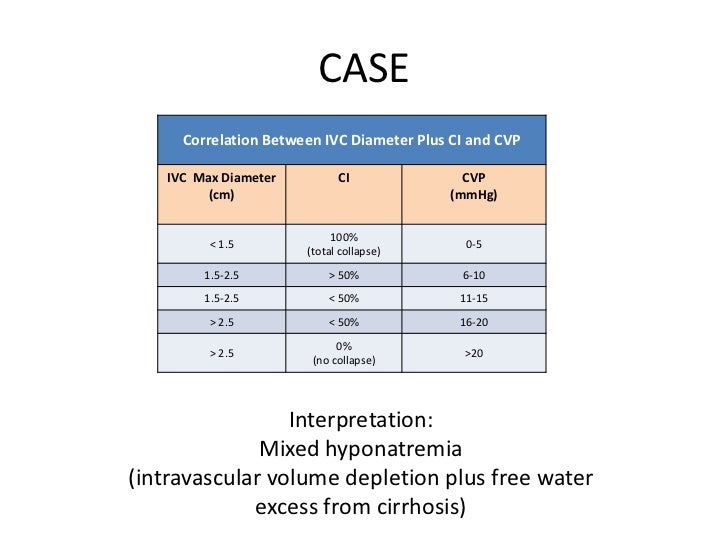
What is the volume status of the vena cava based on IVC?
Interpretation: Volume status based on IVC alone (Respirophasic IVC Variation) 1 Inferior vena cava (IVC) is normally 1.5 to 2.5 cm in diameter (measured 3 cm from right atrium). 2 Inferior vena cava (IVC) normally collapses more than 50% with inspiration or sniffing. 3 Correlation between RA pressure (CVP) and IVC appearance.
How accurate is ultrasound in measuring IVC diameter?
Though controversial, IVC measurement by ultrasound can estimate volume status, fluid responsiveness, and fluid tolerance There is evidence to support that IVC diameter is consistently low in hypovolemia versus euvolemia IVC change can estimate fluid responsiveness with sensitivity of 0.78 and specificity of 0.86
Is IVC measurement by ultrasound reliable in patients with hypovolemia?
Though controversial, IVC measurement by ultrasound can estimate volume status, fluid responsiveness, and fluid tolerance There is evidence to support that IVC diameter is consistently low in hypovolemia versus euvolemia. IVC change can estimate fluid responsiveness with a Sn 0.78 and Sp 0.86.
What is the average diameter of a venae cavity?
The overall mean diameter was 20 mm, the range was 13 to 30 mm, and the standard deviation was 3 mm. Two cavae (3%) were more than 28 mm in diameter. A previous in vitro study has shown that in venae cavae of this size there is a significant risk of reduced clot-capturing ability with the KG filter and migration with the Mobin-Uddin filter.
What is IVC in medical terms?
What do we measure to determine if IVC is dilated?
What happens if you sniff the inferior vena cava?
Why is it important to assess IVC with echo?
Can you do IVC with an echocardiogram?
Is the inferior vena cava the same as the right atrium?
See 1 more
What is the normal value for IVC?
In this study we found that the diameter of IVC ranged from 0.97 to 2.26 cm during expiration and from 0.46 to 1.54 cm during inspiration in normal Indian population. Any values outside this range should be considered abnormal, and needs further investigation and treatment accordingly.
What is IVC normal and collapsing?
The normal IVC diameter is less than 1.7 cm and there is a 50% decrease in the diameter when the RA pressure is normal (0–5 mm Hg). • A dilated IVC (>1.7 cm) with normal inspiratory collapse (>50%) is suggestive of a mildly elevated RA pressure (6–10 mm Hg).
What is considered a dilated IVC?
It is common practice in echocardiography to estimate the right atrial (RA) pressure by examining the inferior vena cava (IVC) size and its response to respiration. A dilated IVC (>2 cm) has been found to indicate high RA pressure, particularly when there is no collapse during inspiration.
What does IVC diameter mean?
Inferior vena cava (IVC) is a compressible vessel whose diameter is subjective to changes in both the intrathoracic pressure during breathing and the systemic venous return [1]. In most cases, the IVC diameter and its collapsibility reflect the right atrial (RA) pressures [2,3].
