What is Skene gland?
Skene gland is also called paraurethral gland, periurethral gland and lesser vestibular. This gland is found in female and is located in the vulva area, outside the vagina wall and near the urethra lower end. The gland may be part or near the G-spot and it drains into the urethra and urethra cavity. Skene gland is encircled...
What is Skene's gland infection?
The Skene's glands are located in the vaginal wall and help lubricate the vagina during sex. These glands can occasionally cause issues if they become infected, which is referred to as skenitis. The Skene's glands are a lesser-known part of female genitalia, and their functions are still being studied.
What is the difference between Skene's glands and periurethral glands?
For for the male periurethral glands, see Urethral gland. In female human anatomy, Skene's glands or the Skene glands ( / skiːn / SKEEN, also known as the lesser vestibular glands, paraurethral glands) are glands located around the lower end of the urethra.
What is the difference between Skene's glands and prostate?
Skene's glands. The Skene’s glands are made of the same cells as the male prostate, and are what is thought to produce the fluid ejected in female ejaculation.The Skene’s glands are also called the lesser vestibular, periurethral or paraurethral glands, or increasingly the more correct name of the female prostate.

What is the purpose of the Skene's gland?
The Skene's glands, which are also known as the lesser vestibular glands (homologous to the prostate glands in males), are two glands located on either side of the urethra. These glands are believed to secrete a substance to lubricate the urethra opening. This substance is also believed to act as an antimicrobial.
How do I know if I have a Skene's gland?
Imaging tests may be required to detect skenitis. Imaging tests, such as an MRI, can help diagnose cancerous cysts of the Skene's glands. Your doctor may suspect cancer if they see a displacement of the opening of the urethra from a cyst. This type of cyst also contains a milk-like fluid.
Why is my Skene gland swollen?
“Skenitis” refers to inflammation of the Skene's glands wherein they become swollen and sore. This inflammation is generally caused by infection linked to bacteria like gonorrhea, E. coli, vaginal flora, and various coliform bacteria. Gonorrhea is particularly notorious for causing skenitis.
How do you drain a Skene's gland?
If the cyst is causing painful symptoms, the preferred treatment is to remove (excise) the cyst in a surgery. Your surgeon might aspirate the fluid from the cyst with a needle or simply drain it. Some surgeons use a technique called marsupialization to treat cysts, including Skene's gland cysts.
Who has Skene glands?
Skene's glands are two glands located on the lower end of the urethra in women or people assigned female at birth (AFAB). Your urethra is a tube-like organ that removes pee from your body. Skene's glands aren't a well-known organ, but they play a role in your sexual and urinary health.
How common are Skene gland cysts?
Skene duct cysts are rare. They form if the duct to the gland is blocked, usually because the gland is infected. These cysts occur mainly in adults.
Why is there a bump on my urethra?
Urethral caruncles are polypoid ("stalk-like") masses hanging from part of the urethral outlet. These are most often spotted during an exam for some other health problem. Urethral caruncles are more common in women who don't use hormone replacement therapy (HRT) after menopause.
What does the urethral opening look like?
When this happens, the opening of the urethra looks like a small purple or red donut and seems larger than normal. Urethral prolapse happens most commonly to school-aged girls before puberty. The urethra is a narrow tube that connects the bladder with the outside of the body. Urine passes through the urethra.
Secretions from the Skene's glands help maintain urinary and sexual health
Amy Kiefer, PhD, is a freelance science writer focused on health and biology.
Location
The Skene's glands are located on the front wall of the vagina, on either side of the lower end of the urethra—the tube through which urine exits the body. 3
Diagnosis and Treatment
If your healthcare provider suspects you have a UTI or skenitis, you will be asked to report your symptoms and will receive a physical exam. Your healthcare provider should perform a urine test (urinalysis) to confirm a UTI.
Summary
The Skene's glands, or the female prostate, are an important part of both urinary and sexual health. The Skene's glands are located in the vaginal wall and help lubricate the vagina during sex. These glands can occasionally cause issues if they become infected, which is referred to as skenitis.
