Joint distension, or hydrodilatation, involves injection of sterile water into the joint to expand the area and help the adhesions loosen and pull away so the shoulder is no longer restricted. Joint distension is a less invasive alternative to shoulder surgery. How joint distension works and what it does
What is arthrographic distension/hydrodilatation?
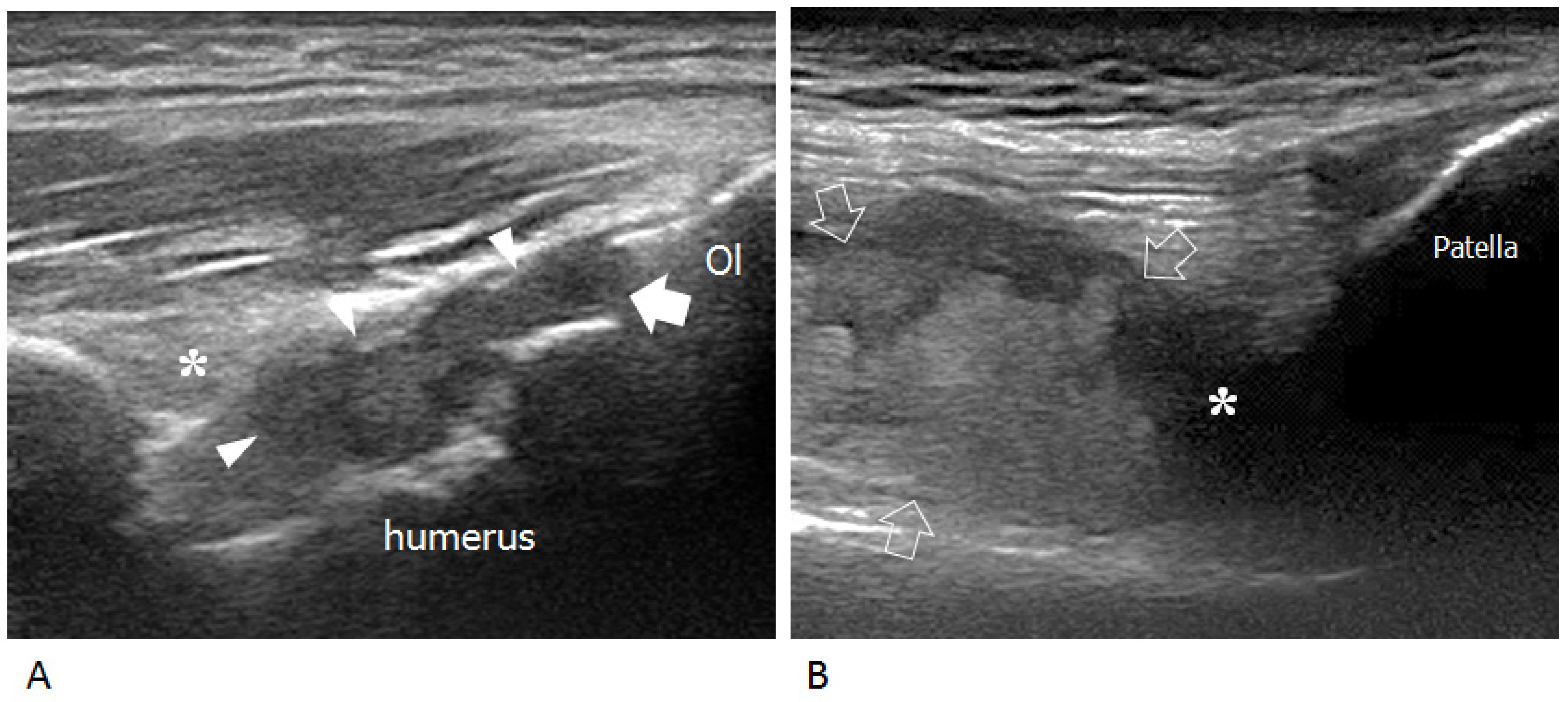
Arthrographic Distension / Hydrodilatation. The injected fluid can be seen to expand the joint and sometimes flow out of the joint in a particular direction. Distension of the glenohumeral joint with fluid is thought to disrupt adhesions (scar tissue), thereby opening or freeing up the joint allowing improved range of movement.
What is the medical definition of distension?
The act or state of being distended or stretched. See also: dilation. n. The act of distending or the state of being distended. The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company.
How does distension of the glenohumeral joint with fluid work?
Distension of the glenohumeral joint with fluid is thought to have a mechanical effect on the cells lining the joint and possibly disrupt adhesions (scar tissue), thereby opening or freeing up the joint allowing improved range of movement. However, the exact mechanism is not fully understood.
What is glenohumeral distension surgery?
Distension of the glenohumeral joint with fluid is thought to disrupt adhesions (scar tissue), thereby opening or freeing up the joint allowing improved range of movement. The procedure is performed under local anaesthetic, takes about 15 minutes to complete and the patient goes home immediately afterwards.

What is distended shoulder?
Shoulder distension is a procedure in which a needle is inserted into the shoulder joint under X-ray or ultrasound guidance. The joint is injected with local anaesthetic and corticosteroid. Filtered air or saline water is then injected into the joint with the aim of stretching and releasing the joint capsule.
What is capsular distension shoulder?
Capsular Distension (Hydrodilation) Capsular distension, also termed 'hydrodilation' or 'distension arthrography', is a therapy for frozen shoulder which involves injecting a large volume of saline containing some combination of steroid and local anesthetic into the glenohumeral joint.