How do you explain IVC on ultrasound?
0:313:35Point of Care Ultrasound of the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) - AMBOSS VideoYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTo assess the ivc. We first scan in the short axis or transverse plane. And center the vessel on theMoreTo assess the ivc. We first scan in the short axis or transverse plane. And center the vessel on the screen. We then rotate to the long axis or sagittal plane for a longitudinal view of the ivc.
What causes IVC to collapse?
A high degree of sonographically-visualised collapse of the inferior vena cava (IVC) during inspiration suggests a volume-responsive cardiac output. This inspiratory collapse is said to be due to a fall in intra-thoracic pressure.
What are the symptoms of inferior vena cava?
Symptoms and signs of IVCS result from a reduced venous return to the heart, as well as a pooling of blood in the IVC, which causes hypotension, tachycardia, lower extremity edema, elevated liver enzymes, end-organ failures and, hypoxia, altered mental status, and death.
What does IVC mean in echocardiogram?
The inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter as measured by echocardiography can be affected by tumour masses, respiration, and right atrial (RA) pressure. 1–3. The IVC has been studied in patients with congestive heart failure and particularly in patients with right-sided cardiovascular disease or pericardial disease.
What is the function of IVC?
The IVC is a large blood vessel responsible for transporting deoxygenated blood from the lower extremities and abdomen back to the right atrium of the heart. It has the largest diameter of the venous system and is a thin-walled vessel.
What does collapsible IVC mean?
The IVC is a highly collapsible major vein whose diameter is altered by respiration, blood volume, and right heart function [16].
What happens if IVC collapses?
Conclusion: A dilated IVC without collapse with inspiration is associated with worse survival in men independent of a history of heart failure, other comorbidities, ventricular function, and pulmonary artery pressure.
How is IVC collapse treated?
Often, treatment includes positional changes, avoidance of supine positioning, especially on the right side. In pregnancy, definitive management of the IVCS is to deliver the baby. In other conditions, medical or surgical treatment to remove or relieve the offending structure will relieve symptoms.
What does IVC mean in echocardiogram?
The inferior vena cava (IVC) diameter as measured by echocardiography can be affected by tumour masses, respiration, and right atrial (RA) pressure. 1–3. The IVC has been studied in patients with congestive heart failure and particularly in patients with right-sided cardiovascular disease or pericardial disease.
What is IVC in medical terms?
The way I like to explain what the IVC is to my patients is that it’s a large vein that brings the blood from the middle and lower half of your body back to your heart.
What do we measure to determine if IVC is dilated?
Essentially, what we do is simply measure the IVC diameter to determine if it’s dilated. If its dilated, then we know the patients RAP is elevated. But by how much? To get an even better idea of the right atrial pressure, we can ask the patient to inhale, or sniff in through their nose.
What happens if you sniff the inferior vena cava?
By asking the patient to sniff, it generates a sudden decrease in intrathoracic pressure, which would normally cause the IVC to collapse at least 50%.
Why is it important to assess IVC with echo?
A couple of the more important are to determine right atrial pressure or central venous pressure, determining the pulmonary artery pressure as well as assessing fluid levels in the patient.
Can you do IVC with an echocardiogram?
Don’t get overwhelmed when it comes to assess the IVC with echocardiography. The biggest thing is to get in there and start practicing. Locating the IVC can take a little time to figure out, but once you do, you’ll be able to do it with your eye’s closed.
Is the inferior vena cava the same as the right atrium?
We know that the inferior vena cava is attached to the right atrium. So if we can estimate what the pressure is in the section of IVC that is in close proximity to that right atrium, then we can assume that the pressure in the right atrium is the same or similar. (This is true because there is no valve between the right atrium and the IVC).
What causes the IVC diameter to fluctuate?
We therefore get the maximum and minimum IVC diameter. These fluctuations in size of the IVC are caused by negative intrathoracic pressure during inspiration which leads to an increase of RV (right ventricular) filling of the systemic veins. We therefore get the minimum IVC diameter during inspiration.
What is the importance of IVC ultrasound?
