What are organic molecules?
What class of molecules are lipids?
What is the simplest carbohydrate?
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
How do sugars bond?
What is the structure of proteins?
What is the major component of every living thing?
See 4 more
About this website

What molecule forms the main chain of organic molecules quizlet?
The molecules of life (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) are organic, which means they consist mainly of carbon and hydrogen atoms. The structure of an organic molecule starts with its carbon backbone, a chain of carbon atoms that may form a ring.
What are the main organic molecules?
Four important classes of organic molecules—carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids—are discussed in the following sections.
Which element forms long chains in organic molecules?
CarbonCarbon is able to form long chains of atoms to form quite stable molecules. The chains may be branched or form loops. Many other atoms will form stable bonds to carbon.
What is the most important organic molecule?
The most important is cholesterol. Prostaglandins are signaling molecules derived from unsaturated fatty acids. Proteins are critical components of all body tissues. They are made up of monomers called amino acids, which contain nitrogen, joined by peptide bonds.
What are organic molecules also called?
Organic molecules associated with living organisms are also called biomolecules.
What are the 4 main organic molecules?
There are 4 major kinds of organic molecules, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.Each of these exists as a polymer, composed of the monomers shown in the table. ... monosaccharide, disaccharides, and polysaccharides; quick energy for the cell. ... and a little O. ... sometimes S.
What process forms large organic molecules?
Polymerization is the process which is responsible for the formation of large number of organic molecules.
What is an example of an organic molecule?
An organic molecule is any molecule containing Carbon. Examples include very small molecules like methane (CH4) and very large macromolecules like carbohydrates (glucose), lipids (triglycerides), nucleic acids (DNA), and proteins (the enzyme lactase).
Why does carbon form long chains?
Because each carbon is identical, they all have four valence electrons, so they can easily bond with other carbon atoms to form long chains or rings. In fact, a carbon atom can bond with another carbon atom two or three times to make double and triple covalent bonds between two carbon atoms.
What is the most common organic molecule in a cell?
Water is the most abundant molecule in cells, accounting for 70% or more of total cell mass.
What are the three types of organic molecules?
Types of Organic MoleculesCarbohydrates. Carbohydrates are the first class of organic molecules. ... Lipids. Lipids belong to the second class of organic molecules which includes oils and fats. ... Proteins. Proteins are long chains of components known as amino acids consisting of layered structures. ... Nucleic Acid.
What are organic molecules made up of?
Organic molecules are molecules that are made of carbon and hydrogen, and can include other elements. Organic molecules must contain carbon atoms covalently bonded to hydrogen atoms (C-H bonds). They usually involve oxygen and can also contain nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorous, and others.
What are 3 examples of organic molecules?
An organic molecule is any molecule containing Carbon. Examples include very small molecules like methane (CH4) and very large macromolecules like carbohydrates (glucose), lipids (triglycerides), nucleic acids (DNA), and proteins (the enzyme lactase).
What are the 4 organic molecules and their functions?
They are: carbohydrates, compounds like sugars that provide energy, proteins, the main molecules that build everything from cell walls to organs, nucleic acids, genetic material and lipids, fats used to store energy or insulate cells.
What are the three types of organic molecules?
There are four main types, or classes, of organic compounds found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
How many organic molecules are there?
More than 16,000,000 organic compounds are known, as opposed to about 600,000 inorganic compounds.
17 List of Organic Chemicals – General Structures – Functions
Organic chemistry is one of the fields of chemistry that studies about the structure, properties, and composition of a compound. Organic chemistry is also often referred as carbonyl chemistry, because the elements that are studied in organic chemistry are elements containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, usually with the addition of nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. Each organic […]
Organic Molecule Overview & Examples - Study.com
Organic Molecules. Organic is big these days. We want everything to be organic, to be fresh and free of contaminants. Turns out we want our molecules to be like that, too.
organic compound chart - Biology Flashcards | Quizlet
biology Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
30 Examples of Organic Compounds and Uses - AZ Chemistry
Organic acids; Organic acids are the organic chemical compound with acidic properties. Carboxylic acids are the most common organic acids. The examples of organic aicd are perchloric acid (HC104), (propanoic acid) CH 3 CH 2 COOH, (ethanoic acid ) CH 3 COOH, (hexanoic acid) CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 COOH, (carbolic acid or hydroxybenzene, not IUPAC names) C 6 H 5 OH, (4-methylbenzenesulfonic ...
