
Top 9 Benefits of NAC (N-Acetyl Cysteine)
- Essential for making the powerful antioxidant glutathione. NAC is valued primarily for its role in antioxidant...
- Helps with detoxification to prevent or diminish kidney and liver damage. NAC plays an important role in your body’s...
- May improve mental health conditions and substance use disorder. NAC helps regulate...
What is cysteine and what is its function?
Cysteine has various physiological functions. It is good source of sulphur in body which helps in metabolism. It is classified as non-essential amino acid but it may be essential for infants. It is important precursor of glutathione which is good antioxidant that prevents the cells from toxins such as free radicals.
What is N-acetyl cysteine used for?
In this Article. N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is used by the body to build antioxidants. Antioxidants are vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that protect and repair cells from damage. You can get NAC as a supplement or a prescription drug.
What is cystine made of?
L-cystine, also known as cystine, is an oxidized union of two molecules of simpler forms. The cysteine amino acid links two cysteine residues with a bond that pertains to amino acids. ( x) Cysteine and cystine are very similar. One can turn one into the other and vice versa.
How does cysteamine work to reduce cystine?
Cysteamine works by reducing the amount of cystine (an amino acid) in the body. Cysteamine is used to treat nephropathic cystinosis (NEF-roe-PATH-ik SIS-tin-OH-sis), a rare genetic condition that causes a build-up of cystine in the kidneys and other organs. Too much cystine can cause kidney failure or other medical problems.
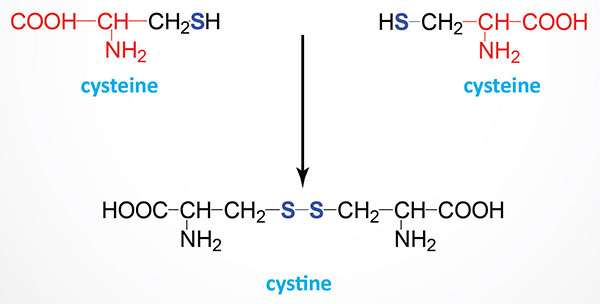
What does the body need to make cysteine?
Your body makes cysteine from methionine, an essential amino acid. Cysteine is also found in most high-protein foods, including: Ricotta.
What happens when you have too much cysteine?
Cysteine Toxicity The University of Maryland Medical Center reports that extremely high doses -- more than 7 grams -- of cysteine may be toxic to your body's cells and may cause death.
What is cystine found in?
Cystine is an amino acid that is found in digestive enzymes, in the cells of the immune system, in skeletal and connective tissues, skin, and hair. Hair and skin are 10% to 14% cystine.
What is special about cysteine?
Cysteine is unique among coded amino acids because it contains a reactive sulph-hydryl group. Therefore, two cysteine residues may form a cystine (disulfide link) between various parts of the same protein or between two separate polypeptide chains.
Does cysteine cause weight gain?
In contrast to low-methionine diets, cysteine and cystine supplementation in rodent models increases weight gain despite reduced or unchanged food intake [16–18].
What is the difference between cysteine and cystine?
Both these amino acids contain sulfur. Despite their similarities, each of this amino acid is responsible for different tasks in the body. Cystine is usually regarded as a semi-essential amino acid whereas Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid. This is the main difference between cystine and cysteine.
What foods are high in cystine?
Cysteine can be found in an array of foods including broccoli, Brussels sprouts, egg yolks, garlic, oats, onions, poultry, red bell peppers, wheat germ and yeast.
How much cysteine should I take?
Dosing. N-acetyl cysteine is an FDA approved prescription drug. It can be taken in various ways, including by mouth, by IV, and by inhalation. It is most commonly taken by mouth in doses of 600-1200 mg daily.
Does cysteine help hair growth?
Cysteine is another hormone produced in the body that contains sulfur. This amino acid supports healthy hair growth, strengthens your hair, and enables it to withstand the daily rigors of manipulation and styling.
Where does cysteine come from?
The body can synthesize cysteine from methionine and other building blocks. Cysteine, the amino acid from which NAC is derived, is found in most high-protein foods.
What is cysteine made up of?
