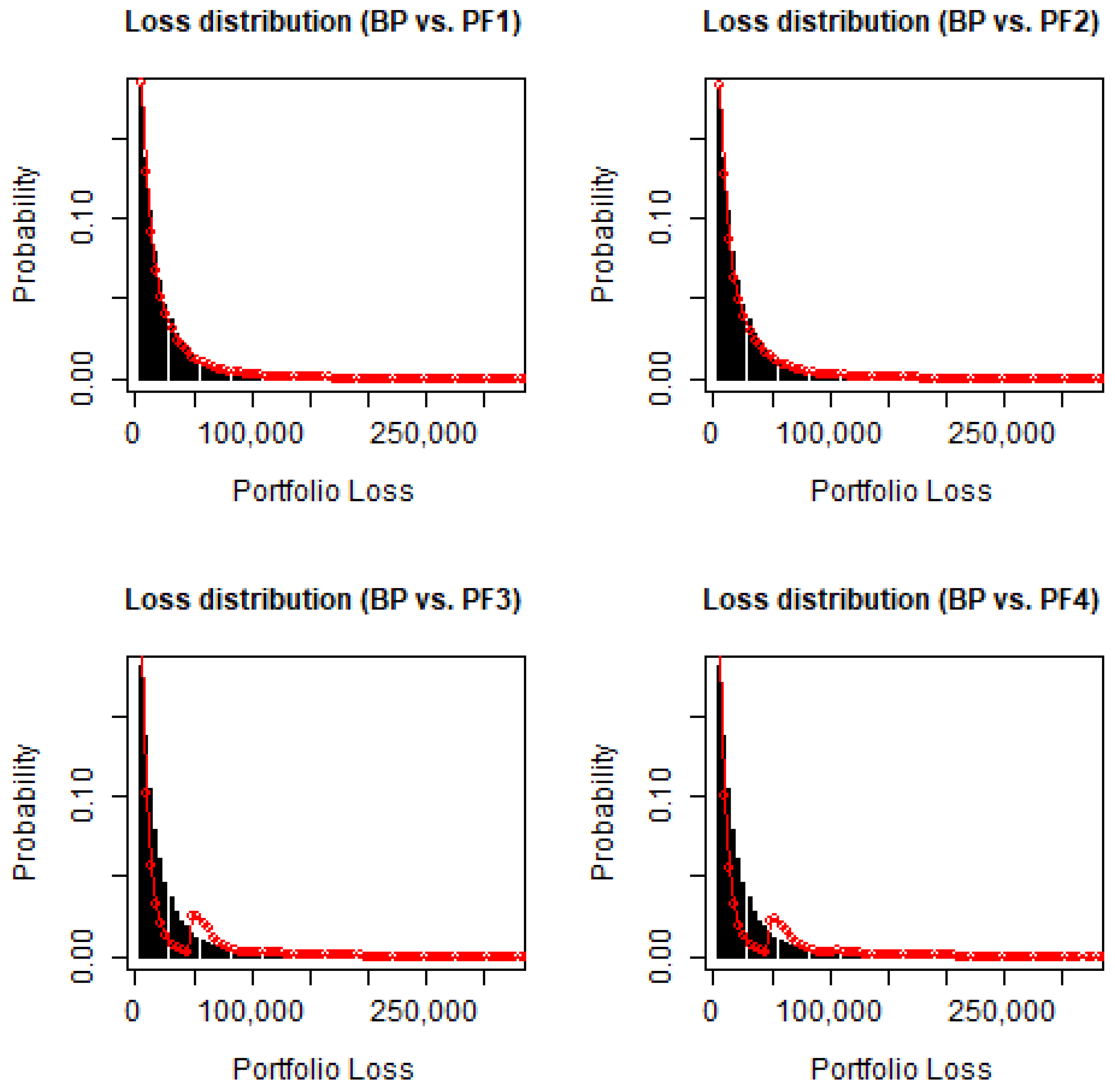
the Herfindahl-Hirshmann index, the Gini coefficient and model-based methods etc. in order to measure concentration risk. To sum up, sectoral concentration may be measured by the HHI index, the Gini coefficient and distance measures indicating the portfolio gap from the basic portfolio.
What causes concentration risk?
Concentration risk is a banking term describing the level of risk in a bank's portfolio arising from concentration to a single counterparty, sector or country. The risk arises from the observation that more concentrated portfolios are less diverse and therefore the returns on the underlying assets are more correlated.
What are the types of credit risk?
The following are the main types of credit risks:Credit default risk. ... Concentration risk. ... Probability of Default (POD) ... Loss Given Default (LGD) ... Exposure at Default (EAD)
What is meant by Tier 1 capital?
Tier 1 capital refers to the core capital held in a bank's reserves and is used to fund business activities for the bank's clients. It includes common stock, as well as disclosed reserves and certain other assets.
