Where is the cranium located and what is its function?
The cranium has bones that protect the face and brain The two main parts of the cranium are the cranial roof and the cranial base. Connected to the cranial bones are facial bones that give structure to the face and a place for the facial muscles to attach.
Which bones are part of cranium?
Cranial BonesParietal (2)Temporal (2)Frontal (1)Occipital (1)Ethmoid (1)Sphenoid (1)
Where is the cranium near?
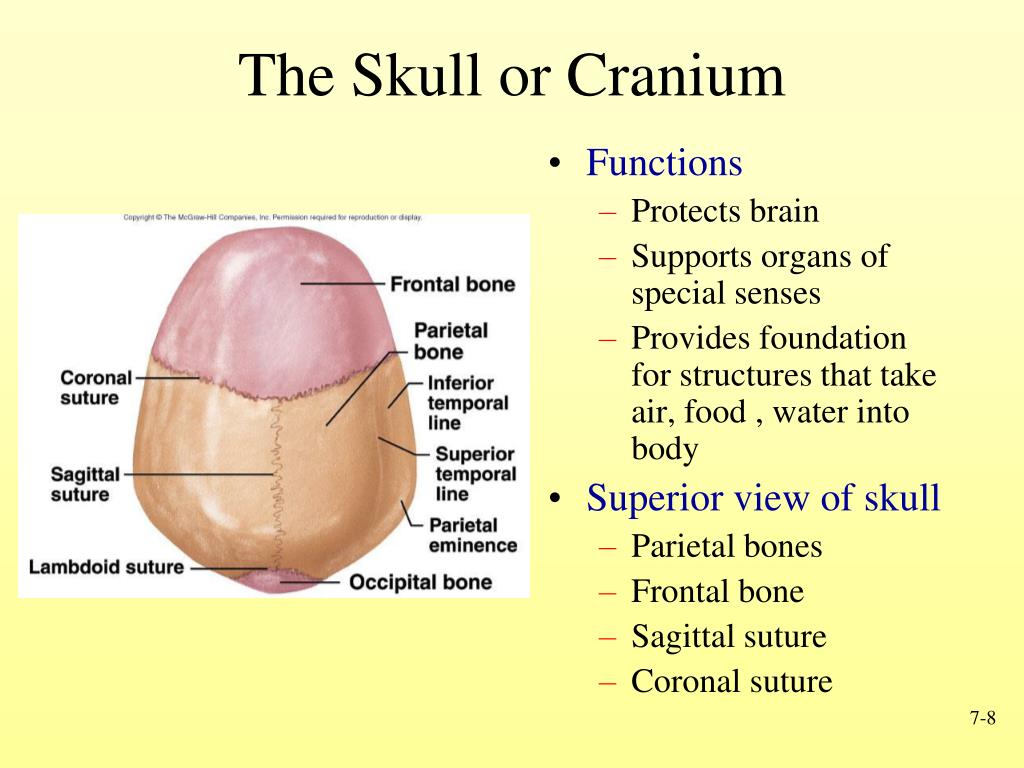
Cranium. The eight bones that protect the brain are called the cranium. The front bone forms the forehead. Two parietal bones form the upper sides of the skull, while two temporal bones form the lower sides.
Does cranium mean head?
Your cranium is your skull, the hard bone of your head that protects your brain from injury. Take care of your cranium; it's your built-in helmet! A skull is made up of a cranium and a mandible, or jaw bone. When you think about the hard top of your head, that's your cranium.
What is a cranium?
(KRAY-nee-um) The bones that form the head. The cranium is made up of cranial bones (bones that surround and protect the brain) and facial bones (bones that form the eye sockets, nose, cheeks, jaw, and other parts of the face). An opening at the base of the cranium is where the spinal cord connects to the brain.
What 8 bones make up the cranium?
The neurocranium is a group of eight bones that form a cover for the brain and brainstem. The 8 cranial bones are the frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones. Some of these are paired bones.
Is the skull the same as the cranium?
Your skull provides structure to your head and face while also protecting your brain. The bones in your skull can be divided into the cranial bones, which form your cranium, and facial bones, which make up your face. There are several types of bones within your body, including: long bones.
What does cranial mean in anatomy?