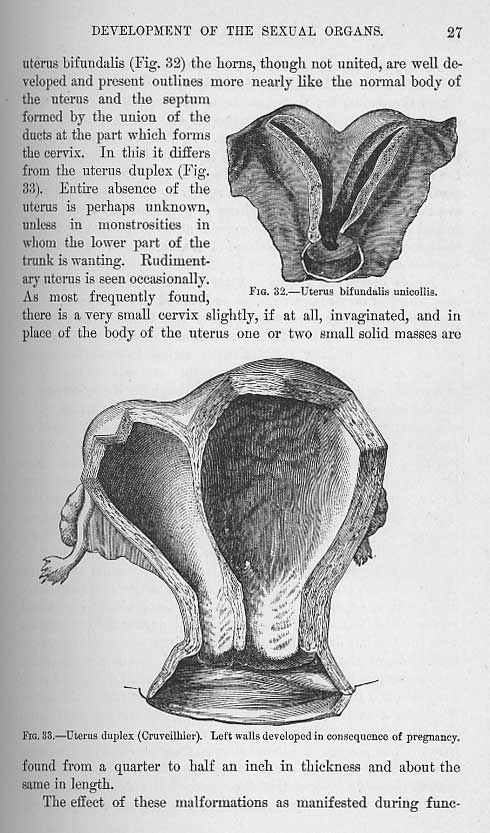
A Word From Verywell
The Skene's glands are a lesser-known part of female genitalia, and their functions are still being studied.
Where are the Skene glands located?
In female human anatomy, Skene's glands or the Skene glands ( / skiːn / SKEEN, also known as the lesser vestibular glands, paraurethral glands or female homologue of the prostate) are glands located around the lower end of the urethra.
What is the purpose of the skeene gland?
Although there remains debate about the function of the Skene's glands, one purpose is to secrete a fluid that helps lubricate the urethral opening. Skene's glands produce a milk-like ultrafiltrate of blood plasma. The glands may be the source of female ejaculation, but this has not been proven.
What is a skene cyst?
A Skene's duct cyst, pressing the urethral opening towards the right side of the image. Disorders of the Skene's glands may include: Infection (called skenitis, urethral syndrome, or female prostatitis) Skene's duct cyst: lined by stratified squamous epithelium, the cyst is caused by obstruction of the Skene's glands.
How to treat a cyst in the skene?
The cyst is treated by surgical excision or marsupialization. Trichomoniasis: the Skene's glands (along with other structures) act as a reservoir for Trichomonas vaginalis, indicating that topical treatments are not as effective as oral medication.
Where does fluid come from in the vagina?
In an amount of a few milliliters, fluid is secreted from these glands when stimulated from inside the vagina. Female ejaculation and squirting (secretion of large amounts of fluid) are believed by researchers to be two different processes. They may occur in combination during orgasm.
Is the Skene's gland a female?
The glands may be the source of female ejaculation, but this has not been proven. Because they and the male prostate act similarly by secreting prostate-specific antigen (PSA), which is an ejaculate protein produced in males, and of prostate-specific acid phosphatase, some authors refer to the Skene's glands as the "female prostate".
Overview
A Skene’s gland cyst is a cyst that's located near the urethral opening in a person assigned female at birth (AFAB). Your urethra is the tube that moves urine from your bladder to outside your body. It's a part of your urinary system.
Diagnosis and Tests
In most cases, your healthcare provider can diagnose a Skene’s gland cyst with a physical examination. If your provider is concerned that the cyst might be a urethral diverticulum (a “pocket” or outpouching that forms next to your urethra), they might order imaging tests, such as ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans.
Management and Treatment
In some cases, particularly in babies, your provider might decide to wait and see what happens. If the cyst isn’t causing problems and is left alone, it might resolve itself.
Prevention
There’s no way that we currently know of to prevent a congenital Skene’s gland cyst from developing in a baby.
