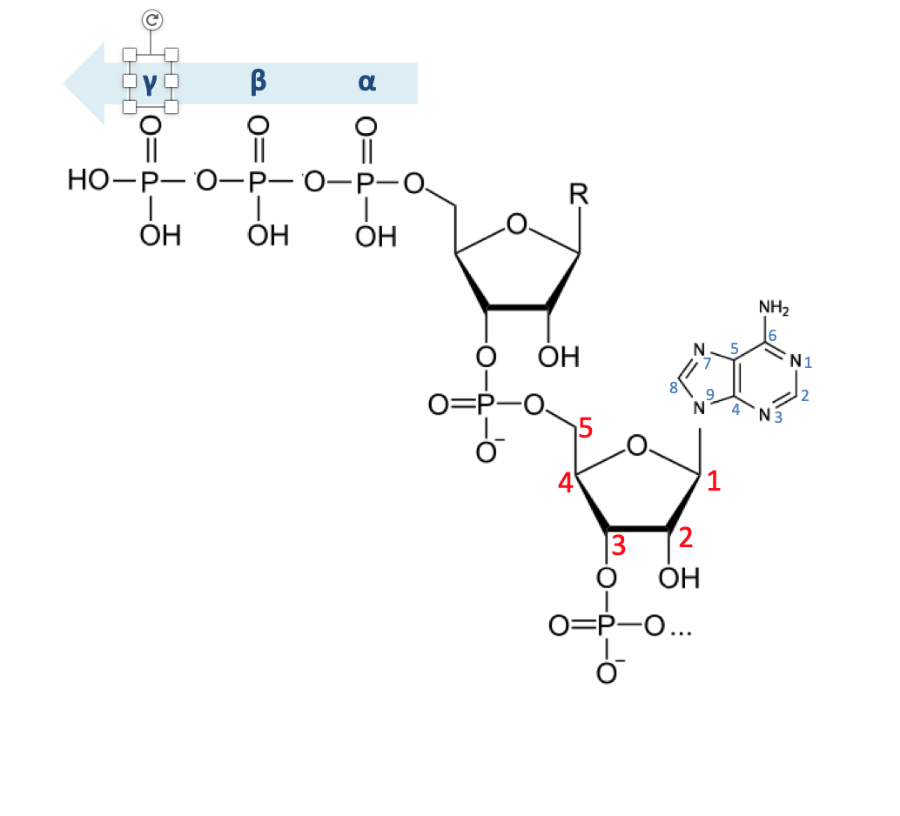
The primary function of mRNA is to act as an intermediary between the genetic information in DNA and the amino acid sequence of proteins. mRNA contains codons that are complementary to the sequence of nucleotides on the template DNA and direct the formation of amino acids through the action of ribosomes
Ribosome
The ribosome is a complex molecular machine found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules.
What is the role of mRNA during transcription?
mRNA’s role in protein synthesis. Through a process known as transcription, an RNA copy of a DNA sequence for creating a given protein is made. This copy – mRNA – travels from the nucleus of the cell to the part of the cell known as the cytoplasm, which houses ribosomes.
What begins the process of transcription?
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene (directly or through helper proteins). RNA polymerase uses one of the DNA strands (the template strand) as a template to make a new, complementary RNA molecule. Transcription ends in a process called termination.
What are the products of transcription?
What is the End Product of Transcription
- Messenger RNA. mRNA is responsible for carrying genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. ...
- Transfer RNA. tRNA is responsible for carrying the corresponding amino acid to the ribosomes during translation. ...
- Ribosomal RNA. rRNA is a component of a ribosome which facilitates translation. ...
- Conclusion. ...
What is the process of transcription and translation?
“The process of transcription and translation is a part of the cell central dogma system helps in tailoring an amino acid sequence from the gene.” The replication, transcription and translation are the part of DNA metabolised in which a new DNA, mRNA and protein constructed, respectively.

What is mRNA transcript?
What is mRNA transcription? mRNA transcription is the process wherein a new RNA molecule is copied by the enzyme RNA polymerase from the template DNA strand. mRNA transcription occurs in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell.
What is the purpose of transcript in biology?
In biology, the process by which a cell makes an RNA copy of a piece of DNA. This RNA copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the genetic information needed to make proteins in a cell. It carries the information from the DNA in the nucleus of the cell to the cytoplasm, where proteins are made.
What happens to the mRNA transcript?
The instructions in a gene (written in the language of DNA nucleotides) are transcribed into a portable gene, called an mRNA transcript. These mRNA transcripts escape the nucleus and travel to the ribosomes, where they deliver their protein assembly instructions.
Is mRNA the same as transcript?
Although the mRNA contains the same information, it is not an identical copy of the DNA segment, because its sequence is complementary to the DNA template. Transcription is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase and a number of accessory proteins called transcription factors.
Where does mRNA go after transcription?