Cysteine and methionine are two amino acids that contain sulfur. Methionine is an essential amino acid, whereas cysteine is synthesized from methionine and therefore is nonessential. Cysteine is classified as a polar, noncharged amino acid while the side chain of methionine is quite hydrophobic.
How much cysteine should I take?
Dosing. N-acetyl cysteine is an FDA approved prescription drug. It can be taken in various ways, including by mouth, by IV, and by inhalation. It is most commonly taken by mouth in doses of 600-1200 mg daily.
How much L-cysteine should I take?
The standard dosage is typically 500 milligrams per day. To treat a respiratory illness, adults can take 200–600 milligrams, twice daily. For COPD, the suggested dose is 600 milligrams, twice daily.
How do you increase cysteine levels?
These nutrients can be found in beans, lentils, spinach, bananas, salmon, and tuna. While most protein-rich foods — such as chicken, turkey, yogurt, cheese, eggs, sunflower seeds, and legumes — contain cysteine, some people choose to supplement with NAC to increase their cysteine intake.
Does cysteine increase glutathione?
Your body's production of glutathione depends on certain amino acids. An amino acid called cysteine is a particularly important amino acid that is involved in glutathione synthesis. Foods rich in cysteine, such as whey protein, may increase your glutathione supply ( 15 ).
What is the role of cystine in the cell?
This transport system, which is highly specific for cystine and glutamate, increases the concentration of cystine inside the cell. In this system, the anionic form of cystine is transported in exchange for glutamate. Cystine is quickly reduced to cysteine. Cysteine prodrugs, e.g. acetylcysteine, induce release of glutamate into the extracellular space.
Where did cystine come from?
It is common in many foods such as eggs, meat, dairy products, and whole grains as well as skin, horns and hair. It was not recognized as being derived of proteins until it was isolated from the horn of a cow in 1899. Human hair and skin contain approximately 10–14% cystine by mass. It was discovered in 1810 by William Hyde Wollaston .
Why is cystine in urine?
The presence of cystine in urine is often indicative of amino acid reabsorption defects. Cystinuria has been reported to occur in dogs. In humans the excretion of high levels of cystine crystals can be indicative of cystinosis, a rare genetic disease.
What is the oxidized dimer form of cysteine?
Cystine is the oxidized dimer form of the amino acid cysteine and has the formula (SCH 2 CH (NH 2 )CO 2 H) 2. It is a white solid that is slightly soluble in water. It serves two biological functions: a site of redox reactions and a mechanical linkage that allows proteins to retain their three-dimensional structure.
Why is cystine the same as cysteine?
Because of the facility of the thiol-disulfide exchange, the nutritional benefits and sources of cystine are identical to those for the more-common cysteine. Disulfide bonds cleave more rapidly at higher temperatures.
Is cystine a hair supplement?
Cystine hair nutritional supplements. Cysteine supplements are sometimes marketed as anti-aging products with claims of improved skin elasticity. Cysteine is more easily absorbed by the body than cystine, so most supplements contain cysteine rather than cystine.
Why do people take L-cysteine?
Many people take L-cysteine supplements because their benefits are experienced with very few side effects. Advertisement. L-cysteine supplementation, is also available as a NAC supplement (also known as N-acetyl-L-cysteine). In this article, you will learn about many of the benefits of L-cysteine.
What is L-cysteine?
L-cysteine is an important amino acid that is required by your body in order to produce the antioxidant glutathione, “the mother of all antioxidants.”
What is the benefit of taking L-cysteine?
The biggest benefit to your health that L-cysteine supplements provide is their role in boosting antioxidants. Research into the benefits of taking L-cysteine supplements and NAC supplements has shown that glutathione protects cell function and prevents DNA damage.
How many mg of L-cysteine is in a tablet?
L-cysteine supplements are available as 400 mg tablets, 500 mg capsules and tablets, or 600 mg capsules. N-Acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is also available as a powder in packs between 100 g and 1 kg.
What are the sources of cysteine?
Important sources of cysteine and other essential amino acids include turkey, chicken, duck, and pork. There are also levels of cysteine in dairy products and eggs.
What is L-cysteine metabolized into?
L-cysteine is metabolized in your body to become cysteine.