Ultrasound evaluation of the IVC can deliver important information on a patient's volume status. As a non-invasive, fast technique POCUS of the IVC has gained means in the assessment of fluid status in critically ill patients. Even in the diagnosis of heart failure IVC ultrasound plays a role. According to the latest ASE guidelines the assessment of the IVC in a subcostal view should be part of every routine transthoracic echocardiographic examination. Measurements should be performed in a subcostal long axis view perpendicular to the IVC with the patient in a supine position at 1.0 to 2.0 cm from the junction with the right atrium.
Can IVC be dilated without collapse?
Note that normal, young athletes may have a dilated IVC with normal pressure. In patients on ventilators the IVC may be commonly dilated without appropriate collapse due to normal respiration . In these cases IVC is not recommended to routinely be used to assess RA pressure according to latest guidelines. Although the measurement of the IVC with TEE had led to a successful measurement of central venous pressure even in ventilated patients. When estimating pulmonary artery pressure with the tricuspid regurgitant jet velocity, individual RA pressures should be added by performing the above listed measurements of the IVC.
What is the sensitivity of IVC?
Though controversial, IVC measurement by ultrasound can estimate volume status, fluid responsiveness, and fluid tolerance#N#There is evidence to support that IVC diameter is consistently low in hypovolemia versus euvolemia#N#IVC change can estimate fluid responsiveness with sensitivity of 0.78 and specificity of 0.86
What is an IVC ultrasound?
A bedside IVC ultrasound was performed to assess volume status in setting of dehydration. The IVC was identified in longitudinal access. The IVC was flat with over 50% collapse with respirophasic measurements. There was evidence of volume depletion and fluid tolerance.
What is the normal colon diameter?
Normal colon diameter is less than 6cm while that of the cecum is less than 9cm. Normal diameter of the appendix is less than 6mm (less than 8mm in patients with cystic fibrosis). Toxic megacolon: In the appropriate clinical setting, transverse colon diameter more than 6cm suggests toxic megacolon.
What is the normal diameter of a portal vein?
Normal portal vein is <12mm in diameter and has hepatopetal (towards liver) flow with velocity in the range of 16-40 cm/sec showing normal respiratory variations.#N#Doppler criteria for portal hypertension:#N#Low portal venous velocity (<16 cm/sec).#N#Hepatofugal portal venous flow (flow away from the liver)#N#Portosystemic shunts (including a recanalized umbilical vein)#N#Dilated portal vein (diameter more than 13 mm)
What is the upper limit of renal volume?
The upper limit of the normal renal length is 11 cm while the upper limit of the renal volume is 140cc.
What does 200 ml PVR mean?
Adults: Over 200mL PVR indicates inadequate emptying, while more than 500 ml if present with other signs is suggestive of cauda equina syndrome.
What is the thickness of a hypertrophic muscle?
Hypertrophic – pyloric muscle thickness is more than 3 mm. This is the main diagnostic criteria.
How many mm is a cystic duct?
The cystic duct is normal up to 5mm.
How long is the liver span?
The normal liver span is less than 16 cm in the mid-clavicular line.
What is IVC in medical terms?
The way I like to explain what the IVC is to my patients is that it’s a large vein that brings the blood from the middle and lower half of your body back to your heart.
What do we measure to determine if IVC is dilated?
Essentially, what we do is simply measure the IVC diameter to determine if it’s dilated. If its dilated, then we know the patients RAP is elevated. But by how much? To get an even better idea of the right atrial pressure, we can ask the patient to inhale, or sniff in through their nose.
What happens if you sniff the inferior vena cava?
By asking the patient to sniff, it generates a sudden decrease in intrathoracic pressure, which would normally cause the IVC to collapse at least 50%.
Why is it important to assess IVC with echo?
A couple of the more important are to determine right atrial pressure or central venous pressure, determining the pulmonary artery pressure as well as assessing fluid levels in the patient.
Can you do IVC with an echocardiogram?
Don’t get overwhelmed when it comes to assess the IVC with echocardiography. The biggest thing is to get in there and start practicing. Locating the IVC can take a little time to figure out, but once you do, you’ll be able to do it with your eye’s closed.
Is the inferior vena cava the same as the right atrium?
We know that the inferior vena cava is attached to the right atrium. So if we can estimate what the pressure is in the section of IVC that is in close proximity to that right atrium, then we can assume that the pressure in the right atrium is the same or similar. (This is true because there is no valve between the right atrium and the IVC).