How to draw organic molecules?
The different ways to draw organic molecules include Kekulé (straight-line), Condensed Formulas, and Bond-Line Formulas (zig-zag). It will be more helpful if you become comfortable going from one style of drawing to another, and look at drawings and understanding what they mean, than knowing which kind of drawing is named what.
What is an example of a drawing that incorporates all three ways to draw organic molecules?
An example of a drawing that incorporates all three ways to draw organic molecules would be the following additional drawing of Retin ol. The majority of the drawing is Bond-line (zig-zag) formula, but the -CH 3 are written as condensed formulas, and the -OH group is written in Kekul é form.
Why do molecules end up looking like zig zag lines?
This formula is full of bonds and lines, and because of the typical (more stable) bonds that atoms tend to make in molecules, they often end up looking like zig-zag lines. If you work with a molecular model kit you will find it difficult to make stick straight molecules (unless they contain sp triple bonds) whereas zig-zag molecules and bonds are much more feasible.
What are the lines in a 4-carbon chain?
Above are 4-carbon chains with attached OH groups or Cl and Br atoms. Remember that each line represents a bond and that the carbons and hydrogens have been omitted. When you look at or draw these structures, the straight lines illustrate atoms and bonds that are in the same plane, the plane of the paper (in this case, computer screen). Dashed lines show atoms and bonds that go into the page, behind the plane, away from you. In the above example, the OH group is going into the plane, while at the same time a hydrogen comes out (wedged).
How to show 3D structure of a molecule?
A widely used way of showing the 3D structure of molecules is the use of dashes, wedges, and straight lines. This drawing method is essential because the placement of different atoms could yield different molecules even if the molecular formulas were exactly the same. Below are two drawings of a 4-carbon molecule with two chlorines and two bromines attached.
How to compare two molecules?
An easier way to compare the two molecules is to rotate one of the bonds (here , it is the bond on the right): Notice how the molecule on the right has both bromines on the same side and chlorines on the same side, whereas the first molecule is different.
Which atoms want to have a closed shell?
All atoms want to have their valence shell full, a "closed shell.". Hydrogen wants to have 2 e - whereas carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen want to have 8 e -. When looking at the different representations of molecules, keep in mind the Octet Rule.
What are organic molecules?
But what is an organic molecule? Organic molecules are usually composed of carbon atoms with other atoms attached, such as hydrogen, oxygen , and nitrogen. The structure of organic molecules generally contains atoms in long chains or rings. Most carbon-containing compounds are classified as organic. However, there are a few, such as oxides, carbonates, and cyanides, that are considered inorganic.
What are the four types of organic molecules?
Most organic compounds in the cells of the human body can be classified as one of four types. These four types are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What are the functional groups of lipids?
Lipids commonly contain hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups. The carboxyl functional group is characterized by a carbon atom bonded to an oxygen atom and a hydroxyl group. The diagram shows a fatty acid with the carboxyl group.
What are the two most important functional groups in proteins?
However, the two most important functional groups are carboxyl and amine groups. The amine group is a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms. The basic structure of an amino acid is shown in the diagram.
Which functional group is composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom?
Carbohydrates can contain hydroxyl, aldehyde or ketone functional groups. The hydroxyl functional group is composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. The aldehyde functional group contains a carbon atom bonded with an oxygen atom in a double bond and a hydrogen atom. The ketone functional group has a carbon atom in a double bond with an oxygen atom. Glucose contains both aldehyde and hydroxyl functional groups, as shown in the diagram.
How many chemical bonds does carbon have?
Carbon can participate in up to four chemical bonds. The way it bonds and the other atoms in the bond determine the properties. This is known as a functional group. Polymers are large complex molecules that are made up of small repeating units, known as monomers. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid all form polymers.
What are carbohydrates made of?
Carbohydrates are molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are referred to as saccharides, which means sugar. Some examples of these are
What are the elements that make up organic compounds?
