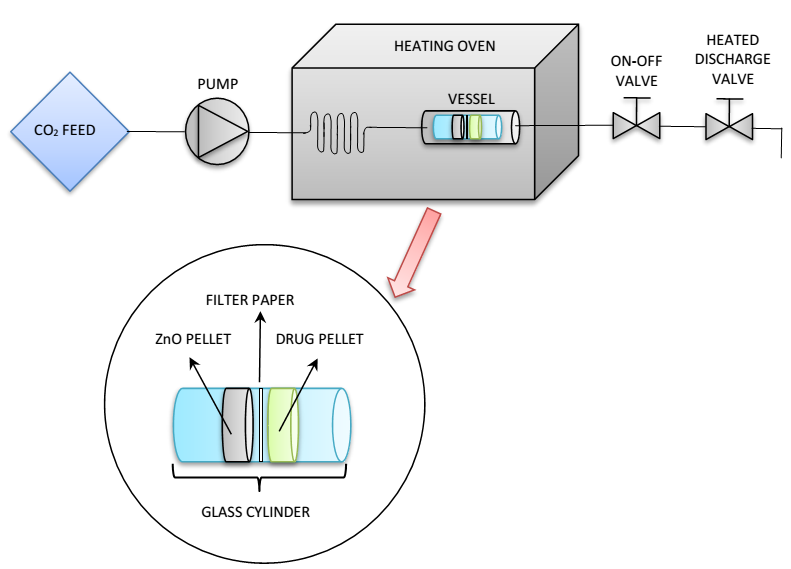
Porosity is a good prediction of how liquids enter into the tablet matrix, and the expectations can be validated by experiment. Dissolution rates do not exclusively depend upon porosity; other predictors are also valid include solubility, surface area, and particle size.
Why is porosity important for tablets?
Porosity is a key attribute of tablets that can strongly influence their performance. By measuring porosity, the manufacturer can design tablets to satisfy critical parameters including: Porosity is a good prediction of how liquids enter into the tablet matrix, and the expectations can be validated by experiment[2].
What is porosity in engineering terms?
Corrosionpedia explains Porosity. Porosity is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume.
How does tablet porosity affect dissolution and recrystallization?
Dissolution and recrystallization of the test API was shown to be due to achange of pore size distribution following moisture conditioning of the tablet The drug release mechanism connected the spatial distribution of tablet porosity to the dissolution profile. This provedtheimpact of tablet porosity on the drug release mechanism 8.
What is porosity of a porous medium?
Used in geology, hydrogeology, soil science, and building science, the porosity of a porous medium (such as rock or sediment) describes the fraction of void space in the material, where the void may contain, for example, air or water. It is defined by the ratio : where VV is the volume of void-space (such as fluids)...
What is pharmaceutical porosity?
Porosity, one of the important quality attributes of pharmaceutical tablets, directly affects the mechanical properties, the mass transport and hence tablet disintegration, dissolution and ultimately the bioavailability of an orally administered drug.
What is porosity and examples?
If an object is porous, it has a great ability to hold fluid within itself. Sponges, wood, rubber, and some rocks are porous materials. In contrast, marble, glass, and some plastics are not porous and contain very few open pockets of air (or pores).
What is porosity and types of porosity?
It is defined as the ratio of void space, commonly called pore volume, to bulk volume and is reported either as a fraction or a percentage. Almost all hydrocarbon reservoirs are composed of sedimentary rocks in which porosity values generally vary from 10 to 40% in sandstones and from 5 to 25% in carbonates.
What is porosity short answer?
Definition of porosity 1a : the quality or state of being porous. b : the ratio of the volume of interstices of a material to the volume of its mass. 2 : pore.
What factors affect porosity?
The principal factors that control porosity are grain size and shape, the degree of sorting (a well-sorted sediment has a narrow range of grain size), the extent to which cement occupies the pore spaces of grains and the amount of fracturing.
What is porosity and how is it determined?
