
How many molecules of ATP are produced in the Calvin cycle?
The next stage in the Calvin cycle is to regenerate RuBP. Five G3P molecules produce three RuBP molecules, using up three molecules of ATP. 2 molecules (as would be expected from the number of carbon atoms involved). The regeneration stage can be broken down into steps.
How does the Calvin cycle convert CO2 to sugar?
The Calvin cycle uses the chemical energy of ATP and reducing power of NADPH from the light dependent reactions to produce sugars for the plant to use. These substrates are used in a series of reduction-oxidation reactions to produce sugars in a step-wise process; there is no direct reaction that converts several molecules of CO 2 to a sugar.
What are the products of the Calvin cycle?
These reactions take the products ( ATP and NADPH) of light-dependent reactions and perform further chemical processes on them. The Calvin cycle uses the chemical energy of ATP and reducing power of NADPH from the light dependent reactions to produce sugars for the plant to use.
Where do the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place?
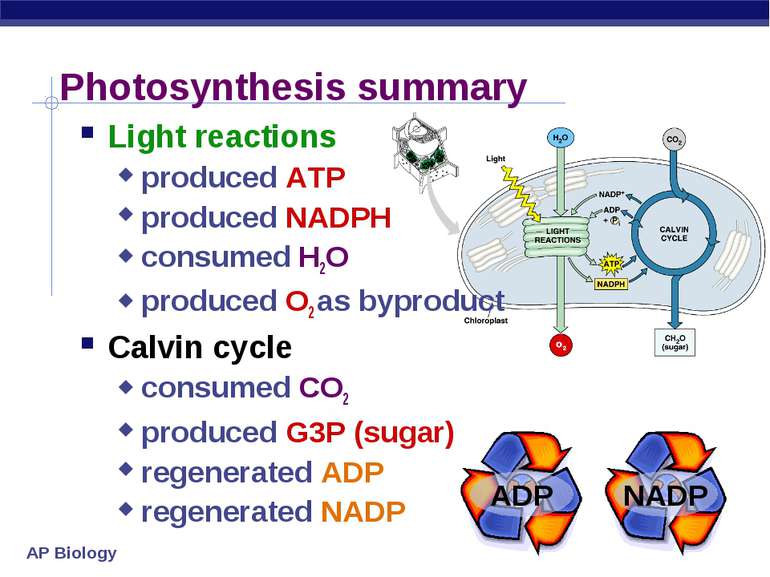
Unlike the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the inner space of chloroplasts). This illustration shows that ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions are used in the Calvin cycle to make sugar.
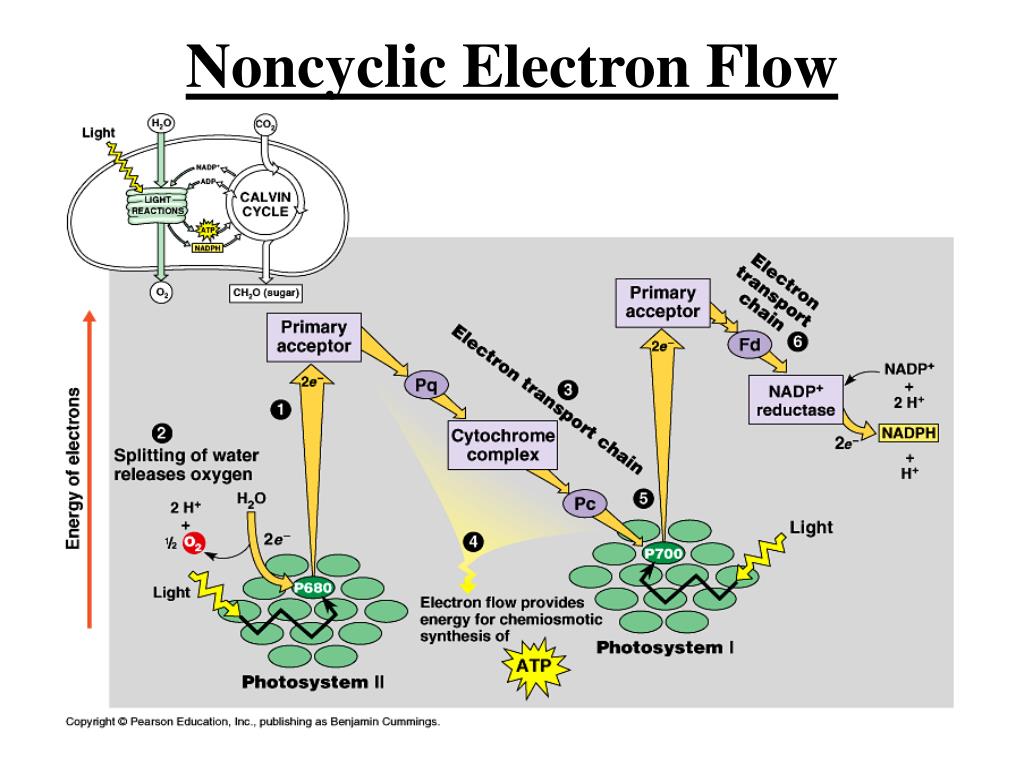
Where does the ATP and NADPH used in the Calvin cycle come from and what is it used for?
