
What does the spleen white pulp show?
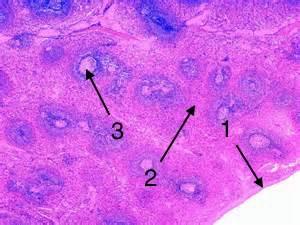
Spleen White Pulp. This section of the white pulp shows a central artery surrounded by peri-arteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS), which is a T-cell zone. It is common to find B-cell lymphoid follicles closely associated with PALSs.
What is the white pulp?
White pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen (named because it appears whiter than the surrounding red pulp on gross section), that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue. White pulp consists entirely of lymphoid tissue. Specifically, the white pulp encompasses several areas with distinct functions:
What is the structure of spleen under light microscope?
In the parenchyma of spleen histology slide, you will find the red pulp and white pulp. Before going to details description of spleen structure I would like to enlist the important structures that you might identify under light microscope. #1. Thick capsule and trabeculae of spleen #2. White pulp area in the section of spleen #3.
What is the splenic pulp made up of?
The splenic pulp is divided into two regions: the red pulps that consist mainly of blood vessels and fibrous strands; and the white pulps that consist of lymphatic tissue. The spleen is a vital organ responsible for filtering out old or damaged red blood cells and removing bacteria and other microorganisms from the blood.
Where is white pulp found?
function in spleen …the red pulp and the white pulp, which do not separate into regions but intermingle and are distributed throughout the spleen. The white pulp is lymphoid tissue that usually surrounds splenic blood vessels.
What is white pulp in spleen?
White pulp contains lymphoid aggregations, mostly lymphocytes, and macrophages which are arranged around the arteries. The lymphocytes are both T (mainly T-helper) and B-cells.
Does the spleen has white pulp associated with the arteries?
Surrounded by a connective tissue capsule, which extends inward to divide the organ into lobules, the spleen consists of two types of tissue called white pulp and red pulp. The white pulp is lymphatic tissue consisting mainly of lymphocytes around arteries.
What do red and white pulp do in the spleen?
Both white and red pulp contains lymphocytes and immune cells called macrophages. These cells dispose of antigens, dead cells, and debris by engulfing and digesting them. While the spleen functions chiefly to filter blood, it also stores red blood cells and platelets.
What does the white pulp of the spleen consist of quizlet?
The white pulp of the spleen contains lymphocytes which monitor the blood for pathogens, and are capable of initiating an immune response.
What tissue is found in the spleen?
The spleen is encased in a thick connective-tissue capsule. Inside, the mass of splenic tissue is of two types, the red pulp and the white pulp, which do not separate into regions but intermingle and are distributed throughout the spleen. The white pulp is lymphoid tissue that usually surrounds splenic blood vessels.
What are the 3 zones of spleen?
In mammals the white pulp of the spleen is composed of three compartments, the periarteriolar lymphatic sheath (PALS), the follicles, and the marginal zone (MZ).
What types of cells are found in the white pulp of the spleen and in the red pulp of the spleen?
Lymphatic vessels have valves, similar to veins, which allow lymph to flow in only one direction. What types of cells are found in the white pulp of the spleen and in the red pulp of the spleen? Lymphocytes are found in the white pulp of the spleen, whereas red blood cells are found in the red pulp of the spleen.
Which type of cells populate the splenic white pulp?
The white pulp is subdivided into the PALS, the follicles, and the marginal zone (Figures 3, 4, and 5). It is composed of lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, plasma cells, arterioles, and capillaries in a reticular framework similar to that found in the red pulp (Saito et al., 1988).
Where is red pulp located?
Red pulp is a loose spongy tissue with chords of reticular cells located between venous sinuses that contains lymphocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and plasma cells.
Which pulp of spleen contains mostly?
The spleen is made of red pulp and white pulp, separated by the marginal zone; 76-79% of a normal spleen is red pulp. Unlike white pulp, which mainly contains lymphocytes such as T cells, red pulp is made up of several different types of blood cells, including platelets, granulocytes, red blood cells, and plasma.
What is found in the red pulp of the spleen?
The red pulp makes up roughly 80% of the spleen parenchyma. It is separated from the white pulp by the marginal zone. The red pulp is primarily made up of tissue known as the cords, which is rich in macrophages, and the venous sinus.
What is the role of the white pulp?
Because of this, the white pulp of the spleen has a very important role in the normal immune response to infection. Antigen presenting cells may enter the white pulp, resulting in activation of the T-lymphocytes stored there.
What is the function of the white pulp of the spleen quizlet?
The white pulp of the spleen contains lymphocytes which monitor the blood for pathogens, and are capable of initiating an immune response.
How do the white pulp and red pulp of the spleen differ with respect to both cell population and function?
The white pulp mounts an immune response when needed, while the red pulp serves as a reservoir for blood as well as phagocytize aged erythrocytes and platelets.
Which type of cells populate the splenic white pulp?