Porosity is the percentage of void space in a rock. Porosity is the percentage of void space in a rock. It is defined as the ratio of the volume of the voids or pore space divided by the total volume. It is written as either a decimal fraction between 0 and 1 or as a percentage.
What are the two main types of porosity?
Hair porosity is typically divided into three broad categories: Low porosity: Cuticles that are close together. Medium porosity: Cuticles that are less tightly bound. High porosity: Cuticles that are more widely spaced.
What is the SI unit of porosity?
Porosity has no such SI units; it has only a numerical value, which falls between 0-1.
What is permeability and porosity?
Porosity: is a measure of the void spaces in a material. Permeability: a measure of the ability of a material (such as rocks) to transmit fluids. Porosity and permeability are related properties of any rock or loose sediment. Both are related to the number, size, and connections of openings in the rock.
How do you measure porosity?
One way is to measure the pore volume by sealing the sample in a pressure vessel, decreasing the pressure by a known amount, and measuring the increase in volume of the contained gas. Conversely, the grain volume can be measured and, if the bulk volume is known, porosity can be determined.
What is total porosity?
The total porosity is the total void space and as such includes isolated pores and the space occupied by clay-bound water. It is the porosity measured by core analysis techniques that involve disaggregating the sample.
What is porosity matter?
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%.
What is permeability example?
Permeability is how easily liquid and gas passes through something. An example of permeability is how fast water flows through a porous rock. The property of a porous substance, as rock or a membrane, of allowing the flow of a fluid through it.
What is an example of a porous surface?
Porous Surfaces These are surfaces of which the latent print is absorbed into the material. Examples include paper, cardboard, and untreated woods.
How do you calculate porosity example?
Soil Porosity = ( 1 - (Bulk Density ÷ Particle Density) ) x 100. This will indicate the percentage of the soil that contains pores. (1 - (0.63) ) x 100 = 37%. The remaining 63% is the solid material of the soil itself.
What is the porosity of the soil?
Soil porosity refers to the fraction of the total soil volume that is taken up by the pore space (Nimmo, 2004). Mainly, pore spaces facilitate the availability and movement of air or water within the soil environment.
What is porosity in tablets?
Porosity is a key attribute of tablets that can strongly influence their performance. By measuring porosity, the manufacturer can design tablets to satisfy critical parameters including: Porosity is a good prediction of how liquids enter into the tablet matrix, and the expectations can be validated by experiment 2.
What is mercury porosimetry?
Mercury porosimetry analysis is based on the ingress of mercury into poresunder strict pressure control. The technique offers speed, accuracy, and a wide measurement range . Benefits includethe calculation of numerous sample properties such as:
What factors influence the release rate of an API?
A 2013 Bristol Myers Squibb study showed that pore size was one of the key factors influencing the release rate of the API. The mercury porosimetry based study also examined the role of water and recrystallization of the API on dissolution slowdown. Dissolution and recrystallization of the test API was shown to be due to achange of pore size distribution following moisture conditioning of the tablet
What is the key attribute of soluble oral tablets that can strongly influence their performance?
The formulation and design of soluble oral tablets needs several factors to be considered: Porosity is a key attribute of tablets that can strongly influence their performance.
What predicts the dissolution rate of liquids?
Porosity is a good prediction of how liquids enter into the tablet matrix, and the expectations can be validated by experiment 2. Dissolution rates do not exclusively depend upon porosity; other predictors are also valid include solubility, surface area, and particle size. In addition to carrying out dissolution testing, establishing porosity, surface area and other characteristics are key to establishing the optimal dissolution rate.
Is porosity a predictor of dissolution?
Tablet porosity is not just a predictor of dissolution and solvent ingress. With the growing importance of Quality by Design (QbD) porosity is also an important Critical Quality Attribute (CQA) for both disintegration and bioavailability properties 4. These parameters are vital to provide data to allow the prediction of API and excipients behaviour in formulations.
What Does Porosity Mean?