The RNA made during transcription (in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, or the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells) will go to the ribosomes. The ribosomes read the RNA during translation to make proteins.
How is mRNA made during transcription?
During transcription, the DNA of a gene serves as a template for complementary base-pairing, and an enzyme called RNA polymerase II catalyzes the formation of a pre-mRNA molecule, which is then processed to form mature mRNA (Figure 1).
What happens to mRNA after translation?
RNA is transcribed in the nucleus; after processing, it is transported to the cytoplasm and translated by the ribosome. Finally, the mRNA is degraded.
What are the three important events in the process of transcription?
Transcription occurs in the three steps—initiation, elongation, and termination—all shown here. Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
How does a mRNA molecule carry information from DNA?
The mRNA carries the information in DNA to the ribosomes found in the cytoplasm, the messenger RNA carries the information in the DNA through process called transcription. Explanation: mRNA carries the genetic information from the DNA to a ribosome. The ribosome will then "read" the mRNA strand and make a protein. ...
Why is transcription important in DNA?
The initiation of transcription is an especially important step in gene expression because it is the main point at which the cell regulates which proteins are to be produced and at what rate.
What is the difference between a primary transcript and mRNA that goes to the ribosome?
Pre-mRNA is the primary transcript which contains both coding and non-coding sequences. mRNA is the mature messenger RNA which contains only the coding sequence of a gene. So, this is the key difference between pre-mRNA and mRNA.
How does mRNA affect the body?
An mRNA can teach the body how to make a specific protein that can help your immune system prevent or treat certain diseases.
How do you do transcription in biology?
Transcription takes place in three steps: initiation, elongation, and termination....The steps are illustrated in Figure 2.Step 1: Initiation. Initiation is the beginning of transcription. ... Step 2: Elongation. Elongation is the addition of nucleotides to the mRNA strand. ... Step 3: Termination.
What is a transcript in genes?
Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene's protein information encoded in DNA.
Which is important for transcription?
The main enzyme involved in transcription is RNA polymerase, which uses a single-stranded DNA template to synthesize a complementary strand of RNA. Specifically, RNA polymerase builds an RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, adding each new nucleotide to the 3' end of the strand.
What is transcription a level biology?
A gene is a sequence of nucleotide bases in a DNA molecule that codes for the production of a specific sequence of amino acids, that in turn make up a specific polypeptide (protein) This process of protein synthesis occurs in two stages: Transcription – DNA is transcribed and an mRNA molecule is produced.
What is mRNA transcription?
mRNA transcription is the process wherein a new RNA molecule is copied by the enzyme RNA polymerase from the template DNA strand. mRNA transcriptio...
Where does mRNA transcribe?
mRNA is transcribed in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. In prokaryotes where the nucleus is absent, mRNA transcription occurs in the cytoplasm.
What are the products produced during transcription?
The products produced during transcription are RNA molecules. There are three major types of RNA found in the cell namely, ribosomal RNA, messenger...
What are the steps in mRNA transcription?
There are three major steps in mRNA transcription namely, initiation, elongation, and termination. RNA polymerase is the main enzyme involved in th...
Why is transcription important?
Transcription is an important part of the process to transform DNA into a living being. Learn about transcription, including when it begins and the three phases in its process. Understand which DNA strand is the template for transcription and explore the purposes of a promoter, polymerase, and mRNA. Updated: 08/17/2021
How does transcription begin?
Transcription begins when RNA polymerase attaches to a promoter within DNA. This is called initiation. The DNA molecule splits open and allows RNA polymerase to add RNA nucleotides onto the DNA template.
How does RNA polymerase work?
Once initiation is done, then RNA polymerase moves down the length of the gene and transcribes it into a strand of mRNA. The enzyme works by matching up the complementary nucleotide bases.
What is the process of copying genetic information from DNA to RNA?
Transcription is the copying of genetic information from the form of DNA to the form of RNA. Remember that RNA is a single-stranded molecule; it doesn't have a complementary strand like DNA does. It's only half a ladder, or a single strand of nucleotides. In order to make the RNA strand, we only need one of the original DNA strands. We'll talk later about how to know which DNA strand to use, but for now, we just need to know that one will be called the sense strand, and the other will be called the antisense strand. The antisense strand is the strand of DNA which serves as the template during the process of transcription . The RNA will become a complement of the antisense strand. This means that with a minor exception we'll address later, it will essentially be a copy of the sense stand.
How many nucleotides does RNA have to be built?
The RNA strand has to be built one nucleotide at a time. Does that sound familiar? It should, because a similar process happens in DNA replication. And just like in DNA replication, we need the help of an enzyme to bus in all the nucleotides. You may recall that DNA polymerase was the enzyme that constructed the DNA. Well, in this case, we have RNA polymerase that constructs the RNA. RNA polymerase is the enzyme that assembles the individual nucleotides to create the RNA strand based on the DNA template.
Why does DNA split open?
