What are the signs and symptoms of gigantism?
What are the signs and symptoms of Pediatric Acromegaly (Gigantism)? Early voice changes in boys; Enlarged facial features; Enlarged hands and feet; Enlarged organs (heart, liver, kidneys, etc.) Enlarged tongue; Enlarged vocal cords; Excessive sweating; Fatigue (extreme tiredness) Headaches; Joint pain; Large chest size (barrel chest) Oily or thick skin
What is the prognosis of gigantism?
When the condition is successfully treated, children with gigantism can have a normal life expectancy and avoid most of the complications caused by it. However, they may still have symptoms such as muscle weakness and restricted movement, and some may also have psychological problems.
What is the difference between gigantism and acromegaly?
Main Differences Between Acromegaly and Gigantism
- Acromegaly often affects people who are over the age of 20. While Gigantism affects people below the age of 20.
- In acromegaly, the height of a person might be average. ...
- Acromegaly can be treated only with medication and surgery. ...
- Acromegaly mainly happens due to the pituitary glands. ...
- Acromegaly is not always fatal. ...
Who is at risk for gigantism?
Middle-aged individuals are at a higher risk of developing acromegaly than those in other age groups. The most specific reason for the existence of this risk factor is that any form of increased growth hormone production in the body that occurs in an individual who is seventeen years old or younger is referred to as a different disease called gigantism.
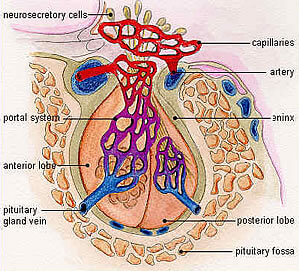
What causes pituitary gigantism?
Gigantism is a serious condition that is nearly always caused by an adenoma, a tumor of the pituitary gland. Gigantism occurs in patients who had excessive growth hormone in childhood. The pituitary tumor cells secrete too much growth hormone (GH), leading to many changes in the body.
What are the symptoms of pituitary gigantism?
Other symptoms of gigantism include:Enlargement of internal organs, especially your child's heart.Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis).Double vision or difficulty with side (peripheral) vision.Headaches.Joint pain.Delayed puberty.Irregular menstruation (periods).Sleeping problems, such as sleep apnea.More items...•
How do you know if you have gigantism?
How is gigantism diagnosed? If gigantism is suspected, the diagnosis is usually confirmed by taking blood tests to measure the levels of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) circulating in the blood. IGF1 is released into the blood primarily by the liver in response to growth hormone.
What does gigantism do to the body?
Gigantism is a rare condition that causes abnormal growth in children. This change is most notable in terms of height, but girth is affected as well. It occurs when your child's pituitary gland makes too much growth hormone, which is also known as somatotropin.
At what age is gigantism diagnosed?
Acromegaly is usually diagnosed in adults aged 30 to 50, but it can affect people of any age. When it develops before the end of puberty, it's known as "gigantism".
What is the life expectancy of someone with gigantism?
Living with gigantism When the condition is successfully treated, children with gigantism can have a normal life expectancy and avoid most of the complications caused by it. However, they may still have symptoms such as muscle weakness and restricted movement, and some may also have psychological problems.
Who is most likely to get gigantism?
Gigantism is an extremely rare condition that only occurs in children. About 100 cases have been reported in the United States. Gigantism has been reported to occur at a female-to-male ratio of 1:2.
How fast do pituitary tumors grow?
How fast do pituitary tumors grow? Most pituitary tumors are slow growing, approximately 1-3mm/year.
What disease causes gigantism?
Acromegaly is a hormonal disorder that develops when your pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone during adulthood. When you have too much growth hormone, your bones increase in size. In childhood, this leads to increased height and is called gigantism.
Can you stop gigantism?
Prevention. Gigantism cannot be prevented. Early treatment may prevent the disease from getting worse and help avoid complications.
What height is considered gigantism?
A person should be 7 feet (2.20 meters) tall or more to be considered a giant. Gigantism is a disorder and the medical reason for gigantism is a surplus of growth hormone. If the doctors diagnose gigantism in an early stage, it is possible to slow down the growth.
Is gigantism a genetic disorder?
Gigantism is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by one or more genes not working correctly.
What height is considered gigantism?
A person should be 7 feet (2.20 meters) tall or more to be considered a giant. Gigantism is a disorder and the medical reason for gigantism is a surplus of growth hormone. If the doctors diagnose gigantism in an early stage, it is possible to slow down the growth.
How do you distinguish between gigantism and acromegaly?
When you have too much growth hormone, your bones increase in size. In childhood, this leads to increased height and is called gigantism. But in adulthood, a change in height doesn't occur. Instead, the increase in bone size is limited to the bones of your hands, feet and face, and is called acromegaly.
How fast do pituitary tumors grow?
How fast do pituitary tumors grow? Most pituitary tumors are slow growing, approximately 1-3mm/year.
What is the most common cause for the overproduction of growth hormone in gigantism?
The most common cause of too much GH release is a noncancerous (benign) tumor of the pituitary gland. Other causes include: Genetic disease that affects the skin color (pigmentation) and causes benign tumors of the skin, heart, and endocrine (hormone) system (Carney complex)
What is gigantism caused by?
a form of gigantism caused by hypersecretion of pituitary growth hormone; a rare disorder commonly the result of a pituitary adenoma.
