How do organisms use matter and energy? The matter is digested into raw materials that are used to build structures and repair damaged body parts. The breakdown of also releases energy that can be used for life processes, such as motion to find more things to eat.
How do matter and energy flow through an organism?
Through cellular respiration, matter and energy flow through different organizational levels of an organism as elements are recombined to form different products and transfer energy By the end of grade 2. All animals need food in order to live and grow.
Why do organisms need matter to live?
What complicates understanding is that matter is needed in two ways (Fig. 1): (1) materially, providing the materials that become part of the larger organism: organisms are made of carbohydrates, (2) energetically, because energy can be made available as matter is rearranged, e.g., converting carbohydrates and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water.
What are the activities that define organisms?
One of the activities that define organisms is that at some point in their life, or throughout it, they grow. Growth requires the acquisition of matter and both the acquisition of matter and the incorporation of this material into a living form (i.e., into biomolecules) involves energy.
How does life sustain itself?
Sustaining life requires substantial energy and matter inputs. The complex structural organization of organisms accommodates the capture, transformation, transport, release, and elimination of the matter and energy needed to sustain them.

How are energy and matter transferred between organisms and their environment?
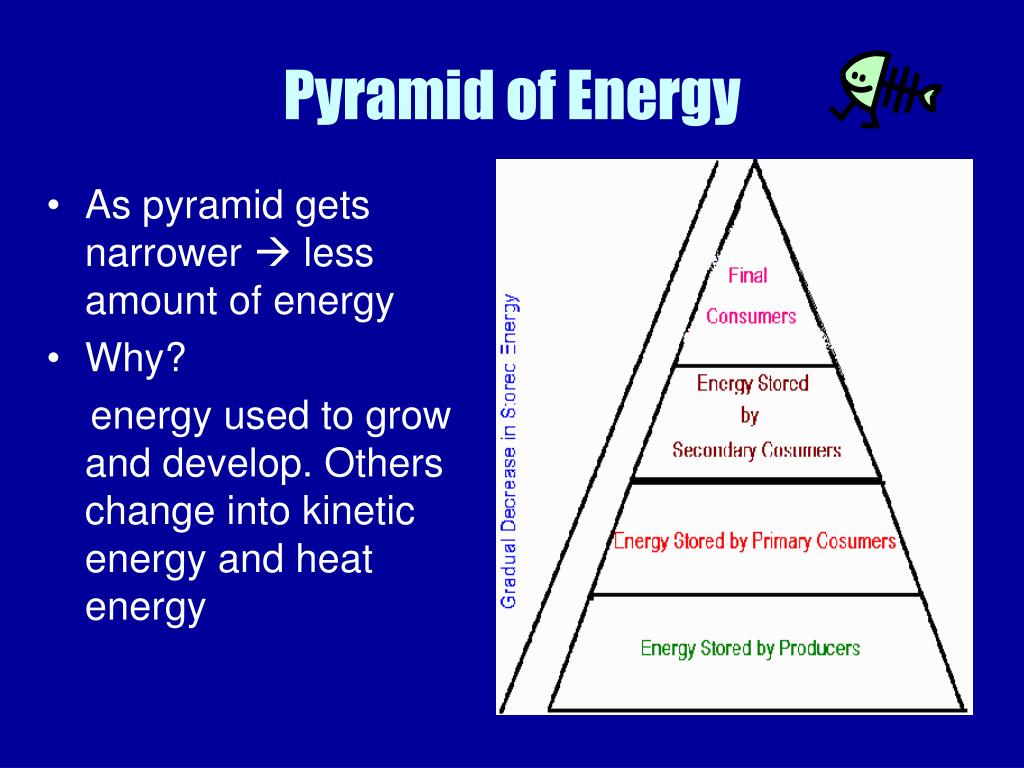
In ecosystems, matter and energy are transferred from one form to another. Matter refers to all of the living and nonliving things in that environment. Nutrients and living matter are passed from producers to consumers, then broken down by decomposers. Decomposers break down dead plant and animal matter.
How do living organisms store energy and matter within themselves?
Food is composed of molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms as energy stored in the molecules is released and used. The breakdown of food molecules enables cells to store energy in new molecules that are used to carry out the many functions of the cell and thus the organism.
How do organisms obtain and use matter and energy they need to live and grow?
Food provides animals with the materials and energy they need for body repair, growth, warmth, and motion. Plants acquire material for growth chiefly from air, water, and process matter and obtain energy from sunlight, which is used to maintain conditions necessary for survival.
How is energy used in a living organism?
Inside every cell of all living things, energy is needed to carry out life processes. Energy is required to break down and build up molecules, and to transport many molecules across plasma membranes. All of life's work needs energy. A lot of energy is also simply lost to the environment as heat.
How do organisms capture and store energy?
Sunlight is converted to chemical energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the main energy-storing molecule in living organisms. ATP is then transported throughout the chloroplast and used to provide the chemical energy necessary to power other metabolic reactions.
How do living organisms maintain themselves?
Organisms are able to maintain internal conditions within a narrow range almost constantly, despite environmental changes, through a process called homeostasis or “steady state”—the ability of an organism to maintain constant internal conditions.
What organisms can store their own energy?
Algae, along with plants and some bacteria and fungi, are autotrophs. Autotrophs are the producers in the food chain, meaning they create their own nutrients and energy.
What do organisms use to store and transport energy?
