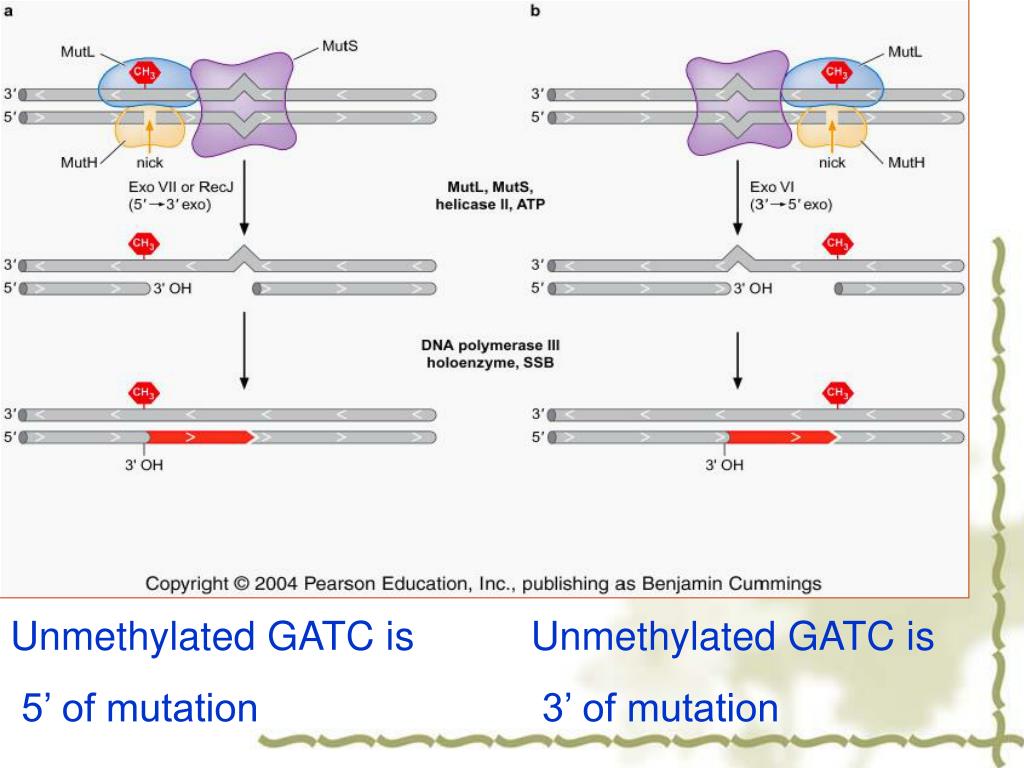
Spontaneous mutations occur without mutation induction and are the result of errors during DNA replication. When DNA Pol III synthesizes a new strand of DNA, occasionally, a nucleotide will be mispaired, added, or omitted.[4] Thus, a point mutation will occur.
What is the difference between spontaneous and induced mutations?
The key difference between spontaneous and induced mutations is the causative agents of these mutations. Thus, spontaneous mutations are unpredictable changes in the DNA caused due to errors in replication, whereas, induced mutations are caused by physical, chemical or biological agents. 1. Overview and Key Difference 2.
Do mutations have a positive effect on an organism?
Some mutations — known as beneficial mutations — have a positive effect on the organism in which they occur. They generally code for new versions of proteins that help organisms adapt to their environment.
Can mutations occur spontaneously?
Some acquired mutations occur spontaneously and randomly in genes. Other mutations are caused by environmental factors, such as exposure to certain chemicals or radiation. Mutations occur throughout the natural world.
Is mutation an evolution or a disease?
Mutations can lead to missing or malformed proteins, and that can lead to disease. We all start out our lives with some mutations. These mutations inherited from your parents are called germ-line mutations. However, you can also acquire mutations during your lifetime. Some mutations happen during cell division, when DNA gets duplicated.

How do spontaneous mutations occur?
Spontaneous mutations are mutations that occur in the absence of exogenous agents. They may be due to errors made by DNA polymerases during replication or repair, errors made during recombination, the movement of genetic elements, or spontaneously occurring DNA damage.
What is responsible for spontaneous mutation?
Spontaneous mutations are "the net result of all that can go wrong with DNA during the life cycle of an organism" (Glickman et al., 1986). Thus, the types and amounts of spontaneous mutations produced are the resultant of all the cellular processes that are mutagenic and those that are antimutagenic.
What causes spontaneous and induced mutations?