What is concentration risk in supply chain?
When an organization is too reliant on one company or market segment to drive revenue or ensure an adequate product supply, it creates concentration risk. In other words, it increases the likelihood that a single point of failure can have a big impact on sales, the supply chain, or the financial health of the business.
What is customer concentration risk?
Customer concentration risk is the level of revenue risk your portfolio holds as a result of relying on a small pool of customers. The bigger the client, the greater the risk your revenue holds. Like the saying goes, don't put all your eggs in one basket. By diversifying your portfolio, you decrease your revenue risk.
What is concentration risk in audit?
Concentration risk is the risk of loss because all or most of your money is in one investment or one type of investment. Diversification spreads the risk over different types of investments helping you to avoid concentration risk.
What is concentration risk in supply chain?
When an organization is too reliant on one company or market segment to drive revenue or ensure an adequate product supply, it creates concentration risk. In other words, it increases the likelihood that a single point of failure can have a big impact on sales, the supply chain, or the financial health of the business.
What is customer concentration risk?
Customer concentration risk is the level of revenue risk your portfolio holds as a result of relying on a small pool of customers. The bigger the client, the greater the risk your revenue holds. Like the saying goes, don't put all your eggs in one basket. By diversifying your portfolio, you decrease your revenue risk.
How is credit risk influenced by credit portfolio concentration?
According to Joseph (2013: 258), Portfolio credit risk is influenced by credit portfolio concentration. Concentration risk is the aggregation of exposure risk within a portfolio, which can be caused by loan facilities to a single borrower or industry, or other comparable concentrations. For each aggregation, a bank or financial institution must understand the various concentration risks and determine permissible portfolio concentrations. Concentration risk in credit portfolios has caused bank hardship on numerous occasions throughout history. Portfolio concentrations determine the extent of challenges that a financial institution will face in the event of a crisis. Concentration can occur in a variety of ways, namely industry or sector concentration, exposure or name concentration, region/location/country concentration, foreign currency concentration, collateral risk concentration.
How to reduce credit risk?
To reduce credit risks, many creditors, particularly banks, accept collateral as security. However, it can be a danger at the portfolio level. Consider a scenario in which the creditor only accepts one type of security: real estate with a 50% margin. The portfolio’s comfort diminishes if the property market falls sharply below 50%. During the late 1980s and early 1990s, Japanese banks faced a similar situation when they financed against real estate and discovered that the liquidation of the collaterals was insufficient not only to cover the loans extended but also to meet the interest obligations, let alone the principal, during the recession that followed. Many of these incidents resulted in bank failures. The significant drop in real estate assets held as collateral contributed to the subprime mortgage crisis in the United States in 2008. The moral of the story is that I collateral portfolio concentration risks can be avoided, (ii) collateral values can peak and collapse, (iii) collateral market value can be positively correlated to business cycles, and (iv) if the collateral value has a strong positive correlation with an obligor’s creditworthiness, this is a significant source of risk known as ‘wrong way correlation.’ The subprime mortgage crisis in the United States in 2008 is similar to what occurred in Japan in the late 1980s.
How does concentration help banks?
As stated above, concentration helps banking institutions in the management of risk in an organization, in the sense that it assists banks in picking the right mixes for a portfolio and thus helps in diversifying the risk across various assets. Positive and negative correlation assets should be mixed in order to spread the risk away. The correlation value ranges from +1 (perfect positive correlation) to –1 (perfect negative correlation), with 0 indicating no association at all. Both variables are flowing in the same direction and may be influenced by the same underlying sources or causes. Negative correlations indicate that both variables react to external stimuli in opposite ways.
What is the correlation between credit risk and economic downturns?
Returning to the importance of correlation in credit portfolio risk management, historical research suggests that credit risk has a correlation that changes across business cycles and enterprises. During economic downturns, the credit risk connection also rises. As a result, it is acceptable to assume that overall credit risk is positively connected with economic downturns from the standpoint of systematic risk. This knowledge should come in handy when putting together a credit portfolio. Because non-cyclical industries are less affected by economic downturns, their correlation to the slump is smaller. Construction, the financial industry, and real estate, on the other hand, have a larger correlation, implying that economic upheaval has a greater impact on these industries. Correlation studies can be divided into various categories based on their needs; for example, sector-specific correlation and default correlation are described below:
What is exposure risk?
According to Joseph (2013:259), the amount exposed to credit risk is termed exposure risk. Even if the firm’s credit risk is adequate, concentrating exposures in a small number of clients can spell disaster. Once this flaw has been found, diversification away from a few concentrated exposures should be prioritized. ABC Ltd, for example, has a credit portfolio of 100 customers worth $200 million. However, one customer’s exposure amounts to $160 million, with the remaining $40 million divided across the remaining 99 customers from various industries. The concentration of exposure is visible in this image. There is an excessive reliance on a single customer, who accounts for 80% of the portfolio. To discover, manage, and minimize similar exposure risks, a portfolio approach is required Joseph (2013:259).
