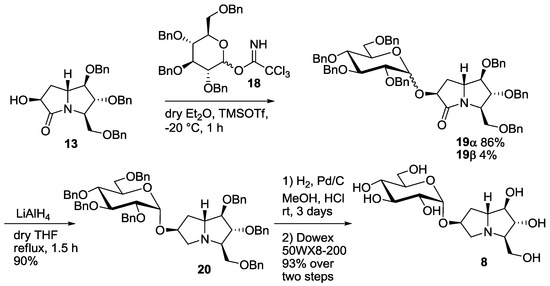
Structure and Functions of Glycogen
- Structure of Glycogen Glycogen is built with long polymer chains of glucose units bonded with alpha acetal linkage. This acetal linkage is formed by combining the carbonyl group and the alcoholic group. ...
- Functions of Glycogen ...
- Other Tissues ...
- Bacteria and Fungi ...
- Metabolism of Glycogen ...
- Glycogenesis or Glycogen Synthesis ...
- Glycogenolysis or Glycogen Breakdown ...
- Glycogen and Diet ...
Is glycogen composed of glucose units?
Glycogen is a polysaccharide composed of glucose units linked by alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds, with occasional alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds which provide branching points.
How many molecules is glycogen made up of?
Linear glycogen chains consist of glucose molecules linked together by α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. At each of the branch points, two glucose molecules are linked together by α-1,6 glycosidic bonds. The non-reducing ends of the glycogen molecule are the sites where both synthesis and degradation occur.
What is the monomer unit of glycogen?
GLUCOSETHE MONOMERS OF STARCH AND GLYCOGEN IS GLUCOSE.
How many units of glucose are in glycogen?
Glycogen is a branched biopolymer consisting of linear chains of glucose residues with an average chain length of approximately 8–12 glucose units and 2,000-60,000 residues per one molecule of glycogen.
What is glycogen made of quizlet?
What is glycogen? A polymer of glucose molecules used to store glucose.
Is glycogen made of alpha glucose?
Glycogen and starch are formed by the condensation of α-glucose.
Is glycogen made from amino acids?
Answer and Explanation: Glycogen does not contain amino acids. Amino acids are the monomer that makes up proteins. Glycogen is made of glucose units and is classified as a carbohydrate.
How many monosaccharides are in glycogen?
Only one monosaccharide makes up glycogen, and that is glucose.
How many atoms are in a glycogen molecule?
To conclude, every molecule of glycogen consists of 24 atoms Carbon, 42 atoms of Hydrogen, and 21 atoms of Oxygen.
What is the molecular mass of glycogen?
GlycogenPubChem CID439177Molecular Weight666.6DatesModify 2022-09-17 Create 2005-06-244 more rows
What type of molecule is glucagon?
Glucagon is a glucoregulatory peptide hormone that counteracts the actions of insulin by stimulating hepatic glucose production and thereby increases blood glucose levels.
How is glycogen made?
Glycogen is synthesized when blood glucose levels are high and broken down when blood glucose levels are low, making it an important buffer of blood glucose levels. When energy is required by the cell or the organism, glycogen serves as a critical energy source by providing glucose to tissues throughout body.
9.2 General Manufacturing Information
XU - indicates a substance exempt from reporting under the Chemical Data Reporting Rule, (40 CFR 711).
11.4 Synthesis References
Parodi A J; Krisman C R; Mordoh J In vitro synthesis of particulate glycogen from uridine diphosphate glucose. II. Some studies on the growth process. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics (1970), 141 (1), 219-27.
What is the structure of glycogen?
Structure of Glycogen. Glycogen is composed of long polymer chains of glucose units which are bonded with an alpha acetal linkage. This acetal linkage forms by the combination of the carbonyl group and alcoholic group.
Why is glycogen stored in protein?
Every glycogen granule has its core a glycogen in protein because of the glycogen is synthesized. In muscles, liver and fat cells glycogen is stored in the hydrated form. It is composed of three to four parts of water of glycogen that are associated with 0.45 millimoles of potassium for per gram of glycogen.
What is a glycogen?
What is Glycogen? Glycogen is a polysaccharide of glucose that serves as a form of energy storage in fungi and animals. The polysaccharide structure of glucose shows the primary storage form of glucose in the body.