Spontaneous mutations, as the name suggests, are mutations that occur randomly due to errors in the replication of DNA, which is a natural biological process. They do not occur as a result of stimuli or environmental factors. Induced mutations occur when DNA is exposed to an agent that causes mutations.
Do spontaneous mutations occur naturally?
Spontaneous mutations occur naturally in the genome. They generally occur due to error during replication, mitosis, meiosis, etc. Mutations may also occur due to mobile genetic elements or transposons.
What causes a spontaneous mutation in a gene quizlet?
Spontaneous mutations are a result of an error in DNA replication or mobile genetic elements. Induced mutations are caused by agents that damage DNA in some way.
What is spontaneous mutation simple?
A 'naturally' occurring mutation in the absence of a mutagen that would otherwise be a known factor for inducing a particular mutation.
How common are spontaneous mutations?
Data from several studies on eukaryotic organisms shows that in general the spontaneous mutation rate is 2-12 x 10-6 mutations per gamete per gene.
Can gene mutations arise spontaneously?
Mutations occur spontaneously in all living things. By changing the chemistry of the organism's genetic material or altering the structure of a chromosome a mutation changes die structure or function of the organism and its offspring. Most often the mutation is harmful, and the change is erased by natural selection.
What factors influence the rate of spontaneous mutation?
Both the nature of the gene and its environment can influence the mutation rate. The size of the gene, its base composition, its position in the genome, and whether or not it is being actively transcribed influence its mutation rate.
Are spontaneous mutations caused by mutagens?
Spontaneous mutation, also known as background mutation, can be defined as genetic changes that occur in the absence of mutagens and have no known cause. It may result from activities of a normal cell, such as mistakes or errors during DNA replication.
Which agents are responsible for mutation?
The chemical or physical agents that cause mutations are called mutagens. Examples of physical mutagens are ultraviolet (UV) and gamma radiation. Radiation exerts its mutagenic effect either directly or by creating free radicals that in turn have mutagenic effects.
What base is responsible for hot spots for spontaneous mutation?
So, the correct answer is '5-bromouracil'.
What is the use of induced mutation?
Geneticists utilize induced mutation to create mutants that help understand the effects of mutation on the phenotype of cells. It is also employed...
What is induced mutation?
An induced mutation is the type of mutation that occurs once an organism's DNA is exposed to a mutagen. Mutagens can be physical or chemical agents.
What is an example of induced mutation?
An example of induced mutation is a change of sex cell genes. The exposure of the gonads to mutagens such as radiation leads to mutation of the sex...
What causes a spontaneous mutation?
Spontaneous mutation occurs naturally with no known cause. However, it may arise from the activities of a normal cell, such as errors that occur du...
What is spontaneous mutation in microbiology?
A spontaneous mutation is a type of mutation that occurs naturally, in the absence of mutagens. Mutagens are agents that cause mutation, such as x-...
What are some examples of spontaneous mutations in mice?
Spontaneous mutations in mice may result in benign phenotypes, such as variable coat colors, or in disorders that have similarities to diseases in man, for example, the hyperphosphatemia (Hyp) mouse, which is representative of X-linked hyperphosphatemia in man. 59 Such spontaneous mutations occur at very-low frequencies, thus several techniques that increase the rate of mutation induction in the mouse genome by either nontargeted (random) or targeted strategies have been developed ( Tables 7.1 and 7.2). An early example of nontargeted mutagenesis is provided by irradiation, which generated the Gy mouse, a second model for X-linked hypophosphatemia.59 More recently, chemical mutagens have been used in large-scale mutagenesis programs. Successful agents include isopropyl methane sulfonate (iPMS) used to generate the Nuf mouse model with an activating calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) mutation, and N -ethyl- N-nitrosourea (ENU) used to generate a mouse model for osteogenesis imperfecta with a collagen 1 alpha 1 (COL1A1) mutation. ENU, which is an alkylating agent that primarily introduces point mutations via transfer of the ENU alkyl group to the DNA base followed by mispairing and subsequent basepair substitution during the next round of DNA replication (Fig. 7.1 A ), is the most potent mutagen in mice.14 Intraperitoneal injections of ENU to male mice generate approximately one mutation per 1–1.5 Mbp of sperm DNA,14 which allows the mutations to be inherited ( Fig. 7.1 B). ENU mutagenesis programs utilize two complementary approaches, which are phenotype-driven and genotype-driven screens. In phenotype-driven screens, the offspring of mutagenized mice are assessed for phenotypic variances, using a panel of morphological, biochemical, or behavioral tests, in a “hypothesis-generating” strategy, which aims to elucidate new genes, pathways, and mechanisms for a disease phenotype 14 ( Fig. 7.1 B). By establishing appropriate matings, phenotype-driven screens can be used to identify dominant or recessive phenotypes. Genotype-driven screens, in which mutations in a gene of interest are sought, are “hypothesis driven” and are feasible by using available parallel archives of DNA and sperm samples from mutagenized male mice ( Fig. 7.1 B). Archived DNA samples from the mutagenized male mice are used to search for mutations in the gene of interest, and once mutations are identified in the mouse DNA, then the corresponding sperm sample for the male mouse harboring the mutation is used to establish progeny carrying the mutation by in vitro fertilization. 14 It is estimated that the probability of finding three or more mutant alleles in an archive of >5000 DNA samples is >90%. 60 Thus, the gene-driven approach can be used to generate an “allelic series” of mutations within one gene, which may yield insights into genotype–phenotype correlations in the gene and disease of interest.61
Why are cog mice unable to produce TH?