Splenic white pulp is organized around central arteries in the form of PALS, which are populated primarily by T lymphocytes (see Figs. 13-38, 13-39, and 13-40). Primary splenic follicles are located eccentrically in PALS and are primarily composed of B lymphocytes.
What does the spleen's white pulp make?
White pulp is a substance found in the immune system (lymphatic tissue) that is mostly composed of white blood cells. The red pulp is made up of bl...
Do lymph nodes have red and white pulp?
Lymphoid aggregations, predominantly lymphocytes and macrophages, are found in white pulp and are organized around the arteries. T (mostly T-helper...
What cells make up the spleen?
The white pulp is separated into three sections: the PALS, the follicles, and the peripheral zone (Figures 3, 4, and 5). Lymphocytes, macrophages,...
What fibers are found in the spleen?
A three-dimensional meshwork of splenic cords and venous sinuses makes up the crimson pulp. The splenic cords are made up of reticular fibers, reti...
What does white pulp do?
Lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate in the white pulp. These cells are then discharged into the circulation after migrating from the marginal...
What is the structure of the spleen?
Structure. Being an intraperitoneal organ, the spleen is covered by a layer of visceral peritoneum. Underneath the peritoneum is the capsule of the spleen, encasing its parenchyma. The capsule of the spleen consists of dense irregular fibroelastic tissue.
What is the spleen made of?
Like every other organ, the spleen consists of stroma and parenchyma. The stroma of the spleen is composed mainly of a network of reticular connective tissue. This mesh provides support for blood cells and cells of the immune system (lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells).
How long is the reading time for a spleen slide?
Reading time: 13 minutes. Spleen histology slide (labeled) The spleen is a fist sized organ located in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen. It is the largest lymphoid organ and thus the largest filter of blood in the human body. The spleen has a unique location, embryological development and histological structure that differs significantly ...
Why is the spleen important?
It can detect and present specific pathogens in the blood and produce an immune response to defend the body against them. The specific structure of the spleen makes it a key spot for defense against encapsulated bacteria. This is why people without a spleen are predisposed for some bacterial infections like pneumonia.
Why is the spleen considered a graveyard for red blood cells?
It is considered a "graveyard for red blood cells" because it removes old and damaged erythrocytes from circulation. This function is mostly due to the unique structure of the blood vessels and macrophages present in the red pulp.
Why are there gaps in the blood?
Due to the lack of junctions, there are wide gaps between the cells that serve as a mechanical filter between the blood and splenic cords. When different antigens (e.g. microorganisms, cellular debris and aged and damaged erythrocytes) cross these gaps they can be phagocytosed and destroyed by macrophages that are waiting on the other side. This type of blood flow is called open circulation which is characteristic for human spleen. In some species (e.g. rodents), the blood from sheathed capillaries enters venous sinuses directly. This is known as closed circulation.
Where are splenic sinusoids found?
Splenic sinusoids are found between the cords of Billroth. They are filled with blood and give the red pulp its distinguishable red appearance. Blood slowly flows through the sinusoids where it is exposed to macrophages from the cords of Billroth, patiently waiting for foreign antigens that can appear in the blood.
What is the white pulp in the spleen?from britannica.com
The white pulp is lymphoid tissue that usually surrounds splenic blood vessels.
Where is the spleen located?from teachmephysiology.com
Figure 1. The spleen. (a): Orientation of the human spleen (arrow) in the abdomen, directly positioned against the stomach. The splenic artery stems directly from the aorta, the collecting vein joins the portal blood supply of the liver. (b): Section of a rat spleen stained with methylgreen pyronin showing the prominent marginal zone of rodent spleen. (c): Section of a rat spleen stained for the presence of IgM-bearing B cells. This way the follicles and marginal zone with the marginal zone B cells can be easily discerned. Note the aggregates of plasma cells in the red pulp staining intensely for IgM. (d): Section of a rat spleen stained for the enzyme acid phosphatase. Macrophages abundantly express this enzyme and all red cells represent macrophages. Note the large numbers of macrophages in the red pulp and the conspicuous ring of marginal metallophilic macrophages at the border of white pulp and marginal zone (arrows). WP: white pulp; RP: red pulp; MZ: marginal zone; F: B cell follicle; P: PALS (periarteriolar lymphocyte sheath).
How are collagen fibers produced?from sciencedirect.com
The fibers are produced by FRCs, the lymphoid organ stromal cell, which surround the extracel lular matrix components they produce. This way a highly organized collagen fiber network is formed, consisting of 20–200 parallel bundles, up to 1 μm in diameter, of mostly type I and type III collagen fibers. The reticular cells are connected to form a three-dimensional reticulum, much like a sponge, whereby lymphoid cells fill up the spaces of this network. The complete circular ensheathment of the collagen bundles by a basement membrane forms a tube, which is the most important feature of the conduit system, with its molecular sieve probably based on the meshwork formed by collagen and connecting fibrils and associated glycosaminoglycans ( Sixt et al., 2005 ). Lymphocytes are not in contact with the constituents of the basement membrane and will have to move directly over the cell membrane of the FRC. This is facilitated by the presence of collage IV on the outer cell membrane of the FRC. Collagen IV can bind and present several chemokines including CCL21 and CCL13 and may thereby play an important role in the movement of lymphocytes across the reticulum. DCs are able to gain access to the contents of the conduit via small gaps between FRC by extending processes through the basement membrane.