What is glenohumeral joint distension?
Distension of the glenohumeral joint with fluid is thought to have a mechanical effect on the cells lining the joint and possibly disrupt adhesions (scar tissue), thereby opening or freeing up the joint allowing improved range of movement.
What is the fastest way to heal a frozen shoulder?
Let your arm hang down like a pendulum, and then gently swing it back and forth or in circles. Pretend your fingers are your feet and walk your fingers up a wall. Most frozen shoulder treatment involves controlling shoulder pain and preserving as much range of motion in the shoulder as possible.
Does cortisone injection work for frozen shoulder?
The treatment of frozen shoulder requires a combination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications, steroid injections, and physical therapy. Cortisone injections: Cortisone injections are given directly into, or near to the shoulder joint. It reduces the inflammation within the frozen shoulder joint.
Where is frozen shoulder pain felt?
Pain from frozen shoulder is usually dull or aching. It is typically worse early in the course of the disease and when you move your arm. The pain is usually located over the outer shoulder area and sometimes the upper arm.
What is capsular distension knee?
Key Words: Knee— Arthrofibrosis—Treatment—Capsular distention. Arthrofibrosis is a specific process in which scar. tissue or fibrous adhesions form diffusely within a joint. 1,2 A thickened, fibrotic capsule, which in its most severe forms can completely prohibit joint mo- tion, is characteristic.
Is shoulder hydrodilatation painful?
The level of discomfort from hydrodilatation varies, depending on the degree of associated inflammation and restricted movement, although the overall procedure is tolerable and takes only about 15 to 30 minutes. There may also be some pain in the injected area that lasts for a few days to one week.
What is capsular thickening?
This is a thickening of a normal part of your eye after successful cataract surgery. After cataract surgery where the cloudy lens has been removed and an intraocular lens (IOL) implant placed inside the eye, the natural lens capsule it sits on can thicken and become cloudy which will again interfere with your vision.
Does frozen shoulder show up on MRI?
Recent studies have shown that Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can provide reliable imaging indicators of frozen shoulder.
What is the main cause of frozen shoulder?
One of the most common causes of frozen shoulder is the immobility that may result during recovery from a shoulder injury, broken arm or a stroke. If you've had an injury that makes it difficult to move your shoulder, talk to your doctor about exercises you can do to maintain the range of motion in your shoulder joint.
Is walking good for frozen shoulder?
If you continue to move your shoulder in painful movements, the tendons in your arm will have to work harder, which may result in tendonitis. Some examples of these include walking the dog or playing contact sports without your doctor's approval. A frozen shoulder may take time to heal, so don't rush your recovery.
Overview
Joint effusion (a swollen joint) happens when extra fluids flood the tissues around your joint. The fluids make your joint look larger and puffier compared to your other joints. Your bones form joints when two or more of them connect. Your knee, for example, is made up of three bones:
Possible Causes
There are several reasons why your knee or other joints might swell with fluid. The most common reasons include:
Care and Treatment
The cause of your knee joint effusion determines its care and treatment. Often once the cause of the swollen joint gets treated, the swelling goes away. However, not all causes of a knee joint effusion are curable. For many, treatment consists of managing your symptoms instead of eliminating them.
When to Call the Doctor
You should contact emergency services or go to the emergency department if you have the following symptoms:
Frequently Asked Questions
Pain sometimes goes along with a joint effusion (swollen joint). You might feel a slight tenderness or a deep ache. Talk to your healthcare provider about what you can do to relieve both the pain and swelling.
What is the inflammation of the sac that cushions a joint?
In people with joint effusion from repetitive stress injuries, bursitis (the inflammation of the fluid-filled sac that cushions a joint) and tenosynovitis (inflammation of the tendon sheath where a muscle attaches to a bone) are also common.
Which type of arthritis is most commonly associated with extensive joint damage?
Autoimmune arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, in which the immune system directly or indirectly attacks joint tissues. With osteoarthritis, joint effusion primarily affects the knee and is most commonly associated with extensive joint damage.
How to tell if you have fluid in your joint?
Regardless of what is causing fluid in your joint, the symptoms are similar. The severity of symptoms can vary by person. Classic symptoms of joint effusion include: 1. Swelling: Ranging from a mild, generalized puffiness to severe swelling and inflammation.
What is the term for a condition where there is fluid in the knee?
Treatment. Prevention. Joint effusion is a condition involving an excess amount of fluid in or around a joint, usually the knee. Commonly referred to as water on the knee or fluid on the knee, it is most commonly caused by infection, injury, and arthritis.
What are the symptoms of joint effusion?
Depending on what is causing your joint effusion, you could have other symptoms such as: Bruising and bleeding in the joint space (caused by an injury) Fever, chills, malaise, and weakness (if infection is present) Progressive muscle loss (from long-term arthritis, also called arthrogenic muscle inhibition )
What causes a knee to effluent?
Injury. A sports injury is a common cause of joint effusion, especially of the knee. 4 Injuries—such as those from a car accident, serious fall, or blunt force impact—can also lead to an effusion. The injury may involve bone, connective tissues (such as tendons and ligaments), or joint cartilage (like the meniscus ).
What causes swelling in the joints?
Septic arthritis, is most commonly caused by an infection in the joint. 3 Infection can come from from a wound, like a deep injury or medical procedure. An infection in the bloodstream—also called a systemic infection —can take hold in a joint and cause swelling and excess fluid.