What diseases benefit from L-cysteine?
People with degenerative brain disorders like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease may benefit from L-cysteine supplements.
Where does cystine come from?
In your body, cystine occurs naturally and abundantly in skin, hair and connective tissues. It’s also in the horn and wool of animals. ( x) Even though it’s a nonessential amino acid, you can consume more of it by eating more whole grains, dairy products and eggs.
Who discovered cystine?
English chemist and physicist William Hyde Wollaston discovered cystine in 1810. He is also renowned for finding the chemical elements palladium and rhodium ( x ). In 1899, eighty years after cystine’s discovery, researchers recognized cystine as a protein derivative after extracting it from a cow’s horn.
What is L-cystine 2021?
by James D. January 27, 2021. What Is L-Cystine? L-cystine, also known as cystine, is an oxidized union of two molecules of simpler forms. The cysteine amino acid links two cysteine residues with a bond that pertains to amino acids. ( x) Cysteine and cystine are very similar.
Why is NAC used?
One study supports NAC’s being used to relieve the adverse effects of diabetes on the cardiovascular system since diabetic patients leading cause of death is heart failure. The report identifies the potential of the supplement being cardioprotective by preventing oxidative damage with a diabetic heart. ( x)
Does cysteine help the immune system?
Cystine reduces into cysteine, and cysteine helps the body make GHS. GHS supports the immune system by protecting cells from oxidative stress and fighting inflammation. ( x) Supplementing these amino acids should help supply enough GHS when the body needs to kick its immune system into gear.
Does cystine help with oxidative stress?
Second, it’s a potent antioxidant source to treat the oxidative stress areas in your body based on glutathione synthesis to reverse the oxidation. ( x ) More Benefits Combining Cystine and Cysteine. Both cystine and cysteine can help modulate the immune system. ( x ).
Does cysteine make you look younger?
Look Younger as You Age. Well, GHS levels in the body decline during aging, and one study suggests that taking supplemental cysteine can help the elderly maintain healthy amounts of GHS. ( x) Cysteine helps your body make collagen (which many consider the glue that holds your body together) and keeps skin elastic.
How does cysteine enter the body?
It enters the body in two ways-first through food containing cysteine and second through a metabolic pathway in which amino acid methionine converts into S-adenosyl methionine to the homocysteine then reacts with serine and results in the formation of cysteine.
Why is a saline solution important?
It is also important for metabolism of lipids. It is also used in treatment of inflammatory disease like rheumatoid arthritis. It is also used in reducing the symptoms associated with asthma, bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis and emphysema. It helps to control blood sugar level.
What is the amino acid that is synthesized in the body?
Cysteine is an amino acid which can be synthesized in the body or it may be consumed through diet. It is a building block of proteins. It is an important amino acid formed in the body which is made from the methionine in the presence of vitamin B6. When it is taken in the form of supplement then it is formed in the form of N-Acetyl Cysteine (NAC).
What are the functions of fatty acids?
Major functions of fatty acids are listed below : 1 It is used in acetaminophen poisoning, angina. 2 It is also important for metabolism of lipids. 3 It is also used in treatment of inflammatory disease like rheumatoid arthritis. 4 It is also used in reducing the symptoms associated with asthma, bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis and emphysema. 5 It helps to control blood sugar level. 6 It helps to treat schizophrenia. 7 It helps to control colon cancer.
Can you take cysteine twice a day?
Cysteine is not recommended for infants. For children and adolescents, it can be used under only physician guidance. For general health 220 mg of cyst eine can be taken twice or thrice in a day. Share On.
Is cysteine an amino acid?
It is good source of sulphur in body which helps in metabolism. It is classified as non-essential amino acid but it may be essential for infants. It is important precursor of glutathione which is good antioxidant that prevents the cells from toxins such as free radicals.
What Is L-Cysteine?
L-Cysteine is an amino acid found in foods and supplements and is used to promote health and reduce typical oxidative damage. It is a semi-essential amino acid, or sometimes it’s called a conditionally essential amino acid. Essential amino acids are ones that your body needs but doesn’t produce on its own – you have to consume them. Semi essential acids step in when you don’t get enough of certain essential amino acids. They’re not quite on the level of essential amino acids, but they are important and have significant health benefits.