All organic compounds contain carbon, usually bonded to hydrogen (other elements may be present as well). Let's take a closer look at the key types of organic compounds and see examples of these important molecules.
Why are organic compounds called organic?
Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D. Updated November 25, 2019. Organic compounds are called "organic" because they are associated with living organisms. These molecules form the basis for life and are studied in great detail in the chemistry disciplines of organic chemistry and biochemistry. There are four main types, or classes, ...
What are carbohydrates made of?
Carbohydrates—Organic Compounds. Carbohydrates are organic compounds made of the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in carbohydrate molecules is 2:1. Organisms use carbohydrates as energy sources, structural units, and for other purposes.
What are the four types of organic compounds?
There are four main types, or classes, of organic compounds found in all living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids . In addition, there are other organic compounds that may be found in or produced by some organisms. All organic compounds contain carbon, usually bonded to hydrogen (other elements may be present as well).
How are carbohydrates classified?
Carbohydrates are classified according to how many subunits they contain. Simple carbohydrates are called sugars. A sugar made of one unit is a monosaccharide. If two units are joined together, a disaccharide is formed. More complex structures form when these smaller units link to each other to form polymers. Examples of these larger carbohydrate compounds include starch and chitin.
Which group of lipids has a higher hydrogen to oxygen ratio than is found in carbohydrates?
Lipids have a higher hydrogen to oxygen ratio than is found in carbohydrates. The three major groups of lipids are triglycerides (fats, oils, waxes), steroids, and phospholipids. Triglycerides consist of three fatty acids joined to a molecule of glycerol.
Why is Helmenstine called organic?
in biomedical sciences and is a science writer, educator, and consultant. She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Organic compounds are called "organic" because they are associated with living organisms. These molecules form the basis for life and are studied in great detail in ...
What are organic molecules used for?
Organic molecules are used in a variety of industries in human society, including food, pharmaceuticals, fuels, and building, to name but a few. Alkanes include chemical substances such as propane, octane, and methane. These are commonly used as oils for items like gasoline in the car and heating/cooking oil in the home.
What is organic chemistry?
Organic chemistry was once thought to be confined to the study of substances produced as part of the natural processes of living organisms, but as Friedrich Wohler discovered in the early 1800s, organic compounds can be synthesized from minerals and other non-organic materials in the laboratory. Indeed, modern chemistry and materials sciences have concentrated on the remarkable properties of carbon atoms for the production of synthetic chemicals, pesticides and a host of other things. Organic compounds contain carbon, almost always bonded to another carbon and/or hydrogen.
What is an Organic Compound?
Organic compounds also contain carbon, along with other elements essential for the reproduction of living organisms. Carbon is the main factor as it has four electrons that can accommodate eight electrons in an outer shell. As a result, several forms of bonds can be formed with other carbon atoms and elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Hydrocarbons and proteins are strong examples of organic molecules capable of producing long chains and complex structures.
What is a homologous series?
Homologous series. A group or a series of organic compounds in which each member contains the same characteristic functional group and differs from each other by a fixed unit form a homologous series and therefore its members are known as homologous. The members of the homologous series can be represented by a general formula and ...
Why are organic compounds important?
Organic compounds are essential because they contain carbon in all living organisms. They are the basic components that move the world in many of the cycles. For example, the carbon cycle which involves exchanging carbon in photosynthesis and cell respiration between plants and animals.
What is the name of the compound that contains carbon?
The compounds in solid, liquid or gaseous state which contain carbon in its molecule are known as organic compounds . There are a large number of organic compounds and therefore a proper systematic classification was required. Organic compounds can be broadly classified as acyclic (open chain) or cyclic (closed chain).
What is a cyclic compound that contains carbon atoms connected to each other in a ring?
These are cyclic compounds which contain carbon atoms connected to each other in a ring (homocyclic). When atoms other than carbon are also present then it is called heterocyclic. Examples of this type are as follows: They exhibit some properties similar to aliphatic compounds. 3.
What are organic molecules?
Molecules containing carbon were assumed to point towards organisms and hence were called as organic molecules. Since we know about carbon’s ability to bond with four other atoms and form complex molecular structure which makes it a perfect candidate to build such organic molecules around.