What is cerebral gigantism?
cerebral gigantismgigantism in the absence of increased levels of growth hormone, attributed to a cerebral defect; infants are large, and accelerated growth continues for the first 4 or 5 years, the rate being normal thereafter. The hands and feet are large, the head is large, narrow and long, and the eyes have an antimongoloid slant with an abnormally wide space between them. The child is clumsy, and mental retardation of varying degree is usually present. Called also Sotos syndrome.
What is the term for the oversecretion of growth hormone by the pituitary gland?
pituitary gigantismthat caused by oversecretion of growth hormone by the pituitary gland; see gigantism. Called also Launois syndrome.
What causes gigantism in the pituitary gland?
A pituitary gland tumor is almost always the cause of gigantism. The pea-sized pituitary gland is located at the base of your brain. It makes hormones that control many functions in your body. Some tasks managed by the gland include: 1 temperature control 2 sexual development 3 growth 4 metabolism 5 urine production
What is the cause of gigantism?
A pituitary gland tumor is almost always the cause of gigantism. The pea-sized pituitary gland is located at the base of your brain. It makes hormones that control many functions in your body. Some tasks managed by the gland include: temperature control. sexual development. growth. metabolism. urine production.
What happens when a tumor grows on the pituitary gland?
sexual development. growth. metabolism. urine production. When a tumor grows on the pituitary gland, the gland makes far more growth hormone than the body needs. There are other less common causes of gigantism:
Why does my baby grow bigger than normal?
It occurs when your child’s pituitary gland makes too much growth hormone, which is also known as somatotropin. Early diagnosis is important. Prompt treatment can stop or slow the changes that may cause your child to grow larger than normal. However, the condition can be hard for parents to detect. The symptoms of gigantism might seem like normal ...
What is the difference between McCune Albright syndrome and Carney complex?
McCune-Albright syndrome causes abnormal growth in bone tissue, patches of light-brown skin, and gland abnormalities. Carney complex is an inherited condition that causes noncancerous tumors on connective tissue, cancerous or noncancerous endocrine tumors, and spots of darker skin. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is an inherited disorder ...
What is the best treatment for gigantism?
Removing the tumor is the preferred treatment for gigantism if it’s the underlying cause.
What test is done for gigantism in children?
If your child’s doctor suspects gigantism, they may recommend a blood test to measure levels of growth hormones and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), which is a hormone produced by the liver. The doctor also may recommend an oral glucose tolerance test.
What is pituitary gigantism?
Pituitary gigantism is a rare but very important subgroup of patients with excessive height, as it has an identifiable and clinically treatable cause . The disease is caused by chronic growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 secretion from a pituitary somatotrope adenoma that forms before the closure of the epiphyses.
Why is early diagnosis important for pituitary gigantism?
Early diagnosis and rapid referral for effective therapy appear to improve outcomes in patients with pituitary gigantism; therefore, a high level of clinical suspicion and efficient use of diagnostic resources is key to controlling overgrowth and preventing patients from reaching very elevated final adult heights.
Is pituitary gigantism male or female?
Pituitary gigantism has a male preponderance, and patients usually have large pituitary adenomas. The large tumour size, together with the young age of patients and frequent resistance to medical therapy, makes the management of pituitary gigantism complex.
What is the pituitary gland?
The pituitary gland is a small gland at the base of your brain, behind the bridge of your nose. It produces GH and a number of other hormones. GH plays an important role in managing your physical growth.
What hormones are released when the pituitary gland releases GH?
When the pituitary gland releases GH into your bloodstream, it triggers your liver to produce a hormone called insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) — sometimes also called insulin-like growth factor-I, or IGF-I. IGF-1 is what causes your bones and other tissues to grow. Too much GH leads to too much IGF-1, which can cause acromegaly signs, ...
What is the name of the hormone that is produced by acromegaly?
Sometimes, these tumors secrete GH. In other cases, the tumors produce a hormone called growth hormone-releasing hormone (GH-RH), which signals the pituitary gland to make more GH.
What are the symptoms of acromegaly?
Overview. Symptoms of acromegaly include an enlarged face and hands. Changes to the face may cause the brow bone and lower jaw to protrude, and the nose and lips to get larger. Acromegaly is a hormonal disorder that develops when your pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone during adulthood.
Which gland controls growth hormone?
Close. Pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Pituitary gland and hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus are located within the brain and control hormone production. Acromegaly occurs when the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone (GH) over a long period of time. The pituitary gland is a small gland at the base of your brain, ...
What happens when you have too much growth hormone?
When you have too much growth hormone, your bones increase in size. In childhood, this leads to increased height and is called gigantism. But in adulthood, a change in height doesn't occur. Instead, the increase in bone size is limited to the bones of your hands, feet and face, and is called acromegaly. Because acromegaly is uncommon and the ...
What causes GH to be too high?
In adults, a tumor is the most common cause of too much GH production:
What is acromegaly referred to as?
Medication or radiation therapy may be used to reduce GH release or block the effect of GH. [1] If the condition occurs after normal bone growth has stopped (in adulthood), it is referred to as acromegaly. [1] Last updated: 2/10/2017.
Why do we post questions on GARD?
Questions sent to GARD may be posted here if the information could be helpful to others . We remove all identifying information when posting a question to protect your privacy. If you do not want your question posted, please let us know. Submit a new question