When was L-cysteine first discovered?
L-Cysteine has been found in scientific journals dating back to 1950, with many different health benefits being chronicled. However, in the last two decades, the number of publications and interest in L-Cysteine has increased dramatically.
Is cysteine an amino acid?
Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid that plays a big role in creating protein, and it’s useful in some metabolic functions in the body. L-Cysteine is a form of cysteine that has been linked to benefits associated with bone, heart, and respiratory health.
Is L-cysteine a non-compliant ingredient?
Recently, N-Acetyl Cysteine was flagged as a non-compliant ingredient in dietary supplements. These two supplements are not the same, but we see how there can be some confusion, so we’d just like to clear that up. We don’t want you to miss out on the wonderful benefits of L-Cysteine.
Is L-cysteine used in medicine?
L-Cysteine has been used in alternative medicine for a long time; unfortunately, there isn’t a lot of research to back up many of its popular uses, but it is common in holistic settings for helping with:
Is L-cysteine good for your immune system?
You can see that L-Cysteine has been linked to many different health benefits, but it’s the immune support that we think is critical, especially at this time. We’re all aware of how important respiratory health is right now. This is why taking a supplement that supports immune health, and proper respiration can be so useful. If you’re looking for additional support to help your immune system and you’re especially concerned about your lungs functioning properly, this could be the supplement you find the most benefit from. L-Cysteine, glutamine, and glycine are three very important amino acids that form the building blocks of the powerful antioxidant glutathione, which can aid in your body’s fight against oxidative stress.
What is NAC good for?
Therefore, it can improve a variety of health conditions. 2. Helps With Detoxification to Prevent or Diminish Kidney and Liver Damage. NAC plays an important role in your body’s detoxification process.
What is NAC in medicine?
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is a supplement form of cyst eine. Consuming adequate cysteine and NAC is important for a variety of health reasons — including replenishing the most powerful antioxidant in your body, glutathione. These amino acids also help with chronic respiratory conditions, fertility and brain health.
What does NAC do?
NAC helps regulate levels of glutamate — the most important neurotransmitter in your brain ( 6. Trusted Source. ). While glutamate is required for normal brain action, excess glutamate paired with glutathione depletion can cause brain damage.
Why is NAC important?
NAC plays several important roles in human health. Renowned for its ability to replenish levels of the antioxidant glutathione, it also regulates the important brain neurotransmitter glutamate. Additionally, NAC helps the body’s detoxification system.
How does NAC help with respiratory problems?
NAC can relieve symptoms of respiratory conditions by acting as an antioxidant and expectorant, loosening mucus in your air passageways. As an antioxidant, NAC helps replenish glutathione levels in your lungs and reduces inflammation in your bronchial tubes and lung tissue.
How does NAC help with heart disease?
NAC may reduce heart disease risk by reducing oxidative damage to tissues in your heart ( 33 ).
What are the benefits of NAC?
Here are the top 9 health benefits of NAC. 1. Essential for Making the Powerful Antioxidant Glutathione. Share on Pinterest. NAC is valued primarily for its role in antioxidant production. Along with two other amino acids — glutamine and glycine — NAC is needed to make and replenish glutathione.
What is NAC in the body?
N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) is used by the body to build antioxidants. Antioxidants are vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients that protect and repair cells from damage.
Why do people take NAC?
As a prescription drug, doctors use NAC to treat acetaminophen overdose. It may also help break up mucus in people with some lung diseases, like chronic bronchitis.
Does NAC help with angina?
There's mixed evidence about whether NAC helps with other conditions, like infertility, the flu, cystic fibrosis, liver disease, angina, HIV, high cholesterol, and some eye conditions. More research is needed. Optimal doses of NAC as a supplement have not been set for any condition.
How does cysteamine work?
What is cysteamine? Cysteamine works by reducing the amount of cystine (an amino acid) in the body. Cysteamine is used to treat nephropathic cystinosis (NEF-roe-PATH-ik SIS-tin-OH-sis), a rare genetic condition that causes a build-up of cystine in the kidneys and other organs.
