Where to plug in power cord for monitor?
Where is the power button on a monitor?
How to connect a monitor to a computer?
What type of connector is used for a flat panel monitor?
How many screws are on a VGA cable?
See 2 more
About this website
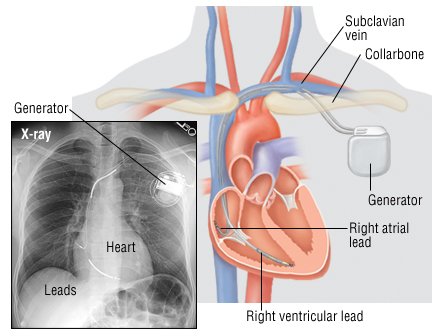
What Is Electrocardiogram
As a non-invasive yet most valuable diagnostic tool, the 12-lead ECG records the heart's electrical activity as waveforms. When interpreted accurat...
12-Lead ECG Electrode Placement
To measure the heart's electrical activity accurately, proper electrode placement is crucial.In a 12-lead ECG, there are 12 leads calculated using...
How to Reduce Significant Artifact
A slight ECG artifact is not uncommon. However, you can reduce further interference through the following steps: 1. Switch off non-essential electr...
Color Coding Standards For The 12-Lead ECG
Currently, there are two color coding standards for 12-lead ECG: 1. IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) system 2. AHA (American Heart A...
How to Connect a Monitor to a Desktop Computer - Glenn's SQL Server ...
Introduction For many tech-savvy people, this may seem like an overly basic concept, but it can still be confusing with modern desktop systems. I have gotten a number of recent questions on YouTube, Reddit and Twitter that have prompted this post. So, lets talk about how to connect a monitor to a desktop computer. How
How to connect a monitor to your laptop (Windows 10 and Mac) - Asurion
Learn how to easily connect an external monitor to your laptop and what to do if your computer has trouble detecting it, plus how to use your iPad as a second monitor.
What is ECG monitoring?
ECG monitoring is used in various situations starting from intensive coronary care units, critical care units, post operative wards and during surgical/interventional procedures. ECG monitoring during treadmill exercise test, Holter monitoring and event monitoring are other applications. In each of these situations, there is a need for modifying the leads used for monitoring. In ambulatory monitoring or monitoring during treadmill test, the lead stability and stability of the baseline of the ECG recording during movement of the subject is important. Movement is also an important factor introducing artefacts in the intensive care units, often triggering false alarms. It is less important in the operating environment when the patient is under anaesthesia. But new concerns arise in the operating environment with interference from electrosurgical equipment. Hence different monitoring lead systems are needed for each application. In the earlier era of coronary care units, all standard 12 leads were sometimes used and the patient asked to stay quiet with limb leads on the extremities, to achieve reasonable quality 12 lead monitoring. Several special leads have been developed for specific purposes over the decades. In this brief review, we will discuss the modified monitoring leads and special leads.
Where are the electrodes in the Lund system?
While the limb electrodes are transposed to the torso in Mason-Likar modification, they are placed on the proximal regions of the limbs in the Lund lead system [5]. The advantage is that movement artefacts are reduced as in Mason-Likar system while changes in the 12 lead ECG pattern are lesser and more comparable to standard 12 lead ECG. Hence Lund system can be used both for diagnostic ECG and monitoring [6]. The difference in noise levels on ECG between the Lund system and Mason-Likar system was not significant, though both were better than standard 12 lead, during monitoring [7].
How many leads does EASI use?
EASI lead system uses five electrodes and derives 12 leads by a computer algorithm [10]. In EASI lead system, A, E and I are same as that of Frank vectorcardiographic system [11]. E is located at the lower end of body of sternum. A and I are located in left and right midaxillary lines in the same horizontal level as E. Electrode S is placed on the manubrium sternum (Fig. 2). Ground electrode for the EASI system is on the torso in same location as in Mason-Likar system. Algebraic transfer coefficients are used to generate a derived 12 lead ECG using 5 electrode EASI system [12]. When the EASI system is used for continuous monitoring, excessive artefacts while turning from supine position to right has been documented [13]. This is due to artefacts picked up by the electrode in the right mid axillary line (I). But myoelectric noise in the limb leads during physical activity was lesser with EASI system than Mason-Likar system. It may be noted that derivation of 12 leads from EASI electrodes is an approximation and a 12/12 match with standard 12 lead ECG should not be expected.