What class of molecules are lipids?
Lipids. Lipids belong to the second class of organic molecules which includes oils and fats. These molecules have a simple with 3 carbon glycerol molecules. Every carbon picks a bit known as the fatty acid that can be long or short.
What is the simplest carbohydrate?
The simplest kind of carbohydrate includes monosaccharide simple sugars which have a basic formula: two hydrogens and one oxygen for every carbon atom or one water for every carbon. Glucose is a common carbohydrate whose formula is C6H12O6. Sugars can be either a single sugar molecule to multiple molecules bound together.
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
Nucleic Acid. Nucleic acids are of two types namely: ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid. These polymers are lengthy chains of components known as the base of which there exist only five kinds. DNA is a spiral of two cross-connected strands.
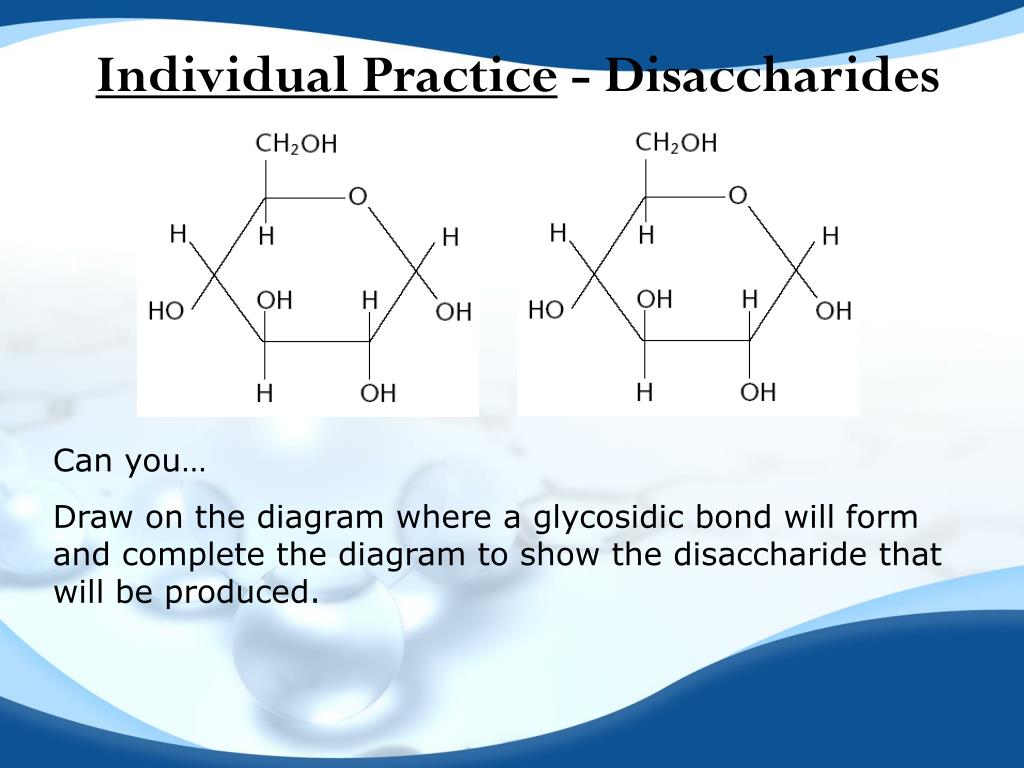
How do sugars bond?
When organic molecules are bound, a bonding site is freed at every member. This occurs by clipping a single hydrogen from one participant and a hydroxide (oxygen-hydrogen) off the other.
What is the structure of proteins?
Proteins are long chains of components known as amino acids consisting of layered structures. The first level is known as the primary structure which is the order of amino acids in every chain. The secondary structure, amino acids is a region that connects to each other and makes local forms like pleated coil sheets. At tertiary structure, the complete molecule is pulled into a 3-dimensional shape mainly through bonds but sometimes via covalent bonds.
What is the major component of every living thing?
With every element learned that were found in living things, experts realized that carbon was stood to be the major component which is found in every kind of organism analysed along with extracted compounds.