Living With
If you’re having pain while urinating or having sex, or if you’re having trouble urinating, contact your healthcare provider. If you’re unable to urinate or are in extreme pain, go to an emergency room. You’ll need a physical exam to determine if you have a Skene’s gland cyst.
Frequently Asked Questions
Urethral diverticulum (UD) and Skene’s gland cyst may cause similar symptoms. You might have pain with urination, pain with sex, urinary tract infections and a lump with either condition. However, the conditions are different. UD is a pocket that forms along your urethra that can hold urine. It’s not part of a gland.
What Is Skene Gland?
This gland is found in female and is located in the vulva area, outside the vagina wall and near the urethra lower end.
What is the condition that causes inflammation in the skene?
Skenitis. Skenitis is a condition that causes inflammation in your skene’s gland. This condition can manifest the following signs and symptoms: Your urinary tract can be infected. Feeling pain at the opening area of the urethra. The area around the urethral opening can be tender to touch.
How do you know if you have a skene cyst?
Symptoms. Female with Skene duct cyst can show any of the following symptoms: A mass which is swollen and soft to touch can develop around opening of the vagina. This mass may not cause any pain in some women. The cyst can grow and become large and block your urethra opening.
Why does my swollen gland swell?
The swelling occurs when the gland is obstructed which causes fluids to build up in the gland forming a cyst. This gland can be infected by microbes such as bacteria, viruses and fungi. The cyst can be painless but can also become severe and form an abscess. This condition affects adult women.
How to treat skenitis?
The gland can also become red and swollen. Skenitis can be managed through antibiotic medications to treat bacterial infection. In case antibiotic are ineffective, surgery and other therapies such as sitz bath can also be used in treating this condition.
How to prevent skene cyst?
Side effects arising from skene’s duct cyst can be managed when you follow the following tips: Use condom each time you engage in sex. Drink a lot of water to help flush out toxic substances in your body. Clean yourself and clothing regularly to prevent microbes from invading your body.
What are the properties of secreted fluids?
The secreted fluids contain antimicrobial properties to protect the urinary tract against infection.
What is the fluid produced by the Skene glands?
The fluid produced by the Skene’s glands is very similar in composition to prostatic fluid , including specific proteins and enzymes (Human Protein 1 and PDE5). The glands – the male prostate and Skene’s – appear to operate very similarly when examined closely.
Who discovered the Skene gland?
History and discovery of the Skene’s glands. The female prostate was recognised by anatomist Regnier de Graaf way back in 1672. In 1880, Alexander Skene brought the attention back to these glands and ducts, which is why these glands are called Skene’s glands and/or ducts.
What glands are made of the same cells as the male prostate?
The Skene’s glands are made of the same cells as the male prostate, and are what is thought to produce the fluid ejected in female ejaculation. The Skene’s glands are also called the lesser vestibular, periurethral or paraurethral glands, or increasingly the more correct name of the female prostate. The Skene’s glands drain both into the urethra ...
Where do skenes drain?
The Skene’s glands drain both into the urethra and near the urethral opening, and are surrounded by tissue that includes a part of the clitoris extending up into the vagina, which swells up with blood during sexual arousal, producing a different type of orgasm, frequently known as the ‘g-spot orgasm’. The never-ending debate about female ...
Where does the female hormone PSA come from?
Women produce PSA from the prostate, of which elevated levels are one of the signs of cancer in the prostate in both men and women.
Where is the G spot on the skene?
To locate the gland, you first have to find the G-spot which is located inside the vagina, right behind the pubic bone. Unlike the Skene's, you can actually feel the G-spot.
Who is the Skene named after?
Big shocker: They're named after a man, Alexander Skene . The Skene's fill with fluid during sexual arousal and if stimulated during sexual arousal, sex, or masturbation, can actually release this liquid. In a very informal Twitter survey, I asked my fellow vagina owners if they had ever squirted.
Can you tell if you're touching a Skene's G spot?