What is Lewis lead used for?
Lewis lead (Fig. 3) is used to enhance the recording of atrial activity in the ECG [15]. Originally it was just a modified lead I with right arm electrode placed in second right intercostal space close to sternum and left arm lead placed in fourth right intercostal space close to sterunum. Lewis lead is useful in recognizing P waves during wide QRS tachycardia and thereby aiding an accurate diagnosis [16]. A modification of Lewis lead in which all 12 leads are recorded, with the right arm and left arm electrodes transposed to the original Lewis lead configuration [17]has been used to detect the type of ventriculoatrial conduction during ventricular pacing.
How to use 3 electrodes?
Simple three electrode monitoring uses two electrodes at a time for active monitoring and third one as ground electrode . But the electrodes can be used in different configurations to get lead I, II or III, one at a time. The signal acquisition is bipolar, between the chosen two electrodes for the given lead. The electrodes are placed in such a location as to obtain the required lead, usually on the torso near the corresponding limb. This is to reduce movement artefacts during continuous monitoring and to avoid tethering of the subject. MCL1 lead configuration can be obtained by keeping the right arm electrode in left infraclavicular region and the left arm electrode in the right fourth intercostal space parasternally (V1 location). Ground electrode can be placed in any convenient location away from the active electrodes [1]. Three electrode system was quite common with telemetry monitors.
What is a modified chest lead?
The most commonly used modified chest lead is MCL1 with the configuration mentioned above and lead selector at lead I position. MCL6 will have one active electrode located at V6 position instead. These leads simulate V5 and V6, though not perfectly well. CS5 lead popular in operating rooms has the right arm electrode placed below the right clavicle and left arm electrode placed at V5 location while the left leg electrode acts as ground electrode [2]. Lead selector is at lead I. CS5 is useful in detection of anterior wall myocardial ischemia. In CM5, the right arm electrode is at the manubrium sternum while the remaining configuration is same as CS5. CB5 has the right arm electrode at right scapula and CC5 has it in right anterior axillary line, with similar configuration of other electrodes. CB5 is good for detection of myocardial ischemia and supraventricular arrhythmias.
How many leads are in a computerized regeneration?
6. Computerized regeneration of 12 leads from reduced lead set
What is a lead ECG?
A lead is a glimpse of the electrical activity of the heart from a particular angle. Put simply, a lead is like a perspective. In 12-lead ECG, there are 10 electrodes providing 12 perspectives of the heart's activity using different angles through two electrical planes - vertical and horizontal planes.
Which leads require a positive electrode?
Leads I, II, and III require a negative and positive electrode (bipolarity) for monitoring. On the other hand, the augmented leads-aVR, aVL, and aVF-are unipolar and requires only a positive electrode for monitoring.
Why are there 6 frontal leads?
The Einthoven's triangle explains why there are 6 frontal leads when there are just 4 limb electrodes. The principle behind Einthoven's triangle describes how electrodes RA, LA and LL do not only record the electrical activity of the heart in relation to themselves through the aVR, aVL and aVF leads.
What is an ECG?
What is Electrocardiogram. As a non-invasive yet most valuable diagnostic tool, the 12-lead ECG records the heart's electrical activity as waveforms. When interpreted accurately, an ECG can detect and monitor a host of heart conditions - from arrhythmias to coronary heart disease to electrolyte imbalance. Since the first telecardiogram recorded in ...
Why is it important to place electrodes correctly?
Exact placement of each electrode on the patient is important. Incorrect placement can lead to false or misleading diagnosis.
How many transverse leads are there in the heart?