Therefore, cog mice receive the pituitary TSH signal to produce and secrete TH, but are unable to produce TH efficiently due to a defect in the Tgn gene. These examples of spontaneous mouse mutations involve the endocrine axis regulating growth. lit, df, and dw are pituitary defects; hyt and cog are thyroid defects.
How do mutagens affect DNA?
Several new mutagens, both physical and chemical, have since been used after the early use of X-rays, radium and UV rays for generating genetic variability. Their mechanism of action at the level of the DNA can vary from single point mutations or base changes to large deletions involving several megabases (large numbers of DNA base pairs). Next-generation genomics technologies have allowed, most recently, the deciphering of the effects of different mutagen sources on the DNA. The use of these various mutagens has given rise to the induction of a wide range of mutations in plant species, several of which have been used in fundamental studies to establish gene-to-phenotype relationships. Mutation studies in the model plant species, Arabidopsis thaliana, a small flowering plant with a small and simple-structured genome (2n = 10; ∼ 120 Mb; few repeats) and the first plant to be fully sequenced, has yielded significant amounts of information over the last 50 years on the molecular biology of plants. These studies also shed light on genes involved in numerous biochemical and hormonal pathways, and morphological and physiological traits. More important, however, has been the use of induced mutations in practical plant breeding for the development of new and improved crop varieties for wide cultivation by farmers.
What is a lit mouse?
The little ( lit) mouse mutation is an autosomal recessive mutation resulting in proportionate dwarfism visible at 2 weeks of age. Adult lit mice have a body weight two-thirds the size of control littermates. Female mice are fertile but often fail to nurse their first litters, whereas male mice have reduced fertility.
What is the mutation in a rat?
A spontaneous mutation was observed in an inbred, albino rat that developed polycystic lesions in the liver as well as the kidneys and that has an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance (Lager et al., 2001 ). The mutation occurred in a colony of CRJ: CD (SD) BR rats in Japan, and the rats develop congenital intrahepatic biliary dilatation associated with congenital hepatic fibrosis. The lesions found in this model are similar to those seen in humans with Caroli's disease ( Sanzen et al., 2001 ). Genetic analysis has shown the polycystic kidney rat model to be orthologous to the autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease that occurs in man ( Harris, 2002 ).
What is G1 male?
G1 males are examined for phenotypic abnormalities (i.e., the phenotype-driven screens). Males with phenotypic abnormalities of interest are then mated with wild-type females to facilitate inheritance testing and genetic mapping in affected offspring (G2) to identify the mutation causing the phenotypic abnormality.
What is a spontaneous mutation?
Spontaneous mutations are alleles of initially unknown genes and are given allele names and symbols based on their phenotype (e.g. diabetes, db). Recessive mutations (i.e. requiring two copies of the mutated allele to manifest the phenotype) are represented by all lower-case letters while dominant (i.e. one or two copies of the mutated allele produces the phenotype) and semidominant (i.e. one mutant allele produces an intermediate phenotype) spontaneous mutations are represented by an upper-case first letter, followed by lower-case letters. Once the gene responsible for the mutant phenotype has been identified, the allele symbol is superscripted to an approved gene symbol (e.g. the diabetes mutation is a point mutation in the leptin receptor gene, Leprdb ). The Mouse Genomic Database Nomenclature Committee approves and assigns gene names and symbols, which may be registered online ( http://www.informatics.jax.org) or requested by email ( [email protected] ). Gene names and symbols may change as the function of a gene is better understood or to better correspond with gene symbols of other species (primarily human).