These reactions take the products (ATP and NADPH) of light-dependent reactions and perform further chemical processes on them. The Calvin cycle uses the chemical energy of ATP and reducing power of NADPH from the light dependent reactions to produce sugars for the plant to use.
Where do NADP and ATP produced in the Calvin cycle go?
Unlike the light reactions, which take place in the thylakoid membrane, the reactions of the Calvin cycle take place in the stroma (the inner space of chloroplasts). This illustration shows that ATP and NADPH produced in the light reactions are used in the Calvin cycle to make sugar.
Where do the ATP and NADPH used in the Calvin cycle come from what happens to the ADP and NADP+ produced by the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma and uses the ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent reactions to fix carbon dioxide, producing three-carbon sugars—glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, or G3P, molecules. The Calvin cycle converts ATP to ADP and Pi, and it converts NADPH to NADP+.
Where does energy come from in the Calvin cycle?
The energy from sunlight is briefly held in NADPH and ATP, which is needed to drive the formation of sugars such as glucose. And this all happens in the Calvin cycle.
How is ATP and NADPH formed in photosynthesis?
This is accomplished by the use of two different photosystems in the light reactions of photosynthesis, one to generate ATP and the other to generate NADPH. Electrons are transferred sequentially between the two photosystems, with photosystem I acting to generate NADPH and photosystem II acting to generate ATP.
Where does NADP+ come from in photosynthesis?
NADP (the vital coenzyme required for photosynthesis) is derived from nicotinic acid, a B-vitamin also known as niacin.
Where does the ATP and NADPH get created?
stromaATP and NADPH are produced on the stroma side of the thylakoid membrane, where they can be used by the Calvin cycle.
What are the inputs to the Calvin cycle where do they come from?
The inputs to the Calvin cycle are CO₂ ATP and NADPH. The CO₂ comes from the atmosphere around the plant and the ATP and NADPH come from the light-dependent reaction.
Where is ATP produced during photosynthesis?
the thylakoid membraneATP is produced on the stromal side of the thylakoid membrane, so it is released into the stroma. The electron arrives at photosystem I and joins the P700 special pair of chlorophylls in the reaction center.
Why are ATP and NADPH important in the Calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH are used to convert the six molecules of 3-PGA into six molecules of a chemical called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). This is a reduction reaction because it involves the gain of electrons by 3-PGA. Recall that a reduction is the gain of an electron by an atom or molecule.
Where are the ATP and NADPH used?
ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions of the photosystems are used by the Calvin cycle in the stroma of the chloroplast.
Where is the most energy used in the Calvin cycle?
Where is the most energy used in the Calvin cycle? Creating the higher-energy bonds in G3P requires the most energy in the Calvin cycle.
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
The Calvin cycle, Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) cycle, reductive pentose phosphate cycle (RPP cycle) or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic organisms .
Which enzymes are activated in the Calvin cycle?