Porosity is the open spaces between grains or trapped in grains in a microstructure — the presence of tiny openings or spaces within a material. Porous materials can absorb fluids or moisture, which causes corrosion. Porosity is a fraction between 0 and 1, typically ranging from less than 0.01 for solid granite to more than 0.5 for peat and clay. It may also be represented in percent terms by multiplying the fraction by 100.
How to test porosity?
There are many ways to test porosity, such as industrial CT scanning. Pores transmit water, so smaller pores and smaller void ratios are important in increasing barrier performance. In general, high total void ratios result in higher permeability.
What is the difference between surface and subsurface porosity?
There are two types of porosity: Surface porosity - Occurs on the surface of the metal and can be detected with the naked eye. Subsurface porosity - Occurs within the metal and can be detected only with specialized testing. There are many ways to test porosity, such as industrial CT scanning.
What is the pore size of granite?
Porosity is a fraction between 0 and 1, typically ranging from less than 0.01 for solid granite to more than 0.5 for peat and clay. It may also be represented in percent terms by multiplying the fraction by 100. Porosity is also known as void fraction. Advertisement.
What is the definition of porosity?
Used in geology, hydrogeology, soil science, and building science, the porosity of a porous medium (such as rock or sediment) describes the fraction of void space in the material, where the void may contain, for example, air or water. It is defined by the ratio :
How is porosity controlled?
Porosity is controlled by: rock type, pore distribution, cementation, diagenetic history and composition. Porosity is not controlled by grain size, as the volume of between-grain space is related only to the method of grain packing. Rocks normally decrease in porosity with age and depth of burial.
How to measure porosity?
Several methods can be employed to measure porosity: 1 Direct methods (determining the bulk volume of the porous sample, and then determining the volume of the skeletal material with no pores (pore volume = total volume − material volume). 2 Optical methods (e.g., determining the area of the material versus the area of the pores visible under the microscope). The "areal" and "volumetric" porosities are equal for porous media with random structure. 3 Computed tomography method (using industrial CT scanning to create a 3D rendering of external and internal geometry, including voids. Then implementing a defect analysis utilizing computer software) 4 Imbibition methods, i.e., immersion of the porous sample, under vacuum, in a fluid that preferentially wets the pores.#N#Water saturation method (pore volume = total volume of water − volume of water left after soaking). 5 Water evaporation method (pore volume = (weight of saturated sample − weight of dried sample)/density of water) 6 Mercury intrusion porosimetry (several non-mercury intrusion techniques have been developed due to toxicological concerns, and the fact that mercury tends to form amalgams with several metals and alloys). 7 Gas expansion method. A sample of known bulk volume is enclosed in a container of known volume. It is connected to another container with a known volume which is evacuated (i.e., near vacuum pressure). When a valve connecting the two containers is opened, gas passes from the first container to the second until a uniform pressure distribution is attained. Using ideal gas law, the volume of the pores is calculated as
How is porosity measured?
Connected porosity is more easily measured through the volume of gas or liquid that can flow into the rock, whereas fluids cannot access unconnected pores. Porosity is the ratio of pore volume to its total volume. Porosity is controlled by: rock type, pore distribution, cementation, diagenetic history and composition.
What is secondary porosity?
This can create secondary porosity in rocks that otherwise would not be reservoirs for hydrocarbons due to their primary porosity being destroyed (for example due to depth of burial) or of a rock type not normally considered a reservoir (for example igneous intrusions or metasediments).
What is the porosity of a rock?
Porosity is a fraction between 0 and 1, typically ranging from less than 0.005 for solid granite to more than 0.5 for peat and clay . The porosity of a rock, or sedimentary layer, is an important consideration when attempting to evaluate the potential volume of water or hydrocarbons it may contain.
Why is the porosity of subsurface soil lower than surface soil?
Porosity of subsurface soil is lower than in surface soil due to compaction by gravity. Porosity of 0.20 is considered normal for unsorted gravel size material at depths below the biomantle. Porosity in finer material below the aggregating influence of pedogenesis can be expected to approximate this value.