Organisms mainly use the molecules glucose and ATP for energy. Glucose is a compact, stable form of energy that is carried in the blood and taken up by cells. ATP contains less energy and is used to power cell processes. The flow of energy through living things begins with photosynthesis, which creates glucose.
What are the hydrocarbons produced in photosynthesis?
The hydrocarbon backbones of sugars produced through photosynthesis are used to make amino acids and other molecules that can be assembled into proteins or DNA. Through cellular respiration, matter and energy flow through different organizational levels of an organism as elements are recombined to form different products and transfer energy.
What do plants use to make sugar?
By the end of grade 8. Plants, algae (including phytoplankton), and many microorganisms use the energy from light to make sugars (food) from carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water through the process of photosynthesis, which also releases oxygen. These sugars can be used immediately or stored for growth or later use.
What chemical reaction does oxygen produce?
In most animals and plants, oxygen reacts with carbon-containing molecules (sugars) to provide energy and produce carbon dioxide; anaerobic bacteria achieve their energy needs in other chemical processes that do not require oxygen. By the end of grade 12.
How do plants use energy?
Plants use the energy from light to make sugars through photosynthesis. Within individual organisms, food is broken down through a series of chemical reactions that rearrange molecules and release energy. The hydrocarbon backbones of sugars produced through photosynthesis are used to make amino acids and other molecules ...
What are sugar molecules made of?
The sugar molecules thus formed contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen ; their hydrocarbon backbones are used to make amino acids and other carbon-based molecules that can be assembled into larger molecules (such as proteins or DNA), used for example to form new cells.
How do matter and energy flow through a living system?
As matter and energy flow through different organizational levels—cells, tissues, organs, organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems—of living systems, chemical elements are recombined in different ways to form different products. The result of these chemical reactions is that energy is transferred from one system ...
How do animals get food?
Animals obtain food from eating plants or eating other animals. Within individual organisms, food moves through a series of chemical reactions in which it is broken down and rearranged to form new molecules, to support growth, or to release energy. In most animals and plants, oxygen reacts with carbon-containing molecules (sugars) ...
What is the function of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration also releases the energy needed to maintain body temperature despite ongoing energy loss to the surrounding environment. Matter and energy are conserved in each change. This is true of all biological systems, from individual cells to ecosystems.
What are sugar molecules made of?
The sugar molecules thus formed contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen ; their hydrocarbon backbones are used to make amino acids and other carbon-based molecules that can be assembled into larger molecules (such as proteins or DNA), used for example to form new cells.
How do matter and energy flow through different organizational levels of living systems?
As matter and energy flow through different organizational levels of living systems, chemical elements are recombined in different ways to form different products. As a result of these chemical reactions, energy is transferred from one system of interacting molecules to another.
What do plants use to make food?
By the end of grade 8. Plants, algae (including phytoplankton), and many microorganisms use the energy from light to make sugars (food) from carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water through the process of photosynthesis, which also releases oxygen.
How do plants get their material?
Plants acquire their material for growth chiefly from air and water. (5-LS1-1) Plants, algae (including phytoplankton), and many microorganisms use the energy from light to make sugars (food) from carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water through the process of photosynthesis, which also releases oxygen. These sugars can be used immediately ...
What do plants need to live?
Plants need water and light to live and grow. (K-LS1-1) Plants, algae (including phytoplankton), and many microorganisms use the energy from light to make sugars (food) from carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water through the process of photosynthesis, which also releases oxygen.
How does matter sustain life?
The complex structural organization of organisms accommodates the capture, transformation, transport, release, and elimination of the matter and energy needed to sustain them. As matter and energy flow through different organizational levels—cells, tissues, organs, organisms, populations, communities, and ecosystems—of living systems, chemical elements are recombined in different ways to form different products. The result of these chemical reactions is that energy is transferred from one system of interacting molecules to another.
What is the Clarification Statement and Assessment Boundary?
Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on describing that molecules are broken apart and put back together and that in this process, energy is released. Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include details of the chemical reactions for photosynthesis or respiration.
What is Journey to El Yunque?
Journey to El Yunque engages students in authentic ecological research about the effects of hurricane disturbance on the El Yunque rainforest in Puerto Rico, which is being conducted as part of the NSF-funded Long-Term Ecological Research program. St...
What is the meaning of "construct" in science?
Construct an oral and written argument supported by empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support or refute an explanation or a model for a phenomenon or a solution to a problem. (MS-LS2-4)
What is the purpose of data analysis in 6-8?
Analyzing data in 6–8 builds on K–5 experiences and progresses to extending quantitative analysis to investigations, distinguishing between correlation and causation, and basic statistical techniques of data and error analysis.
What is a PE in engineering?
A Peformance Expectation (PE) is what a student should be able to do to show mastery of a concept. Some PEs include a Clarification Statement and/or an Assessment Boundary. These can be found by clicking the PE for "More Info." By hovering over a PE, its corresponding pieces from the Science and Engineering Practices, Disciplinary Core Ideas, and Crosscutting Concepts will be highlighted.
What is the purpose of MS-LS2-1?
Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem. MS-LS2-1
How many lessons are there in Michigan Forests?
The Middle School unit entitled Climate Change and Michigan Forests consists of 10 lessons on climate change and the local environment in Michigan based on forest ecology research conducted at the University of Michigan. The lessons can be adapted to ...
High Resolution PDF of These Resources
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
Citing Research References
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).