Why is a portfolio spread throughout a large area important?
It assures that the whims of a specific region will have no bearing on the portfolio. It’s worth having a classification of regions/countries based on riskiness, just as it is for sectors.
What is currency risk?
Currency risk is minimal when credit assets and liabilities are denominated in local currency. Currency risk exists if liabilities and obligations are to be met through the realization of credit assets designated in multiple currencies. Any foreign currency concentration that is exposed to market swings can be troublesome. Even if the currencies are tied, relying on inexpensive foreign currency loans to finance local credit assets may not be optimum, as several Far East Asian enterprises discovered in 1997/98. The abrupt depreciation of local currencies produced major problems for various enterprises in Far East Asian nations, resulting in credit losses for the region’s banks. Diversification and hedging can both be considered currency risk mitigation strategies.
What is asset concentration risk?
Asset concentration risk, when investors rely too much on a single investment or portfolio of different kinds of securities and asset classes. According to the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), “Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) can be helpful in achieving broad diversification.”
What is Geographic/sectorial concentration?
Geographic/sectorial concentration of your high-risk or critical vendors, which can arise from a third party being in a region feeling the effects of geopolitical, weather, or civil unrest.
How to manage concentration risk?
The best way to manage concentration risk is to diversify your vendors. But how can you gather the necessary data to implement such a plan?
What is Geographic/sectorial concentration?
Geographic/sectorial concentration of your high-risk or critical vendors, which can arise from a third party being in a region feeling the effects of geopolitical, weather, or civil unrest.
What is vendor risk management?
Vendor risk management is an ongoing process—one that begins with due diligence before a contract is signed and continues with monitoring throughout the length of the relationship. This blog series on the Top 10 risks will help you more effectively address how third-party vendor risk throughout every department in your financial institution.
What are the concerns of regulators?
Regulators are looking at two main concerns: 1 Over-reliance on a single vendor. This is a classic case of putting all your eggs in one basket. If an institution relies heavily on a single provider for many products and services—especially critical ones—that institution might be unable to conduct business if something catastrophic happens to that vendor. 2 Geographic concentration. If both an institution and its third-party vendors and subcontractors are in the same region, it’s possible the same event could impact everyone’s operations since they all rely on the same power and telecommunications infrastructure.
Does OCC include concentrations?
In fact, the OCC includes concentrations under operational risk. But the Federal Reserve takes a different position, expecting banks to specifically consider concentration risk when considering new vendors and managing existing ones.
Why do banks have credit concentrations?
In other cases, concentrations may be the result of mergers or acquisitions. Alternatively, credit concentrations may be unavoidable due to a bank’s limited geographic footprint combined with its market’s dependence on a relatively few employers or industries. Whatever the reason, effective processes to identify, measure, monitor, and control concentration risk are important. It is also important that the bank maintain adequate capital relative to concentration risks.
What is a bank's concentration?
A “concentration” is defined as the sum of direct, indirect, or contingent obligations exceeding 25 percent of the bank’s tier 1 capital plus the ALLL or ACL, as applicable.11 Obligations include the bank-wide aggregate (across all lines of business) of all types of loans; overdrafts; cash items; securities purchases outright or under resale agreements; sale of federal funds; suspense assets; leases; acceptances; letters of credit; placements; loans
What is the OCC?
The OCC expects a bank to implement policies and processes appropriate to the size and complexity of the bank’s portfolios. These processes, coupled with risk management, loan review, and audit oversight, should form an internal governance function that effectively identifies, measures, monitors, and controls concentration risks to the bank both as a legal entity and on a consolidated basis. Processes should consider the potential impact of known and potential concentrations on the bank’s earnings, capital, and operations under normal and stressed market conditions, such as economic downturns and periods of general market illiquidity. The results of such analyses should be important considerations in the bank’s ALLL or ACL, as appropriate, and capital and liquidity planning processes. Results should be taken into consideration as part of the board’s action to approve the bank’s risk appetite and limits.
What are the two types of concentration risk?
There are two types of concentration risk. These types are based on the sources of the risk. Concentration risk can arise from uneven distribution of exposures (or loan) to its borrowers. Such a risk is called name concentration risk. Another type is sectoral concentration risk, which can arise from uneven distribution of exposures ...
What is the key component of concentration risk management?
A key component to the management of concentration risk is accurately defining thresholds across various concentrations to minimize the combined risks across concentrations.
Why is risk more correlated with more concentrated portfolios?
The risk arises from the observation that more concentrated portfolios are less diverse and therefore the returns on the underlying assets are more correlated.