Why is mercury intrusion porosimetry used?
Mercury intrusion porosimetry is commonly used for the compari-son of granule porosity among different samples because it represents the fluid-penetrable portion of the total porosity.
Why is density important in pharmaceuticals?
The drug must be uniformly mixed for the dosage form to have a uniform amount of drug between different dosage units .
What is the method of estimating the amount of gas penetrated against that expected?
This method is based on the penetration of an inert gas inside a chamber of known volume that contains the powder sample under constant temperature and pressure. Estimation of the actual amount of gas penetrated against that expected based on the ideal gas law, as mentioned in the following equation, allows the calculation of the vol-ume occupied by the solid mass and, thus, the determination of total porosity of the sample.
How to find the total pore volume of a powder?
Total pore volume in a defined mass of powder can be estimated by the penetration of mercury, a nonwetting (high contact angle) liquid, inside the sample under externally applied pressure.
Why is particle density important?
Control of particle density is important to ensure uniformity of mixing of two or more powders. Powders with significant differences in particle density tend to segregate during processing. In addition, particle density influences powder flow.
How to estimate bulk powder density?
The bulk and tapped powder densities are estimated using a simple volu-metric cylinder. The compendia, such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), have standardized the equipment and process for the measure-ment of bulk and tapped densities, and also for the pretreatment of the sample before loading in the measuring cylinder. This harmonization of testing procedure helps reduce variability due to material handling and other subjective parameters that may differ between personnel and laboratories.
Which law describes the inverse proportionality of pressure and volume of a gas at a constant tem-per?
These calculations are based on the Archimedes’ principle that fluid displacement by the solid phase of the particles is proportional to the volume of the solid phase. Boyle’s law describing the inverse proportionality of pressure and volume of a gas at a constant tem-perature allows the determination of volume occupied by the gas in the sample chamber as a function of its pressure.
Popular Answers (1)
Porosity is an important item in directly compressible ecipients. So, new grade of microcrystalline cellulose was developed by treatment the commercial grade Avicel PH 102 with 5N or more of NaOH.
All Answers (1)
Porosity is an important item in directly compressible ecipients. So, new grade of microcrystalline cellulose was developed by treatment the commercial grade Avicel PH 102 with 5N or more of NaOH.
Similar questions and discussions
What is the difference between bulk density, tapped density and true density of a food product?
Overview
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam).
There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning.
Void fraction in two-phase flow
In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase.
Void fraction usually varies from location to location in the flow channel (depending on the two-phase flow pattern). It fluctuates with time and its value is usually time averaged. In separated (i…
Porosity in earth sciences and construction
Used in geology, hydrogeology, soil science, and building science, the porosity of a porous medium (such as rock or sediment) describes the fraction of void space in the material, where the void may contain, for example, air or water. It is defined by the ratio:
where VV is the volume of void-space (such as fluids) and VT is the total or bul…
Porosity of fabric or aerodynamic porosity
The ratio of holes to solid that the wind "sees". Aerodynamic porosity is less than visual porosity, by an amount that depends on the constriction of holes.
Die casting porosity
Casting porosity is a consequence of one or more of the following: gasification of contaminants at molten-metal temperatures; shrinkage that takes place as molten metal solidifies; and unexpected or uncontrolled changes in temperature or humidity.
While porosity is inherent in die casting manufacturing, its presence may lead to component failure where pressure integrity is a critical characteristic. Porosity may take on several forms fr…
Measuring porosity
Several methods can be employed to measure porosity:
• Direct methods (determining the bulk volume of the porous sample, and then determining the volume of the skeletal material with no pores (pore volume = total volume − material volume).
• Optical methods (e.g., determining the area of the material versus the area of the pores visible under the microscope). The "a…
See also
• Void ratio
• Petroleum geology
• Poromechanics
• Bulk density
• Particle density (packed density)
External links
• Absolute Porosity & Effective Porosity Calculations
• Geology Buzz: Porosity