It's a pretty intricate dance here, because the DNA molecule has to split open to allow transcription to occur, and it has to come back together as soon as that part is transcribed. So, DNA splits open, gets transcribed and zips back together all within a very short distance. There's no room for extra molecules in there. So, what happens to the mRNA that's still growing longer? Well, it just peels away from the DNA template and hangs off to the side.
Which strand of DNA is the template?
The DNA strand that serves as the template is called the antisense strand. Elongation is the phase in which the RNA molecule grows longer as transcription continues down the length of the gene. Termination occurs when RNA polymerase reaches the terminator and detaches from both strands.
What is mRNA used for?
mRNA, after its first therapeutic description in 1992, has recently come into increased focus as a method to deliver genetic information. The recent solution to the two main difficulties in using mRNA as a therapeutic, immune stimulation and potency, has provided the basis for a wide range of applications. While mRNA-based cancer immunotherapies have been in clinical trials for a few years, novel approaches; including, in vivo delivery of mRNA to replace or supplement proteins, mRNA-based generation of pluripotent stem cells, or genome engineering using mRNA-encoded meganucleases are beginning to be realized. This review presents the current state of mRNA drug technologies and potential applications, as well as discussing the challenges and prospects in mRNA development and drug discovery.
Is mRNA used in immunotherapy?
While mRNA-based cancer immunotherapies have been in clinical trials for a few years, novel approaches; including, in vivo delivery of mRNA to replace or supplement proteins, mRNA-based generation of pluripotent stem cells, or genome engineering using mRNA-encoded meganucleases are beginning to be realized.
What is the purpose of mRNA?
What is the purpose of mRNA? The purpose of mRNA and the role of mRNA is to bring the instructions from the DNA to the ribosome for protein production. The role of mRNA in protein production is essential. So, what is the job of mRNA? The mRNA function is to carry the genetic code from DNA to the ribosome. In eukaryotes, this allows DNA to stay safe inside the nucleus. It also allows for a tighter level of control and more specific regulation of protein production.
What is the function of mRNA?
The main job of mRNA is to carry the code of DNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where it can be used in protein synthesis in eukaryotes , like those that are found in human cells. Prokaryotic cells also use mRNA but there is no nucleus so the process from creating mRNA to creating protein is more streamlined.
What is the role of transcription factors in initiation?
During initiation, transcription factors locate around the start of a gene, called a promoter sequence, and recruit RNA polymerase. Helicase opens up the DNA, which serves as a template. During elongation, the RNA polymerase reads the message in the DNA strand and adds new nucleotides according to Chargaff's rule. Chargaff's rule states that adenine pairs with thymine in DNA, and cytosine pairs with guanine. However, in RNA thymine is replaced with uracil. So, adenine pairs with uracil in mRNA. In termination, the RNA polymerase and associated enzymes leave the mRNA molecule and it dissociates from the DNA.
How do ribosomes make proteins?
Ribosomes are organelles that read the mRNA and create the correct protein sequence. Ribosomes are located in the cytoplasm and thus do not have access to the DNA in the nucleus. The process that ribosomes use to read the mRNA and make protein is called translation. During this process, the ribosome sandwiches its two subunits around the mRNA. The ribosome reads the mRNA in groups of three nucleotides called codons. Each codon is read by an additional molecule, called transfer RNA (tRNA). The tRNA brings the correct amino acids based on the codons to the ribosome. The ribosome then catalyzes a peptide bond in between the amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Eventually, the chain is released and can fold into a complete protein.
How is messenger RNA made?
Messenger RNA is made during the process of transcription. During transcription, RNA polymerase accesses DNA in the nucleus. The RNA polymerase reads one strand of DNA and adds complementary ribonucleotides to form the mRNA strand product as well.
What is the difference between RNA and DNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA. RNA is a type of nucleic acid and carries the genetic information for the cell. RNA is similar to DNA but there are several structural differences. RNA uses the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. It also exists as a single strand in cells and only sometimes is double-stranded. DNA in contrast is always double-stranded. RNA uses the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil, whereas DNA uses adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. DNA is a more permanent structure in the cell and can be found in the nucleus of eukaryotes. In contrast, RNA is more readily created and destroyed and can be found in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The table below explains the difference between DNA and RNA.
What is the RNA that is attached to DNA during transcription?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is attached briefly to DNA during the transcription process. RNA polymerase uses the DNA strand as a template to synthesize mRNA.
What is the process of turning DNA into RNA?
Transcription is one of the fundamental processes that happens to our genome. It's the process of turning DNA into RNA. And you may have heard about the central dogma, which is DNA, to RNA, to protein. Well, transcription refers to that first part of going from DNA to RNA.
What is the process of making a copy of a gene?
Transcription is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene sequence. This copy, called a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule, leaves the cell nucleus and enters the cytoplasm, where it directs the synthesis of the protein, which it encodes.