Where is glycogen stored?
Glycogen is made and stored in the cells of liver and muscles that are hydrated with the four parts of water. It acts as the secondary long-term energy storage. Muscle glycogen is quickly converted into glucose by muscle cells and liver glycogen that converts into glucose for use throughout the body which includes the central nervous system.
Where is glycogen found in the cell?
It is found in the form of granules in the cytoplasm in different cell types and plays a vital role in the glucose cycle. It forms an energy reserve that can be easily mobilized to meet sudden needs for glucose. Every glycogen granule has its core a glycogen in protein because of the glycogen is synthesized.
When does glycogen start to accumulate in the lungs?
It has a specialized role in fetal lung type II pulmonary cells. These cells start to accumulate glycogen at about 26 weeks of gestation and then synthesize pulmonary surfactant. Take up a quiz on Glycogen. Q 5.
Is amylopectin a polymer?
It has a similar structure to amylopectin which is a component of starch, more extensively branched and compact than starch. This polymer of glucose residues linked by a - (1,4) and a- (1,6)- glycosidic bonds. It is found in the form of granules in the cytoplasm in different cell types and plays a vital role in the glucose cycle.
How many glucose units are in a globular glycogen granule?
The entire globular granule may contain around 30,000 glucose units.
How many glycosidic residues are in a glycogen oligomer?
Glycogen is a branched biopolymer consisting of linear chains of glucose residues with an average chain length of approximately 8–12 glucose units and 2,000-60,000 residues per one molecule of glycogen.
What is the function of glycogen stores in skeletal muscle?
Glycogen stores in skeletal muscle serve as a form of energy storage for the muscle itself ; however, the breakdown of muscle glycogen impedes muscle glucose uptake from the blood, thereby increasing the amount of blood glucose available for use in other tissues. Liver glycogen stores serve as a store of glucose for use throughout the body, ...
What percentage of glucose is consumed by the brain?
The human brain consumes approximately 60% of blood glucose in fasted, sedentary individuals. Glycogen is the analogue of starch, a glucose polymer that functions as energy storage in plants. It has a structure similar to amylopectin (a component of starch), but is more extensively branched and compact than starch.
How much glycogen is in skeletal muscle?
In skeletal muscle, glycogen is found in a low concentration (1–2% of the muscle mass) and the skeletal muscle of an adult weighing 70 kg stores roughly 400 grams of glycogen.
Which enzyme cleaves the end of the glycogen chain?
Glycogen is cleaved from the nonreducing ends of the chain by the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase to produce monomers of glucose-1 phosphate:
Which enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a terminal fragment of six or seven glucose residues from a?
The glycogen branching enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a terminal fragment of six or seven glucose residues from a nonreducing end to the C-6 hydroxyl group of a glucose residue deeper into the interior of the glycogen molecule.
How is the linear glycogen chain constructed?
Once the primer has been constructed, the linear glycogen chain is constructed by joining the glucose molecules via alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds. It involves the transfer of glucose molecule from UDP-glucose to the non-reducing end of the glycogen chain.
What is the center of the glycogen molecule?
Branching takes place at an interval of 8 to 12 glucose subunits. Glycogen molecule also has a protein at its center known as glycogenin protein . This protein forms the core of the glycogen molecule.
How are glucose molecules linked?
All the glucose molecules in the linear chain of glycogen are linked via alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds. Branches arise from this linear chain via an alpha 1-6 glycosidic bond. It means that the glucose molecule at the branch point is attached to the main chain via alpha 1-6 bond.
What is glycogen made of?
Glycogen is made up of long chains of glucose molecules that show abundant branching.
How does glycogen organize itself?
Glycogen molecule organizes itself in a spherical form around the glycogen in protein in such a way that the whole structure looks like a tree with the branches arising from the center. In the cytoplasm of living cells, glycogen is present in the form of granules.
What is the precursor of all glucose molecules found in glycogen?
It involves the following steps; Synthesis of UDP-Glucose. Uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-Glucose) acts as the precursor of all glucose molecules found in glycogen. It is synthesized from a molecule of glucose-1-phosphate and UTP by UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase enzyme.
Where is glycogen synthesized?
