Why there is uracil instead of thymine in RNA?
Uracil is found only in RNA and DNA has thymine which is the methylated form of uracil. One main reason is that uracil production is less engery consuming than thymine and uracil forms relatively weaker bond with adenine while thymine forms a stronger one.
What Sugar is found only in RNA?
What sugar is in RNA? The 5-carbon sugars ribose and deoxyribose are important components of nucleotides, and are found in RNA and DNA, respectively. The sugars found in nucleic acids are pentose sugars; a pentose sugar has five carbon atoms. What is the function of DNA?
What Sugar distinguishes from RNA from DNA?
deoxyribose sugar DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, contains deoxyribose sugar whereas RNA, or ribonucleic acid, contains ribose sugar. A ribose sugar contains a hydroxyl group on its 2' carbon whereas the deoxyribose sugar contains a hydrogen; therefore, the RNA pentose sugar has an extra hydroxyl group.
What is the five carbon sugar found in RNA?
RNA and DNA contain pentose sugar, which contains five carbon atoms. The carbon atoms are numbered as 1′, 2′, 3′, and 5′. The number is used to identify the major functional groups of the nucleotide. The 5′ carbon of the sugar has a phosphate residue attached to it, while the 3′ carbon possesses a hydroxyl group.

What type of sugar is in DNA and RNA?
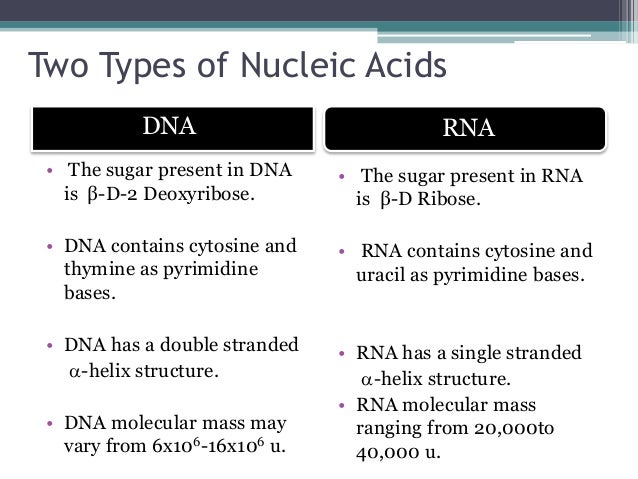
There are two differences that distinguish DNA from RNA: (a) RNA contains the sugar ribose, while DNA contains the slightly different sugar deoxyribose (a type of ribose that lacks one oxygen atom), and (b) RNA has the nucleobase uracil while DNA contains thymine.
What type of sugar is DNA?
deoxyriboseDNA consists of a pair of chains of a sugar-phosphate backbone linked by pyrimidine and purine bases to form adouble helix (Fig. 96.1). The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose.
Does RNA use 5 carbon sugar?
Ribonucleic acid (RNA), unlike DNA, is usually single-stranded. A nucleotide in an RNA chain will contain ribose (the five-carbon sugar), one of the four nitrogenous bases (A, U, G, or C), and a phosphate group.
What is the difference between the sugar in RNA and the sugar in DNA?
The pentose sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose, and in RNA, the sugar is ribose. The difference between the sugars is the presence of the hydroxyl group on the 2' carbon of the ribose and its absence on the 2' carbon of the deoxyribose.
What is difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides. DNA replicates on its own, it is self-replicating. RNA does not replicate on its own.
Does RNA run from 5 to 3?
RNA polymerase synthesizes an RNA strand complementary to a template DNA strand. It synthesizes the RNA strand in the 5' to 3' direction, while reading the template DNA strand in the 3' to 5' direction. The template DNA strand and RNA strand are antiparallel.
Is 5 carbon sugar found in DNA or RNA?
Deoxyribose is a five-carbon sugar found in DNA. It is the nucleotide's central molecule.
Is ribose 5 or 6 carbon sugar?
Ribose is a single-ring pentose [5-Carbon] sugar. The numbering of the carbon atoms runs clockwise, following organic chemistry rules. Note the absence of the hydroxyl (-OH) group on the 2' carbon in the deoxy-ribose sugar in DNA as compared with the ribose sugar in RNA.