How should I use cysteamine?
Follow all directions on your prescription label and read all medication guides or instruction sheets. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose. Use the medicine exactly as directed.
What should I avoid while taking cysteamine?
Avoid driving or hazardous activity until you know how cysteamine will affect you. Your reactions could be impaired.
What other drugs will affect cysteamine?
Take Procysbi at least 1 hour before or 1 hour after taking any medicine that contains bicarbonate or carbonate.
How to treat cytosis?
Cystinosis is often treated with a combination of drugs, including vitamin and mineral supplements. Use all medications as directed and read all medication guides you receive. Do not change your dose or dosing schedule without your doctor's advice. Store at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
Can cystinosis cause a seizure?
Call your doctor at once if you have any of these side effects ( some of these may be caused by your cystinosis disorder and not by this medicine ): depressed mood, extreme drowsiness; a seizure; unusual bruising or streaks on the skin; bone pain, abnormal joint movement;
Can you take cysteamine if you are allergic to it?
You should not use cysteamine if you are allergic to cysteamine or penicillamine.
What is NAC treatment?
bipolar disorder. obsessive-compulsive disorder. schizophrenia. While research into NAC as a means of relieving psychiatric symptoms may be promising, most doctors would not recommend it as a sole treatment. Instead, a person should rely upon evidence-based treatments, such as therapy and medication, when applicable.
Why do people take NAC?
People take it for various reasons, including to help treat medical issues ranging from psychological disorders to chronic lung conditions and to improve athletic performance.
What is NAC for bronchitis?
Treating lung conditions and excess mucus. For people with chronic lung conditions, such as bronchitis or cystic fibrosis, some doctors recommend NAC. It is available in an inhalable form that may help reduce excess mucus.
What are the benefits of NAC?
According to a 2011 review#N#Trusted Source#N#, NAC may also help alleviate symptoms of various psychiatric conditions, including: 1 bipolar disorder 2 obsessive-compulsive disorder 3 schizophrenia
Does NAC help with health issues?
Researchers have investigated the potential for NAC to help treat a wide variety of health issues. Some research indicates that NAC supplementation may help in the following ways.
Does NAC help with inflammation?
Doctors believe that NAC may stimulate the synthesis of glutathione — a compound that helps fight free radicals, unstable atoms that can cause inflammation and damage. Keep reading to learn how NAC may benefit the body. We also describe risks, including side effects, associated with the supplement.
Is NAC a supplement?
Summary. NAC is an antioxidant that may reduce inflammation. Taking it as a supplement may help improve symptoms of a number of medical conditions. It is crucial to note, however, that most research into NAC supplementation has taken place on a small scale.

Overview
Cystine is the oxidized dimer form of the amino acid cysteine and has the formula (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid that is slightly soluble in water. It serves two biological functions: a site of redox reactions and a mechanical linkage that allows proteins to retain their three-dimensional structure.
Formation and reactions
It is common in many foods such as eggs, meat, dairy products, and whole grains as well as skin, horns and hair. It was not recognized as being derived of proteins until it was isolated from the horn of a cow in 1899. Human hair and skin contain approximately 10–14% cystine by mass. It was discovered in 1810 by William Hyde Wollaston.
It is formed from the oxidation of two cysteine molecules, which results in the formation of a dis…
Biological transport
Cystine serves as a substrate for the cystine-glutamate antiporter. This transport system, which is highly specific for cystine and glutamate, increases the concentration of cystine inside the cell. In this system, the anionic form of cystine is transported in exchange for glutamate. Cystine is quickly reduced to cysteine. Cysteine prodrugs, e.g. acetylcysteine, induce release of glutamate into the extracellular space.
Cystine hair nutritional supplements
Cysteine supplements are sometimes marketed as anti-aging products with claims of improved skin elasticity. Cysteine is more easily absorbed by the body than cystine, so most supplements contain cysteine rather than cystine. N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) is better absorbed than other cysteine or cystine supplements.
See also
• Lanthionine, similar with mono-sulfide link
• Protein tertiary structure
• Sullivan reaction
• Cystinosis
External links
• Media related to Cystine at Wikimedia Commons