Synthesis. Glycogen is synthesized majorly in the liver and muscle cells by a process known as glycogenesis. This process takes place in the cytosol and uses energy in the form of ATP and UTP. Glycogenesis is the process in which glycogen molecules are synthesized from glucose monomers.
How are glucose units linked in the main chain?
As in the amylopectin, glucose units in the main chain and in the lateral chain s are linked by α- (1→4) glycosidic bonds. Lateral chains are joined to the main chain by an α- (1→6) glycosidic bond; unlike amylopectin branches are more frequent, approximately every 10 glucose units (rather than every 25-30 as in amylopectin) ...
Which enzyme grows the glycogen molecule exponentially?
Due to the action of glycogenin, and then of glycogen synthase and branching enzyme (EC 2.4.1.18), glycogen molecule grows exponentially in concentric tiers around the glycogenin core. According to Whelan’s model of glycogen structure, two types of glucose chain can be categorized:
Which end of glycogen phosphorylase can act as a substrate for glycogen phosphorylase?
The non-reducing ends present on the outermost tier can act as a substrate for glycogen phosphorylase. Therefore, many glycogen phosphorylases can work simultaneously allowing a rapid mobilization of stored glucose as glucose 1-phosphate.
How much water is bound to glycogen?
They can be stored in anhydrous form, whereas the amount of water bound to glycogen is equal to 2-3 times its weight.
What is the only food that contains glycogen?
The only dietary sources are oysters and other shellfish that are eaten virtually alive: they contain about 5% glycogen. In humans, accumulation of glycogen is associated with weight gain due to water retention: for each gram of stored glycogen 3 grams of water are retained.
What is the molecular weight of glycogen?
Chemically similar to amylopectin, and therefore sometimes referred to as animal starch, compared to the latter it is more compact, extensively branched and larger, reaching a molecular weight up to 10 8 Da corresponding to about 600000 ...
Where is glycogen located in the cell?
Glycogen is located in the cytosol of the cell in the form of hydrated granules of diameter between 1 to 4 µm and forms complexes with regulatory proteins and enzymes responsible for its synthesis and degradation.
Overview
Structure
Glycogen is a branched biopolymer consisting of linear chains of glucose residues with an average chain length of approximately 8–12 glucose units and 2,000-60,000 residues per one molecule of glycogen.
Like amylopectin, glucose units are linked together linearly by α(1→4) glycosidic bonds from one glucose to the next. Branches are linked to the chains from wh…
Functions
As a meal containing carbohydrates or protein is eaten and digested, blood glucose levels rise, and the pancreas secretes insulin. Blood glucose from the portal vein enters liver cells (hepatocytes). Insulin acts on the hepatocytes to stimulate the action of several enzymes, including glycogen synthase. Glucose molecules are added to the chains of glycogen as long as both insulin and glucose remain plentiful. In this postprandial or "fed" state, the liver takes in more glucose from th…
History
Glycogen was discovered by Claude Bernard. His experiments showed that the liver contained a substance that could give rise to reducing sugar by the action of a "ferment" in the liver. By 1857, he described the isolation of a substance he called "la matière glycogène", or "sugar-forming substance". Soon after the discovery of glycogen in the liver, A. Sanson found that muscular tissue also contains glycogen. The empirical formula for glycogen of (C 6H 10O 5)n was establis…
Metabolism
Glycogen synthesis is, unlike its breakdown, endergonic—it requires the input of energy. Energy for glycogen synthesis comes from uridine triphosphate (UTP), which reacts with glucose-1-phosphate, forming UDP-glucose, in a reaction catalysed by UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase. Glycogen is synthesized from monomers of UDP-glucose initially by the protein glycogenin, …
Clinical relevance
The most common disease in which glycogen metabolism becomes abnormal is diabetes, in which, because of abnormal amounts of insulin, liver glycogen can be abnormally accumulated or depleted. Restoration of normal glucose metabolism usually normalizes glycogen metabolism, as well.
In hypoglycemia caused by excessive insulin, liver glycogen levels are high, but the high insulin le…
See also
• Chitin
• Peptidoglycan
External links
• "Glycogen storage disease". McArdle's Diseases.
• Glycogen at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)