If you can find the G-spot, the Skene's isn't far off. The problem? You won't be able to actually know if you're touching it. You have to get into the general area, listen to your body's pleasure centers, and hope for the best.

Location
Health-Related Problems
- Health problems related to the Skene's glands are uncommon, but the glands do occasionally become infected or, very rarely, develop cancers.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- If your healthcare provider suspects you have a UTI or skenitis, you will be asked to report your symptoms and will receive a physical exam. Your healthcare provider should perform a urine test (urinalysis) to confirm a UTI. Skenitis can often be detected by a physical exam alone, but sometimes imaging is required.19 Both UTIs and skenitis should be treated promptly with antibio…
Summary
- The Skene's glands, or the female prostate, are an important part of both urinary and sexual health. The Skene's glands are located in the vaginal wall and help lubricate the vagina during sex. These glands can occasionally cause issues if they become infected, which is referred to as skenitis.
A Word from Verywell
- The Skene's glands are a lesser-known part of female genitalia, and their functions are still being studied. So far, it is known that these glands help lubricate the urethra and provide vaginal lubrication during sexual arousal. The glands' other functions, as part of female ejaculation process or in causing G-spot orgasms, are still controversial. Although studies find these pheno…
Overview
In female human anatomy, Skene's glands or the Skene glands are glands located around the lower end of the urethra. The glands are surrounded by tissue that swells with blood during sexual arousal, and secrete a fluid from openings near the urethra, particularly during orgasm.
Structure and function
The Skene's glands are located in the vestibule of the vulva, around the lower end of the urethra. The two Skene's ducts lead from the Skene's glands to the vulvar vestibule, to the left and right of the urethral opening, from which they are structurally capable of secreting fluid. Although there remains debate about the function of the Skene's glands, one purpose is to secrete a fluid that helps lubricate the urethral opening.
Clinical significance
Disorders of the Skene's glands may include:
• Infection (called skenitis, urethral syndrome, or female prostatitis)
• Skene's duct cyst: lined by stratified squamous epithelium, the cyst is caused by obstruction of the Skene's glands. It is located lateral to the urinary meatus. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is used for diagnosis. The cyst is treated by surgical excision or marsupialization.
History
While the glands were first described in 1672 by Regnier de Graaf and by the French surgeon Alphonse Guérin (1816–1895), they were named after the Scottish gynaecologist Alexander Skene, who wrote about it in Western medical literature in 1880. In 2002, the term female prostate as a second term after paraurethral gland was added in Terminologia Histologica by the Federative International Committee on Anatomical Terminology. The 2008 edition notes that the term was i…
See also
• Bartholin's gland
• List of related male and female reproductive organs
• Mesonephric duct
• Pudendal nerve
Further reading
• Pastor Z (2013). "Female ejaculation orgasm vs. coital incontinence: a systematic review". J Sex Med. 10 (7): 1682–91. doi:10.1111/jsm.12166. PMID 23634659.
Place
Health Related Issues
- Health problems associated with Skene’s glands are uncommon, but the glands can occasionally become infected or, rarely, develop cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- If your healthcare provider suspects that you have a UTI or dermatitis, you will be asked to report your symptoms and undergo a physical exam. Your healthcare provider should perform a urine test (urinalysis) to confirm a UTI. Tendonitis can usually be detected with a separate physical examination, but imaging is sometimes required. Both UTIs and skenitis should be treated prom…
Generalize
- Skene’s glands, or female prostate, are an important part of urinary and sexual health. Skene’s glands are located in the vaginal wall and help lubricate the vagina during intercourse. These glands can occasionally cause problems if they become infected, which is called dermatitis.
Vigortip Words
- Skene’s glands are a little-known part of the female genitalia whose function is still being studied. Until now, these glands were known to help lubricate the urethra and provide vaginal lubrication during sexual arousal. Other functions of the glands, as part of the female ejaculation process or to cause the G-spot orgasm, remain controversial. While research has found that these phenom…