By using 6 chest electrodes, you get 6 transverse leads that provide information about the heart's horizontal plane: V1, V2, V3, V4, V5, and V6. Like the augmented leads, the transverse leads are unipolar and requires only a positive electrode. The negative pole of all 6 leads is found at the center of the heart.
How many frontal leads are there?
By using 4 limb electrodes, you get 6 frontal leads that provide information about the heart's vertical plane:
Where to place right sided leads?
A complete set of right-sided leads is obtained by placing leads V1-6 in a mirror-image position on the right side of the chest (see diagram, below).
Where to place electrodes for heart?
To get best results – Place electrodes on the chest wall equidistant from the heart (rather than the specific limbs)
What is Lewis lead?
Lewis lead (S5-lead) The Lewis lead configuration can help to detect atrial activity and its relationship to ventricular activity. Named after Welsh cardiologist Sir Thomas Lewis (1881-1945) who first described in 1913. Useful in: Observing flutter waves in atrial flutter.
Which bipolar leads record the atrial potentials?
Instead of regular leads I, II, and III there are now three bipolar chest leads that are termed FI, FII, and FIII which record the potentials developed in the right ventricle, from the infundibulum to the diaphragm. The vertical bipolar lead FI, (similar to aVF) magnifies the atrial potentials and can be used to record:
What are the little lights on a tele monitor?
Most of them have little lights that will cycle through when they are placed right and just around the little lights are color coded rings on a figure of a chest. If you have a light on it isnt making contact. Most tele monitors are like that anyway. Check both sides of the tele transmitter. 1 Likes.
What does the tele box tell you?
I second meownsmile's post. The tele boxes will tell you where to put the leads.
Where is the red electrode in the rib cage?
RA: placed the red electrode within the frame of rib cage,right under the clavicle near shoulder ( see chart in follow picture) LA: the yellow electrode is placed below left clavicle, which is in the same level of the Red electrode.
What is the purpose of an ECG electrode?
ECG Electrodes are small sensor pads (self adhesive,disposable, pre gelled) applied on the skin to enable detection of the electrical activity of the heart, ...
Creating an Account
Create an account if you want to receive leads and invite in users (Collectors) to start collecting.
Creating a User
If you just want to create an Individual User you can do that here; in order to share leads the user has to be linked to an account.
Pricing
The pricing logic of LeadsGO is based on 4 steps (packages) with an entry level Starter subscription at 55 EUR (560 NOK) pr. Month to an Unlimited subscription (call for price). The different packages contain batches of users that can be created for free - but will need to be linked to an Account to be able to exchange leads.
Where should EKG leads be placed?
I asked nurses, EKG technicians, medical assistance, and even cardiology fellows where ECG leads/electrodes should be placed on the patient’s body. Most of the time the answer is “somewhere around here, and they point to areas on the arms, legs, and chest. Additionally, having interpreted tens of thousands ECGs, I have seen significant variations in the electrocardiograms done on the same person, even in the same day.
Where should lead V4 be placed?
Breast tissue can have an impact on the electrocardiogram. As such, the electrode for lead V4 should be placed underneath the breast tissue in women. If necessary, the electrode for lead V5 should also be placed underneath breast tissue.
Where to place lead V5?
To place the electrode for lead V5 start in the intercostal space associated with lead V4 (5th intercostal space) and move to the left to an imaginary line associated with the front portion of the armpit going down toward the anterior hip.
Where is the lead V1?
Placement of Lead V1. Locate the sternal notch (Angle of Louis) by feeling the top portion of the breast bone, and moving your fingers downward until you feel a bump. Move your fingers to the right, off of the bump, and you will feel some soft tissue in between the 2nd and 3rd rib. This is the 2nd intercostal space.
Where do limb leads go?
Limb Lead Placement. Setting up the limb leads is quite simple. They can essentially go anywhere on the limbs, as long as they are place symmetrically and do not go over bone. For example, the right and left arm electrodes can go anywhere between the wrists and the shoulders, but should be symmetrically placed.
Is EKG lead placement done correctly?
