What units are used to measure temperature?
Resources for Students and Teachers
- Kelvin: Introduction – Temperature is one of the most important and ubiquitous measurements in human life. ...
- Absolutely Hot (link is external) – Analyze a common chemical reaction. ...
- Kelvin Temperatures and Very Cold Things! ...
- Building a Thermometer – Build an instrument to measure water temperature. ...
What is the basic unit of temperature?
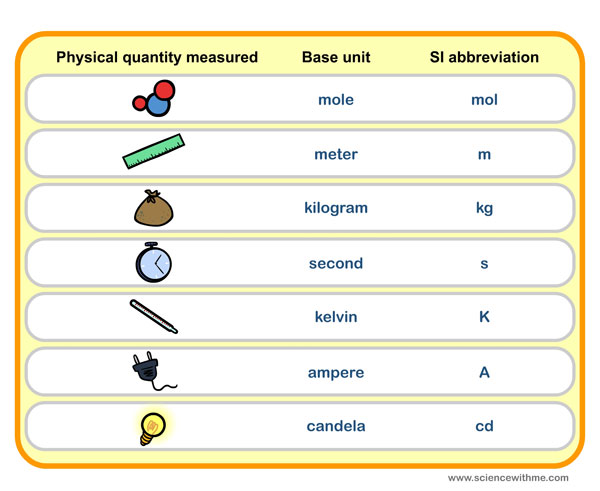
What are the five basic units of measurement?
- Length – meter (m)
- Time – second (s)
- Amount of substance – mole (mole)
- Electric current – ampere (A)
- Temperature – kelvin (K)
- Luminous intensity – candela (cd)
- Mass – kilogram (kg)
What is the metric unit for temperature?
Units of temperature (degrees Celsius or Centigrade): The basic metric unit of temperature is the Celsius degree (°C), also called the Centigrade degree. The Celsius scale is set up so that at sea level, water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C.
What is the SI unit for temperature?
Unit of thermodynamic temperature, Kelvin (K): Kelvin is the SI unit of thermodynamic ...
What is the temperature of water at 0 degrees Celsius?
On the widely used Celsius temperature scale, water freezes at 0 °C and boils at about 100 °C. One Celsius degree is an interval of 1 K, and zero degrees Celsius is 273.15 K. An interval of one Celsius degree corresponds to an interval of 1.8 Fahrenheit degrees on the Fahrenheit temperature scale.
What is the standard temperature of water at the triple point?
When the cell is cooled enough so that a mantle of ice forms around the reentrant well, the temperature at the interface of solid, liquid, and vapor is 273.16 K.
What is the Kelvin constant?
The kelvin (K) is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the Boltzmann constant k to be 1.380 649 ×10 −23 when expressed in the unit J K −1, which is equal to kg m 2 s −2 K −1, where the kilogram, meter and second are defined in terms of h, c and ∆ν Cs. The temperature 0 K is commonly referred to as "absolute zero." On the widely used Celsius temperature scale, water freezes at 0 °C and boils at about 100 °C. One Celsius degree is an interval of 1 K, and zero degrees Celsius is 273.15 K. An interval of one Celsius degree corresponds to an interval of 1.8 Fahrenheit degrees on the Fahrenheit temperature scale.
S.I Unit of Temperature
The S.I unit of temperature is Kelvin, denoted by K. It was devised by Lord Kelvin. Though the scientists commonly use the scale Celsius or Centigrade (°C). Kelvin degree scale has the same measurement as the Celsius degree scale. In Kelvin’s scale, the zero point is 273.15 which is considered to be below that of the Celsius scale.
Common Unit of Temperature
The scale used in most of the world is in degrees Celsius, sometimes called “centigrade”. It is most widely used in everyday applications. It is a convenient and comfortable unit of temperature measurement since it measures the freezing point of water at 0 o C and boiling points at 100 o C respectively.
Interconversion between units of temperature
The temperature units are easily inter-convertible to different formats by small formulae:
What is the definition of temperature?
v. t. e. Average daily variation in human body temperature. Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses hot and cold. It is the manifestation of thermal energy, present in all matter, which is the source of the occurrence of heat, a flow of energy, when a body is in contact with another that is colder or hotter.
Why is the temperature scale absolute?
Referring to the Boltzmann constant, to the Maxwell–Boltzmann distribution, and to the Boltzmann statistical mechanical definition of entropy, as distinct from the Gibbs definition, for independently moving microscopic particles, disregarding interparticle potential energy, by international agreement, a temperature scale is defined and said to be absolute because it is independent of the characteristics of particular thermometric substances and thermometer mechanisms. Apart from the absolute zero, it does not have a reference temperature. It is known as the Kelvin scale, widely used in science and technology. The kelvin (the word is spelled with a lower-case k) is the unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The temperature of a body in its own state of thermodynamic equilibrium is always positive, relative to the absolute zero .
Why is the entropy of an ideal gas at its absolute zero of temperature not a positive semi-definite
This is because the entropy of an ideal gas at its absolute zero of temperature is not a positive semi-definite quantity, which puts the gas in violation of the third law of thermodynamics. In contrast to real materials, the ideal gas does not liquefy or solidify, no matter how cold it is.
What is the lowest temperature?
The lowest theoretical temperature is absolute zero, at which no more thermal energy can be extracted from a body. Experimentally, it can only be approached very closely (100 pK), but not reached, which is recognized in the third law of thermodynamics .
What is the magnitude of Kelvin?
Since May 2019, the magnitude of the kelvin is defined in relation to microscopic phenomena, characterized in terms of statistical mechanics. Previously, since 1954, the International System of Units defined a scale and unit for the kelvin as a thermodynamic temperature, by using the reliably reproducible temperature of the triple point of water as a second reference point, the first reference point being 0 K at absolute zero.
What is absolute zero temperature?
Experimentally, absolute zero can be approached only very closely; it can never be reached (least temperature attained by experiment is 100 pK). Theoretically, in a body at absolute zero temperature, all classical motion of its particles has ceased and they are at complete rest in this classical sense. The absolute zero, defined as 0 K, is approximately equal to −273.15 °C, or −459.67 °F .
What is the Celsius scale?
The Celsius scale (°C) is used for common temperature measurements in most of the world. It is an empirical scale that was developed by historical progress, which led to its zero point 0 °C being defined by the freezing point of water, and additional degrees defined so that 100 °C was the boiling point of water, both at sea-level atmospheric pressure. Because of the 100-degree interval, it was called a centigrade scale. Since the standardization of the kelvin in the International System of Units, it has subsequently been redefined in terms of the equivalent fixing points on the Kelvin scale, and so that a temperature increment of one degree Celsius is the same as an increment of one kelvin, though they differ by an additive offset of approximately 273.15.