There are two regulation systems at work when the cycle must be turned on or off: the thioredoxin / ferredoxin activation system, which activates some of the cycle enzymes; and the RuBisCo enzyme activation, active in the Calvin cycle, which involves its own activase.
How many turns of the Calvin cycle are needed to make one surplus G3P?
Therefore, there is only 1 net carbon produced to play with for each turn. To create 1 surplus G3P requires 3 carbons, and therefore 3 turns of the Calvin cycle. To make one glucose molecule (which can be created from 2 G3P molecules) would require 6 turns of the Calvin cycle.
How many G3P molecules are produced in a 2 molecule?
2 molecule produces two G3P molecules, three CO. 2 molecules produce six G3P molecules, of which five are used to regenerate RuBP, leaving a net gain of one G3P molecule per three CO. 2 molecules (as would be expected from the number of carbon atoms involved). Simplified C3 cycle with structural formulas.
What are the immediate products of the Calvin cycle?
The immediate products of one turn of the Calvin cycle are 2 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P) molecules, 3 ADP, and 2 NADP +. (ADP and NADP + are not really "products." They are regenerated and later used again in the Light-dependent reactions ). Each G3P molecule is composed of 3 carbons. For the Calvin cycle to continue, RuBP (ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate) must be regenerated. So, 5 out of 6 carbons from the 2 G3P molecules are used for this purpose. Therefore, there is only 1 net carbon produced to play with for each turn. To create 1 surplus G3P requires 3 carbons, and therefore 3 turns of the Calvin cycle. To make one glucose molecule (which can be created from 2 G3P molecules) would require 6 turns of the Calvin cycle. Surplus G3P can also be used to form other carbohydrates such as starch, sucrose, and cellulose, depending on what the plant needs.
What is the enzyme that catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bis
The enzyme RuBisCO catalyses the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, RuBP, a 5-carbon compound, by carbon dioxide (a total of 6 carbons) in a two-step reaction. The product of the first step is enediol-enzyme complex that can capture CO. 2 or O. 2. Thus, enediol-enzyme complex is the real carboxylase/oxygenase.
What enzyme converts sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate to sedohept
2 fixation) are converted into sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate (7C) by aldolase enzyme. Sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase (one of only three enzymes of the Calvin cycle that are unique to plants) cleaves sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphate into sedoheptulose-7-phosphate, releasing an inorganic phosphate ion into solution.
Overview
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle of photosynthesis are the chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into glucose. The Calvin cycle is present in all photosynthetic eukaryotes and also many photosynthetic bacteria. In plants, these reactions o…
Coupling to other metabolic pathways
The reactions of the Calvin cycle are closely coupled to the thylakoid electron transport chain as the energy required to reduce the carbon dioxide is provided by NADPH produced during the light dependent reactions. The process of photorespiration, also known as C2 cycle, is also coupled to the Calvin cycle, as it results from an alternative reaction of the RuBisCO enzyme, and its final byproduct is another glyceraldehyde-3-P molecule.
Calvin cycle
The Calvin cycle, Calvin–Benson–Bassham (CBB) cycle, reductive pentose phosphate cycle (RPP cycle) or C3 cycle is a series of biochemical redox reactions that take place in the stroma of chloroplast in photosynthetic organisms. The cycle was discovered in 1950 by Melvin Calvin, James Bassham, and Andrew Benson at the University of California, Berkeley by using the radioactive isotope c…
Light-dependent regulation
These reactions do not occur in the dark or at night. There is a light-dependent regulation of the cycle enzymes, as the third step requires NADPH.
There are two regulation systems at work when the cycle must be turned on or off: the thioredoxin/ferredoxin activation system, which activates some of the cycle enzymes; and the RuBisCo enzyme activation, active in the Calvin cycle, which involves its own activase.
Further reading
• Rubisco Activase, from the Plant Physiology Online website
• Thioredoxins, from the Plant Physiology Online website
External links
• The Biochemistry of the Calvin Cycle at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
• The Calvin Cycle and the Pentose Phosphate Pathway from Biochemistry, Fifth Edition by Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko and Lubert Stryer. Published by W. H. Freeman and Company (2002).