Superior or cranial - toward the head end of the body; upper (example, the hand is part of the superior extremity). Inferior or caudal - away from the head; lower (example, the foot is part of the inferior extremity).
What is inside cranium?
The cranial cavity, also known as intracranial space, is the space within the skull that accommodates the brain. The skull minus the mandible is called the cranium. The cavity is formed by eight cranial bones known as the neurocranium that in humans includes the skull cap and forms the protective case around the brain.
How many bones are in the cranium?
The skull (also known as cranium) consists of 22 bones which can be subdivided into 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones. The main function of the bones of the skull along with the surrounded meninges, is to provide protection and structure.
What's the back of the head called?
occipital boneThe occipital bone is a bone that covers the back of your head; an area called the occiput. The occipital bone is the only bone in your head that connects with your cervical spine (neck). The occipital bone surrounds a large opening known as the foramen magnum.
What is the difference between cranium and facial bones?
The main difference between skull and cranium is that the skull is composed of both facial bones and the cranium whereas the cranium is the upper part of the skull, composed of bones that do not move....Facial Bones and their Role.Facial BoneRoleVomerForms the posterior part of the nasal septum7 more rows•Aug 6, 2018
How many bones are there in cranium?
eight cranial bonesThe human skull is generally considered to consist of twenty-two bones—eight cranial bones and fourteen facial skeleton bones. In the neurocranium these are the occipital bone, two temporal bones, two parietal bones, the sphenoid, ethmoid and frontal bones.
Which is not a cranial bone?
So, the correct answer is 'Zygomatic bone'.
Diagram of cranial bones
Explore the interactive 3-D diagram below to learn more about the cranial bones.
Cranial bone conditions
Several injuries and health conditions can impact your cranial bones, including fractures and congenital conditions.
Tips for healthy cranial bones
Your cranial bones are the main defense system for your brain, so it’s important to maintain their health by:
The cranium has bones that protect the face and brain
Emily is a health communication consultant, writer, and editor at EVR Creative, specializing in public health research and health promotion.
Anatomy
The cranium is located at the top of the head and is somewhat spherical in shape, like the shape of a baseball cap. It connects to the facial skeleton.
Function
The main function of the cranium is to protect the brain, which includes the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. It also gives a surface for the facial muscles to attach to. 1 The cranium isn't involved with any sort of movement or activity.
Associated Conditions
There are a few categories of conditions associated with the cranium: craniofacial abnormalities, cranial tumors, and cranial fractures.
Treatment
Treatment of cranial injuries depends on the type of injury. For example, some craniofacial abnormalities can be corrected with surgery.
Summary
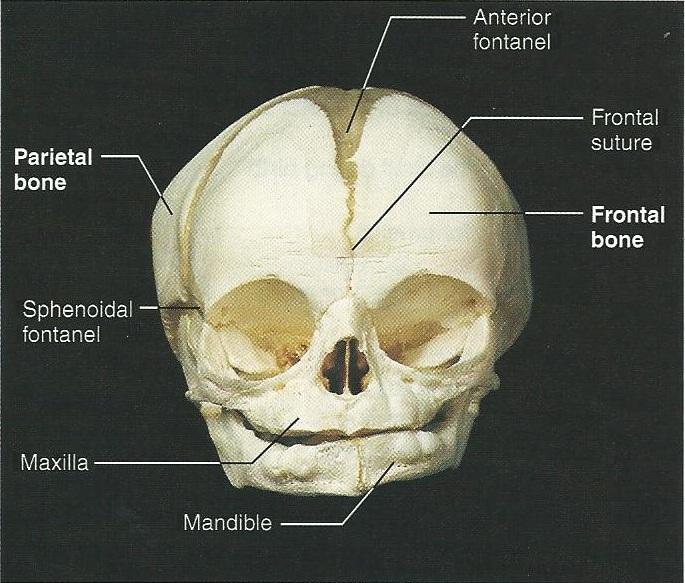
The cranium houses and protects the brain. In infancy, the eight cranial bones are not quite sewn together, which allows for brain growth. Once fused, they help keep the brain out of harm's way. The cranium can be affected by structural abnormalities, tumors, or traumatic injury.