Does DNA use 5 carbon sugar?
A single basic unit or "building block" of DNA consists of a sugar , a phosphate group and a base. Sugars are rings of carbon and oxygen atoms. The sugar in DNA has 5 carbon atoms (labelled 1' - 5'), and is called deoxy-ribose (hence the "Deoxy-ribo" in DNA).
How many carbons does RNA sugar have?
five carbon atomsThe full names of the sugars used in nucleic acid structures are ribose (for RNA) and deoxyribose (for DNA). Both sugars have five carbon atoms arranged in a ring.
Do nucleic acids have 5 carbon sugar?
The 5-carbon sugar (known as a pentose) includes ribose and deoxyribose, which are present in nucleic acid. Both ribose and deoxyribose have five carbon atoms and one oxygen atom.
Do RNA nucleotides contain 5 carbon sugar ribose?
Each of the nucleotides in RNA is made up of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. In the case of RNA, the five-carbon sugar is ribose, not deoxyribose. Ribose has a hydroxyl group at the 2′ carbon, unlike deoxyribose, which has only a hydrogen atom (Figure 9.5).
What is the sugar in DNA called?
It is called Deoxyribose. If you know the full form of DNA, it's Deoxyribonucleic acid. And for RNA the 5-carbon sugar is called Ribose. In this photo, You can see the basic difference between ribose and deoxyribose sugar. The 2nd Carbon of Deoxyribose contains H instead of OH in Ribose. You can remember it like DE-OXY, where the Oxygen gets diminished from a ribose. 😊
What is the backbone of RNA?
Both RNA and DNA are built from nucleobases linked to a phosphate-sugar backbone. In DNA, the phosphate-sugar backbone contains deoxyribose, and in RNA it contains ribose, as below.
What is the difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
As you can see, the only difference is that ribose has an OH group on position 2', whereas deoxyribose does not (hence, deoxy). This makes sense when you compare the structures of DNA and RNA (below) and see that:
Why is thymine used in DNA?
Thymine is used at the DNA level to enhance fidelity. Both cytosine and thymine naturally undergo degradation, both through chemical and enzymatic means. This means that you have some basal rate at which cytosine and thymine become uracil. Consequently, any cytosine that has deaminated will now base pair with adenine instead of the desired guanine. This can result in gross changes in genetic information, so organisms evolved to use thymine at the DNA level to prevent this. Along with using thymine, organisms developed enzymes that recognize uracils in DNA (uracil-DNA glycosylases) which recognize any aberrant cytosines which have degraded to uracil and clip them out before any damage can be propagated.
Which is the cheapest RNA?
Uracil is the cheapest to produce energetically, and is therefore favored at the RNA level where fidelity is not as important and large quantities are produced.
Why do we have two nucleotides in each family?
Since the stability of the double helix requires the strand separation to be as uniform as possible , and since we have only two nucleotides each in two families (one with large molecules, the other with smaller molecules), it makes sense to have one nucleotide from each family in opposing positions in the double helix. And, indeed, that is exactly what cells have been doing since their inception. What remains is the reason why we have the particular pairings we have and no others. To help to answer that I present you the following diagram:
Is DNA a sugar?
DNA posses hexose deoxyribose sugar derived from ribose where there is Hydrogen group present at C2' position therefore there is one less oxygen atom present in it's sugar than that of ribose sugar.
What is RNA in a cell?
RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is a nucleic acid that is similar in structure to DNA but different in subtle ways. The cell uses RNA for a number of different tasks, one of which is called messenger RNA, or mRNA. And that is the nucleic acid information molecule that transfers information from the genome into proteins by translation. Another form of RNA is tRNA, or transfer RNA, and these are non-protein encoding RNA molecules that physically carry amino acids to the translation site that allows them to be assembled into chains of proteins in the process of translation.
What is the backbone of RNA?
An RNA strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar (ribose) and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), or guanine (G).
What is the name of the RNA that is used to transport amino acids to the translation site?
Another form of RNA is tRNA, or transfer RNA, and these are non-protein encoding RNA molecules that physically carry amino acids to the translation site that allows them to be assembled into chains of proteins in the process of translation.