How to assess spleen size?from teachmephysiology.com
To assess the size of the spleen, a patient’s abdomen should be palpated diagonally from right iliac fossa (RIF) to LUQ as it tends to enlarge towards the RIF. Underlying cause for the splenomegaly should be treated and in some cases a splenectomy (removing the spleen) may be suggested.
Why does my spleen feel so big?from my.clevelandclinic.org
Splenomegaly is a dangerous condition because the spleen can rupture (tear) or bleed.
Why is splenomegaly dangerous?from my.clevelandclinic.org
Splenomegaly is a dangerous condition because the spleen can rupture (tear) or bleed. The spleen can become enlarged from: Blood cancers, such as leukemia and Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and cancer in other parts of the body that metastasize (spread) to the spleen. Blood clots in the spleen or the liver.
What is white pulp?from en.wikipedia.org
White pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen (named because it appears whiter than the surrounding red pulp on gross section), that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue. White pulp consists entirely of lymphoid tissue . Specifically, the white pulp encompasses several areas ...
Do lymph nodes have red and white pulp?
Lymphoid aggregations, predominantly lymphocytes and macrophages, are found in white pulp and are organized around the arteries. T (mostly T-helper) and B-cell lymphocytes are present. Red pulp is vascular, with parencyhma and many vascular sinuses. There are also areas where the white pulp appears to be absent, such as in the spleen.
What cells make up the spleen?
The white pulp is separated into three sections: the PALS, the follicles, and the peripheral zone (Figures 3, 4, and 5). Lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, plasma cells, arterioles, and capillaries are arranged in a reticular framework similar to that of the red pulp (Saito et al., 1988). The marginal zone is located next to the white pulp.
What fibers are found in the spleen?
A three-dimensional meshwork of splenic cords and venous sinuses makes up the crimson pulp. The splenic cords are made up of reticular fibers, reticular cells, and macrophages (Saito et al., 1988). The macrophages contain large amounts of iron heme that gives them their red color.
What does white pulp do?
Lymphocytes proliferate and differentiate in the white pulp. These cells are then discharged into the circulation after migrating from the marginal zone into the red pulp venous sinusoids. It also plays a crucial function in the body's immunological defense. It is made up of a large number of T and B lymphocytes as well as phagocytic immune cells.
What is the white pulp of the spleen?
(Lymphatic nodule labeled at center right.) White pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen (named because it appears whiter than the surrounding red pul p on gross section), that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue.
Where are the white pulp cells located?
It is located farther away from the central arteriole, in proximity to the red pulp. It contains antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells and macrophages. Some of the white pulp's macrophages are of a specialized kind known as metallophilic macrophages.
What is white pulp?
White pulp is a histological designation for regions of the spleen (named because it appears whiter than the surrounding red pulp on gross section), that encompasses approximately 25% of splenic tissue. White pulp consists entirely of lymphoid tissue . Specifically, the white pulp encompasses several areas ...
Where are the periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths located?
Lymph follicles with dividing B lymphocytes are located between the PALS and the marginal zone bordering on the red pulp. IgM and IgG2 are produced in this zone.
Where are macrophages found?
This population of macrophages can be found in all the other T cell zones of the secondary lymphoid organs. It is possible that these macrophages are descendants of patrolling monocytes that entered the white pulp from the blood.
What kind of pulp does the spleen contain?
The spleen contains two main types of tissue – white pulp and red pulp. White pulp is material which is part of the immune system (lymphatic tissue) mainly made up of white blood cells. Red pulp is made up of blood-filled cavities (venous sinuses) and splenic cords.
Are lymphocytes in red pulp?
Red pulp is a loose spongy tissue with chords of reticular cells located between venous sinuses that contains lymphocytes, macrophages, granulocytes, and plasma cells.
How do lymphocytes enter the spleen?
While antigen can reach lymph nodes via afferent lymphatics, either taken up by dendritic cells or by drainage in lymph fluid, lymphocytes enter this organ via the specialized high endothelial venules (HEV).
How are lymphocytes produced in the spleen and liver?
Lymphocytes in the spleen react to pathogens in the blood and attempt to destroy them. Macrophages then engulf the resulting debris, the damaged cells, and the other large particles. The spleen, along with the liver, removes old and damaged erythrocytes from the circulating blood. Like other lymphatic tissue, it produces lymphocytes,…