A Word From Verywell
The cranium is like a helmet for the brain. You can further protect your cranium and brain from traumatic injury by using safety equipment such as helmets, seat belts, and harnesses during sports, on the job, and while driving, riding, or taking transportation.
What is the interior of the cranium?
Interior of the cranium. The interior of the cranium shows a multitude of details, reflecting the shapes of the softer structures that are in contact with the bones. The internal surface of the vault is relatively uncomplicated. In the midline front to back, along the sagittal suture, the seam between the two parietal bones, ...
Where is the foramen magnum?
The foramen magnum, the opening through which the brain and the spinal cord make connection, is in the lowest part of the fossa. Between its forward margin and the base of the dorsum sellae is a broad, smooth, bony surface called the clivus (Latin for “hill”).
What is the posterior cranial fossa?
The posterior cranial fossa serves as a bed for the hemispheres of the cerebellum (a mass of brain tissue behind the brain stem and beneath the rear portion of the cerebrum) and for the front and middle portion of the brain stem. Major portions of the brain are thus partially enfolded by the bones of the cranial wall.
Where are the ridges of the dura mater?
Near the foramen magnum are ridges for attachment of folds of the dura mater. In the sides of the posterior cranial fossa are two transverse grooves, each of which, in part of its course, is separated by extremely thin bone from the mastoid air cells in back of the ear.
What are the markings on the internal surface of the bones?
There are openings in the three fossae for the passage of nerves and blood vessels, and the markings on the internal surface of the bones are from the attachments of the brain coverings —the meninges —and venous sinuses and other blood vessels. The anterior cranial fossa shows a crestlike projection in the midline, ...
What bone is attached to the falx cerebri?
On either side of the crest is the cribriform (pierced with small holes) plate of the ethmoid bone, a midline bone important as a part both of the cranium and of the nose.
Where is the pituitary gland located?
The pituitary gland is thus situated in almost the centre of the cranial cavity. It is covered also by the brain coverings and has no connection with the exterior of the cranium except by blood vessels. The deep lateral portions of the middle cranial fossa contain the temporal lobes of the cerebrum.
Where is the base of the skull?
The base of the skull extends from the superior nuchal lines of the occipital bones posteriorly to the upper incisors teeth anteriorly. This aspect of the skull contains a lot of important structures, including the largest skull foramen; the foramen magnum. We can divide this part of the skull into five, to make it easier to study:
What is the skull base?
The skull base is the inferior portion of the neurocranium. Looking at it from the inside it can be subdivided into the anterior, middle and posterior cranial fossae. The skull base comprises parts of the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, occipital and temporal bones.
How many bones are in the occipital bone?
It is formed by four bones; the frontal bone, the two parietal bones, and the occipital bone. These bones articulate through three sutures: The coronal suture: between the frontal and parietal bones. The lambdoid suture: between the occipital and parietal bones. The sagittal suture: between the two parietal bones.
What is the anterior cranial fossa?
The anterior cranial fossa comprises a holey plate at the center, the so called cribriform plate (lamina cribrosa). The approximately 20 cribriform foramina serve as a passageway for the olfactory nerves to the olfactory mucosa in the nasal cavity.
What is the largest opening in the skull?
The largest opening in the skull is the foramen magnum. Here the brainstem leaves the skull and becomes the spinal cord. The foramen magnum is situated in the center of the posterior cranial fossa. It is separated from the middle cranial fossa by the dorsum sellae and the upper edge of the petrous bone.
What are the components of the brain?
Components and features. The braincase consists of the skullcap ( calvarium) and the skull base. The skull cap is made up of the pairs of parietal bones and parts of the frontal bone as well as the occipital bone. The most important sutures in the human skull are:
What is the facial skeleton?
The facial skeleton is referred to as all skull bones anteroinferior to the cranial cavity. Prominent representatives are the maxilla (upper jaw) and the mandible (lower jaw). The orbita and the nasal cavity are formed by the zygomatic, nasal, palatine, lacrimal bones, the vomer and the inferior nasal concha (lower turbinate).
What is the cranium?
The cranium (also known as the neurocranium) is formed by the superior aspect of the skull. It encloses and protects the brain, meninges, and cerebral vasculature. Anatomically, the cranium can be subdivided into a roof and a base: Cranial roof – comprised of the frontal, occipital and two parietal bones.
What is the skull?
Log In. The skull is a bony structure that supports the face and forms a protective cavity for the brain. It is comprised of many bones, which are formed by intramembranous ossification, and joined by sutures (fibrous joints). The bones of the skull can be considered as two groups: those of the cranium ...
What is the pterion of cranial fracture?
When considering cranial fractures, one area of clinical importance is the pterion – a H-shaped junction between the temporal, parietal, frontal, and sphenoid bones.
How many bones are in the cranial base?
Cranial base – comprised of six bones: frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, occipital, parietal and temporal. These bones articulate with the 1st cervical vertebra (atlas), the facial bones, and the mandible (jaw). By TeachMeSeries Ltd (2021) Fig 1 – Bones of the calvarium and cranial base.
Which part of the mouth is the Palatine?
Palatine (2) – situated at the rear of oral cavity and forms part of the hard palate. Maxilla (2) – comprises part of the upper jaw and hard palate. Vomer – forms the posterior aspect of the nasal septum. Mandible (jaw) – articulates with the base of the cranium at the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
What bones are found in the face?
The vomer, palatine and inferior conchae bone s lie deep within the face. caption] [start-clinical] Clinical Relevance: Facial Fractures. Fractures of the facial skeleton are relatively common and most frequently result from road traffic collisions, fist fights, and falls.
What are the bones that make up the nose?
Nasal (2) - two slender bones that are located at the bridge of the nose. Inferior nasal con chae (2) - located within the nasal cavity, these bones increase the surface area of the nasal cavity, thus increasing the amount of inspired air that can come into contact with the cavity walls.
What are the bones of the cranium?
The eight major bones of the cranium are connected by cranial sutures, which are fibrous bands of tissue that resemble seams. The eight major bones of cranium are: 1 Ethmoid bone: a small, rectangular bone inside the cavity of the eye that is located behind the bridge of the nose. 2 Frontal bone: the bone that extends from the forehead to the coronal suture (a suture located at the top of the head that extends from one side to the other) and forms a joint with the parietal bones that allows movement. 3 Occipital bone: the bone that forms the back of the head and connects with the occipital condyles and foramen magnum — skeletal structures located on the underside of the skull, near the spine — and the lambdodial suture, which is at the back of the skull. 4 Parietal bone: the main side of the skull. 5 Sphenoid bone: the bone located under the frontal bone, behind the nose and eye cavities. 6 Temporal bone: the bones that form the inside of the sides of the skull and contain the zygomatic processes (the cheekbone), external auditory meatus (ear canal), styloid process and mastoid process, two points of the temporal bone located behind the ear.
Which bones are located behind the ear?
Temporal bone: the bones that form the inside of the sides of the skull and contain the zygomatic processes (the cheekbone), external auditory meatus (ear canal), styloid process and mastoid process, two points of the temporal bone located behind the ear. The eight auxiliary bones of cranium are: Zygomatic: the cheekbones.
Anatomy
The skull is composed of two parts: the cranium and the mandible.
Function
Drag and drop each name onto the correct bone.
Associated Conditions
Select an answer for each question and see how you did.
Treatment
Summary
- The main function of the cranium is to protect the brain, which includes the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. It also gives a surface for the facial muscles to attach to.1The cranium isn't involved with any sort of movement or activity. The cranial nerves originate inside the cranium and exit through passages in the cranial bones. These nerves are essential to everyday functioni…
A Word from Verywell
- There are a few categories of conditions associated with the cranium: craniofacial abnormalities, cranial tumors, and cranial fractures. Some craniofacial abnormalities result from the skull bones fusing together too soon or in an abnormal way during infancy. For example, craniosynostosis is a condition in which the sutures of a baby’s skull (where you feel the soft spots) close too early, ca…
Frequently Asked Questions
- Treatment of cranial injuries depends on the type of injury. For example, some craniofacial abnormalities can be corrected with surgery. A linear skull fracture, the most common type of skull fracture where the bone is broken but the bone does not move, usually doesn't require more intervention than brief observation in the hospital. As for hematomas caused by fractures, a sev…