Abstract
SPONTANEOUS mutations are generally supposed to be induced by some unknown external agent. However, it may be expected that mutation is influenced also by certain intracellular processes which develop automatically and may be created or accelerated by artificial means (for example, by X-rays).
Author information
Timiriazev Biological Institute, Laboratory of Cytogenetics, Moscow, U.S.S.R.
What is an example of a spontaneous mutation that stuck around to future generations?
Sickle cell anemia is an example of a spontaneous mutation that stuck around to future generations because it is occasionally beneficial. The other type of mutation is induced mutation. These are purposefully started by exposing living tissue to mutagenic agents.
How does evolution happen?
One way that evolution proceeds is through mutation, and there are two overarching types of mutations. The first is spontaneous mutation. This type occurs naturally, and it is infrequent and unpredictable. It might be affected by several different naturally occurring mutagenic agents, such as UV rays or heat. Sickle cell anemia is an example of a spontaneous mutation that stuck around to future generations because it is occasionally beneficial. The other type of mutation is induced mutation. These are purposefully started by exposing living tissue to mutagenic agents. Physical agents include X-rays and UV rays, while chemical agents include mustard gas and formaldehyde. Point mutations are most common with induced mutations, especially those done with chemical agents. Point mutations happen when one half of a base DNA pair is changed. Deletion, where part of a chromosome is removed, might also occur. Fruit flies are used to study both types of mutation because they have very short life spans, so the effect of mutation is easily observable across generations.
Why are spontaneous mutations not reliable?
Due to their infrequent and unpredictable nature, spontaneous mutations are not a reliable source for scientists who want to study mutations and how they work. Induced mutations are a solution to this issue. Induced mutations are purposefully started (they are induced) by exposing living tissue to mutagenic agents.
What are the causes of spontaneous mutations?
There are several factors that can influence spontaneous mutation. These include natural sources of radiation, such as UV rays from the sun. Heat can also cause mutation. Sources that can cause mutations are known as mutagenic agents.
How are mutations induced?
Mutations can be induced using physical agents, such as X-rays or UV rays, or chemical agents , such as mustard gas and formaldehyde.
What are the two types of mutations in fruit flies?
Fruit flies have been studied as part of both of the two main types of mutation: spontaneous mutation, which occurs naturally, and induced mutation, which is purposefully set in motion by humans. You must c C reate an account to continue watching. Register to view this lesson.
Why are spontaneous mutations called spontaneous mutations?
Spontaneous Mutation. Spontaneous mutations get their name because they are unpredictable. New spontaneous mutations are not particularly frequent, and scientists are not sure exactly how they work or what causes them. These mutations occur naturally, without human interference.
What is a mutation in a genome?
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a short region of a genome, and phenotypic results may vary on the severity and location of the mutation. Mutations can result from errors during DNA replication or induced by exposure to mutagens (like chemicals and radiation). Spontaneous mutations occur at a rate of 1 in 10^5 to 10^8 and contribute to random population variation.[3] Since bacteria are haploid for the majority of their genes and have short generation turnover, phenotypic variation due to point mutations can occur relatively quickly.
What is the function of a gene in bacteria?
Bacterial genes with similar functions often share one promoter (RNA polymerase binding site) and are transcribed simultan eously; this system is called an operon. Typical operons consist of several structural genes that code for the enzymes required for the pathway. Regulation occurs through transcription factors binding to a short sequence of DNA between the promoter region and the structural genes called an operator. [2]
What are the elements that contribute to recombination?
Elements like plasmids, transposons, integrons, or gene cassettes are shorter sequences that mainly contribute to recombination events. Bacterial DNA replication and transcription co-occur and utilize the same template DNA. Replication forks proceed bi-directionally with a single origin of replication, OriC.
How does alkylation affect nucleotide base?
However, alkylation can cause crosslink formation, which inhibits replication.
What is NCBI bookshelf?
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Why do amino acid substitutions change protein structure?
More specifically, non-synonymous amino acid substitutions produce dramatic changes in protein structures because of the chemical dis-similarities of the mutated strand amino acid. However, there are inherent protections against these types of mutations. The redundancy of codon translation mechanisms and the occurrence of non-coding regions result in few mutations expressing phenotypically. [10]
What happens to a nucleotide when it is mispaired?
For example, when nucleotides are mispaired, it will appear that one nucleotide substitutes for another leading to one mutated granddaughter DNA strand . Two separate malfunctions must happen in the bacteria's DNA replication machinery for this to occur:[5]