Proper Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG) Lead Placement. Although electrocardiograms (ECGs/EKGs) are performed routinely, they are not always done correctly and consistently. As such, I wrote this article to explain proper electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG) set up and lead placement. The goal is to help standardize all ECGs.
Where are the limb leads placed?
Leads I, II, III, aVF, aVL and aVR are all derived using three electrodes, which are placed on the right arm, the left arm and the left leg. Given the electrode placements, in relation to the heart, these leads primarily detect electrical activity in the frontal plane.
What is an ECG lead?
An ECG lead is a graphical description of the electrical activity of the heart and it is created by analysing several electrodes.
How does an electrocardiograph generate an ECG lead?
Figure 16. The electrocardiograph generates an ECG lead by comparing the electrical potential difference in two points in space. In the simplest leads these two points are two electrodes (illustrated in this figure). One electrode serves as exploring electrode (positive) and the other as the reference electrode. The electrocardiograph is constructed such that an electrical current traveling towards the exploring electrode yields a positive deflection, and vice versa.
What is Mason Likar's lead system?
Mason-Likar’s lead system simply implies that the limb electrodes have been relocated to the trunk. This is used in all types of ECG monitoring (arrhythmias, ischemia etc). It is also used for exercise stress testing (as it avoids muscle disturbances from the limbs).
What is the order of the leads in the Cabrera system?
In the Cabrera system, the leads are placed in their anatomical order. The inferior limb leads (II, aVF and III) are juxtaposed, and the same goes for the lateral limb leads and the chest leads. As mentioned earlier, inverting lead aVR into –aVR improves diagnostics additionally.
What is the lateral limb lead?
Lead aVL, I and –aVR are called lateral limb leads, because they primarily observe the lateral wall of the left ventricle. Note that lead aVR differs from lead –aVR (discussed below). All six limb leads are presented in a coordinate system, which the right hand side of Figure 18 (panel A) shows.
Where is the central terminal?
This terminal is a theoretical reference point located approximately in the center of thorax, or more precisely in the centre or Einthoven’s triangle. WCT is computed by connecting all three limb electrodes (via electrical resistance) to one terminal. This terminal will represent the average of the electrical potentials recorded in the limb electrodes. Under ideal circumstances, the sum of these potentials is zero (Kirchoff’s law). WCT serves as the reference point for each of the six electrodes which are placed anteriorly on the chest wall. The chest leads are derived by comparing the electrical potentials in WCT to the potentials recorded by each of the electrodes placed on the chest wall. There are six electrodes on the chest wall and thus six chest leads ( Figure 19 ). Each chest lead offers unique information that cannot be derived mathematically from other leads. Since the exploring electrode and the reference is placed in the horizontal plane, these leads primarily observe vectors moving in that plane.
Where to plug in power cord for monitor?
If not already done, plug the flat end of the monitor power cord (left cable end shown below) into the back of the monitor. The power cord may also be built into the back of the monitor. Plug the other end of the monitor power cord (shown on the right in the above picture) into a power outlet.
Where is the power button on a monitor?
The power button for the button is often found on the front or bottom of the monitor on the right side. If your monitor has different connectors, you may need to switch the input type you're using with the buttons next to the power button.
How to connect a monitor to a computer?
How to connect a monitor. For most monitors, there are two cables included with your monitor. One is the connector cable, for connection between the monitor and the computer. The second is the power cable for connection between the monitor and the power outlet. Find the monitor's connector cable.
What type of connector is used for a flat panel monitor?
There are two types of flat-panel displays available: LCD, and LED. These monitors are very similar and use a VGA, DVI, HDMI, or DisplayPort, or USB-C connector to connect to the computer. VGA and DVI are older connections, whereas HDMI, DisplayPort, and especially USB-C are newer.
How many screws are on a VGA cable?
The VGA and DVI cables have two screws, one on either side of the connector. Make sure the cable screws line up and then alternate turning each screw until they are secure. Tip. If your monitor does not have the same connector as your computer, or you'd prefer a different interface, you have a few options: