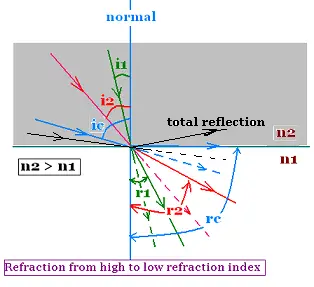
Total Internal Reflection (TIR) When a ray of light goes from denser to rarer medium it bends away from the normal and as the angle of incidence in denser medium increases, the angle of refraction in rarer medium also increases and at a certain angle, angle of refraction becomes 90°, this angle of incidence is called critical angle (C).
What is the equation for total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection. n 1 / n 2 = sin r / sin i. Total internal reflection Critical angle. sin = n 2 / n 1. The list of the names of the symbols that are used in the total internal reflection formula and critical angle: r = angle of refraction. I = angle of incidence. n 1 = refractive index in medium 1. n 2 = refractive index in medium 2. θ = critical angle. Practical Applications of Total Internal Reflection
How to find critical angle physics?
Θcrit= sine-1 (nr/ni) = invsine (nr/ni) The critical angle can be calculated by taking the inverse-sine of the ratio of the indices of refraction. The ratio of n r /n i is a value less than 1.0. In fact, for the equation to even give a correct answer, the ratio of n r /n i must be less than 1.0.
What is the definition of critical angle?
critical angle, in optics, the greatest angle at which a ray of light, travelling in one transparent medium, can strike the boundary between that medium and a second of lower refractive index without being totally reflected within the first medium.
What is the critical angle?
The critical angle is the angle of incidence that gives a 90-degree angle of refraction. The water-air boundary has a critical angle of 48.6 degrees. What is the critical angle GCSE? Light moves from one place to another. The angle of incidence is not as important as the angle of reparative.

What is critical angle and total internal angle?
if the angle of refraction in the air becomes 90°, the angle of incidence in the glass is called the critical angle; if the angle of incidence in the glass is greater than the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs.
What is total internal reflection and critical angle Class 10?
Total internal reflection is a phenomenon which takes place when light travels from denser medium to rarer medium. Critical angle is angle of incidence for which angle of refraction is a right angle.
What is the critical angle?
critical angle, in optics, the greatest angle at which a ray of light, travelling in one transparent medium, can strike the boundary between that medium and a second of lower refractive index without being totally reflected within the first medium.
What is the relation between critical angle and total internal reflection?
This particular angle of incidence is called the critical angle. Here the angle of refraction is 90 degrees. When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the incident ray is reflected back to the medium. We call this phenomenon total internal reflection.
What's total internal reflection?
total internal reflection, in physics, complete reflection of a ray of light within a medium such as water or glass from the surrounding surfaces back into the medium. The phenomenon occurs if the angle of incidence is greater than a certain limiting angle, called the critical angle.
Where is the critical angle?
As we increase the angle of incidence, we reach a point where the angle of refraction is 90° and the refracted ray travels along the boundary of the two media. This angle of incidence is called the critical angle. The critical angle is the angle of incidence where the angle of refraction is 90°.
What is critical angle and its formula?
Critical Angle can be described as the angle of incidence that offers an angle of refraction of 90 degrees. Remember that the critical angle is defined as an angle of incidence value. The critical angle will be 48.6 degrees for water-air boundaries and 61.0 degrees for crown glass-water boundary.
What is critical angle with diagram?
Critical angle: The angle of incidence in the denser medium corresponding to which the angle of refraction in the rarer medium is 90∘ is called the critical angle.
What is another name for critical angle?
Also called angle of stall, critical angle of attack, stalling angle. Aeronautics. the angle of attack, greater than or equal to the angle of attack for maximum lift, at which there is a sudden change in the airflow around an airfoil with a subsequent decrease in lift and increase in drag.
What is total internal reflection give two examples?
Some examples of total internal reflection in daily life are the formation of a mirage, shining of empty test-tube in water, shining of crack in a glass-vessel, sparkling of a diamond, transmission of light rays in an optical fibre, etc.
What is the formula of total internal reflection?
The formula and Applications of Total Internal Reflection θ' becomes π /2 (i.e. 90o) for a certain incident angle θ = θc. Now, at an incident angle θ > θc, Light is completely reflected in material 1 (water) since refracted light can no longer exist.
What are the 2 conditions for total internal reflection?
the light must be travelling from a more dense medium into a less dense medium (ie glass to air) the angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
What is total internal reflection class 10?
Total internal reflection is a phenomenon of reflection of ray back to the same medium when passing from denser medium to rarer medium in a such away that angle of incidence greater than its critical angle.
What is critical angle for class 10th?
The critical angle of a medium can be defined as the angle of incidence of a light ray in the denser medium which is such that the angle of refraction obtained is equal to 90∘.
What is total internal reflection give two examples?
Some examples of total internal reflection in daily life are the formation of a mirage, shining of empty test-tube in water, shining of crack in a glass-vessel, sparkling of a diamond, transmission of light rays in an optical fibre, etc.
What is critical angle formula?
Critical Angle Formula = the inverse function of the sine (refraction index / incident index). Critical Angle is the angle of incidence corresponding to the angle of refraction of 90°.
What is mirage?
Mirage is an optical illusion that is responsible for the emergence of the water layer at short distances in a desert or on the road.
What is the formula to find the critical angle?
The formula to find the critical angle is: \(\begin{array}{l}sin \Theta =\frac{n_{2}}{n_{1}}\end{array} \) Where, n1 is the refractive index in m...
What is the formula to find the total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection is given by the formula: \(\begin{array}{l}\frac{n_{1}}{n_{2}}=\frac{sin r}{sin i}\end{array} \) Where, r is the angle...
Give some examples where optical fibre is used?
Optical fibres are used in telecommunication for information transfer. It is also used in endoscopy.
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection is defined as: The phenomenon which occurs when the light rays travel from a more optically denser medium to a less optically denser medium. Consider the following situation. A ray of light passes from a medium of water to that of air.
What is the critical value of a diamond?
The critical value of the diamond is 23°. This condition is responsible for the total internal reflection in a diamond which makes it shine.
What happens when an incident ray falls on a cladding?
When the incident ray falls on the cladding, it suffers total internal reflection as the angle formed by the ray is greater than the critical angle. Optical fibers have revolutionised the speed with which signals are transferred, not only across cities but across countries and continents making telecommunication one of the fastest modes of information transfer. Optical fibers are also used in endoscopy.
What is the optical illusion that is responsible for the appearance of the water layer at short distances in a desert or?
Mirage: It is an optical illusion that is responsible for the appearance of the water layer at short distances in a desert or on the road. Mirage is an example of total internal reflection which occurs due to atmospheric refraction.
What is the move of light rays?
The light ray moves from a more dense medium to a less dense medium.
What is the total internal reflection and critical angle?
What are the total internal reflection and critical angle? When a ray of light passes from denser to rarer medium, the refracted ray bends away from the normal. Hence, the angle of refraction is greater than the angle of incidence. Gradually if the angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction also increases.
When the angle of incidence in a denser medium is more than the critical angle, the ray of light?
And finally when the angle of incidence in the denser medium is more than the critical angle then the ray of light reflects totally and comes back totally to the denser medium . And thus this total internal reflection is only possible if the light passes from denser to rarer medium.
Why does the light need to pass from denser to rarer medium only (not the reverse one) for Total Internal Reflection to happen?
When light passes from an optically rarer to an optically denser medium, it refracts towards the normal.
What happens when the angle of incidence is increased?
If the angle of incidence is further increased, the rays do not undergo refraction, it gets reflected into the same optically denser medium. This is known as total internal reflection. Definition of total internal reflection: When the angle of incidence in the denser medium is greater than the critical angle the light reflected back into ...
What is the angle of incidence of a denser medium?
Definition of critical angle: At a particular angle of incidence in the denser medium, the refracted ray just grazes the refracting surface making the angle of refraction is equal to 90° . This angle of incidence in the denser medium is called ‘critical angle’,
What is the critical angle of reflection?
When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to 90 ∘ . Mathematically, the critical angle for a medium can be given as, c = ( 1 μ d) for light moving from the medium into air.
What is Total Internal Reflection?
Refraction is the bending of light as it travels from one medium to another of different refractive indexes. When a ray of light moves from one transparent medium to another, its path depends upon the nature of the two mediums and the angle at which the ray strikes the interface between the two mediums.
What is the angle of incidence above which total internal reflection of light takes place?
The angle of incidence above which total internal reflection of light takes place is known as the critical angle . When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to 90 ∘ . It is represented by i c. For the glass-air interface, the critical angle is maximum for red colour and minimum for violet colour.
What happens if the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle?
If the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle, the total internal reflection will occur.
What is the refractive index of a diamond?
The refractive index of diamond is μ d = 2.8 while the refractive index of air is μ d = 1 For a ray of light travelling from diamond to air, the change in the refractive index is huge. Thus, the critical angle for light moving from diamond to air is quite small, just 24.4 ∘
What is the difference between an optical fiber and an inner fibre?
An optical fibre consists of two layers; an outer layer of fibre is composed of a lower refractive index material, while the inner fibre is composed of a higher refractive index material. The inner layer is called the core, while the outer layer is called cladding. The light enters the fibre from one end of the core at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle. It strikes the interface between denser to rarer medium, and it undergoes total internal reflection within the fibre multiple times before coming out from the other end.
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle none of it is refracted, the ray is answer?
When the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle none of it is refracted, the ray is totally internally reflected , and the law of reflection is obeyed, i = r.
What is the angle of incidence in a dense medium?
the angle of incidence in the dense medium is greater than the critical angle; if the angle of refraction in the air becomes 90°, the angle of incidence in the glass is called the critical angle; if the angle of incidence in the glass is greater than the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs.
What happens if a ray leaves a dense medium?
If it is leaving the more dense medium, this refraction would be expected to bend the ray away from the normal as it emerges.
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection is a very useful natural phenomenon since it can be used to confine light. One of the most common applications of total internal reflection is in fibre optics. An optical fibre is a thin, transparent fibre, usually made of glass or plastic, for transmitting light.
What is the critical angle of light moving from glass to air?
Each pair of media have their own unique critical angle. For example, the critical angle for light moving from glass to air is 42 °, and that of water to air is 48,8 °.
What is the critical angle of incidence?
As we increase the angle of incidence, we reach a point where the angle of refraction is 90 ° and the refracted ray travels along the boundary of the two media. This angle of incidence is called the critical angle.
What is it called when light rays are reflected back into the air?
When the entire incident light ray travelling through an optically denser medium is reflected back at the boundary between that medium and another of lower optical density, instead of passing through and being refracted, this is called total internal reflection.
When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to?
Figure 5.15: When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to 90 °.
Which medium is the incident ray always in?
Remember that for total internal reflection the incident ray is always in the denser medium!
Is refraction towards the normal or the less dense?
Refraction towards the normal (air is less dense than water).
What is total internal reflection?
Total internal reflection is a very useful natural phenomenon since it can be used to confine light. One of the most common applications of total internal reflection is in fibre optics. An optical fibre is a thin, transparent fibre, usually made of glass or plastic, for transmitting light.
What is the total internal reflection of an incident angle?
For incident angles greater than 48,8 ° total internal reflection will occur.
What is the critical angle of incidence?
As we increase the angle of incidence, we reach a point where the angle of refraction is 90 ° and the refracted ray travels along the boundary of the two media. This angle of incidence is called the critical angle.
What is it called when light rays are reflected back into the air?
When the entire incident light ray travelling through an optically denser medium is reflected back at the boundary between that medium and another of lower optical density, instead of passing through and being refracted, this is called total internal reflection.
When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to?
Figure 5.15: When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to 90 °.
What is the critical angle of light moving from glass to air?
Each pair of media have their own unique critical angle. For example, the critical angle for light moving from glass to air is 42 °, and that of water to air is 48,8 °.
Which medium is the incident ray always in?
Remember that for total internal reflection the incident ray is always in the denser medium!
What is the angle of incidence of total internal reflection?
The phenomenon occurs if the angle of incidence is greater than a certain limiting angle, called the critical angle. In general, total internal reflection takes place at the boundary between two transparent media when a ray of light in a medium of higher index of refraction approaches the other medium at an angle of incidence greater than ...
Why do indices of refraction depend on wavelength?
Because indices of refraction depend on wavelength, the critical angle (and hence the angle of total internal reflection) will vary slightly with wavelength and, therefore, with colour. At all angles less than the critical angle, both refraction and reflection occur in varying proportions.
How are light rays conducted?
Light rays may be conducted over long, twisting paths by multiple total internal reflection in glass or plastic rods or fibres. See also fibre optics. Read More on This Topic. optics: Total internal reflection. When a ray of light emerges obliquely from glass into air, the angle of refraction between ray and normal is greater than the angle ...
What is Total Internal Reflection?
Total internal reflection happens at a time when a light ray that travels from a denser to a rarer medium. The ray is incident at an angle of incidence that is greater than the critical angle. After that, the light rays are reflected in another denser medium. It is the same medium before reflection. The entire process is known as Total internal reflection.
When a light ray is incident on a surface at an angle greater than the critical angle, the ray?
That time when the ray is incident on the surface at an angle greater than the critical angle, the ray comes back to the same medium. The entire procedure of returning a light ray away from the denser medium is known as Total Internal Reflection. (Image to be added soon)
What is the incident ray angle of a denser medium corresponding with the refracted ray angle?
The incident ray angle of the denser medium corresponding with the refracted ray angle of the rarer medium is 90°. This is called the Total internal reflection critical angle (ic).
What is the critical angle between two claddings?
Calculate the value of other glass’s refractive index such that the critical angle between the two cladding is 60°.
What is the process of a light ray incident at an angle of incidence greater than the critical angle?
After that, the light rays are reflected in another denser medium. It is the same medium before reflection. The entire process is known as Total internal reflection.
What does the increase in angle of incident result in?
The above statement explains that the increase in the angle of incident results in the increment of the angle of refraction.
What is the refractive index?
Refractive index is the measurement of the curving of a ray that passes from one medium to another medium.

What Is Total Internal Reflection?
- Refraction is the bending of light as it travels from one medium to another of different refractive indexes. When a ray of light moves from one transparent medium to another, its path depends upon the nature of the two mediums and the angle at which the ray strikes the interface between the two mediums. When a ray of light moving from one medium to another undergoes complete …
Understanding Total Internal Reflection
- Consider the situation given below: A point source of light, marked as \(O\), is kept at the corner of a denser medium. Let this medium be water. \(XY\) represents the interface that separates the denser medium from the rarer medium (let it be air). As the light rays move from a denser medium to the rarer medium, it undergoes refraction and moves away from the normal. Suppose we incr…
Critical Angle
- The angle of incidence above which total internal reflection of light takes place is known as the critical angle. When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to \(90^\circ \). It is represented by \({i_c}\). For the glass-air interface, the critical angle is maximum for red colour and minimum for vio...
Applications of Total Internal Reflection
- The phenomenon of total internal reflection is responsible for the functioning of various optical instruments like periscopes, binoculars, spectroscopes, and microscopes. Here are a few more applications of the total internal reflection: 1. Optical Fibre An optical fibre consists of two layers; an outer layer of fibre is composed of a lower refractive index material, while the inner fibre is co…
Summary
- When a ray of light moving from one medium to another undergoes complete reflection back into the medium that it came from, such a phenomenon is known as the total internal reflection of light. The minimum angle of incidence for which total internal reflection of light takes place is the critical angle. When the angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle, the angle of refraction is …
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q.1. What are the basic conditions for total internal reflection? Ans: Two conditions are: 1. The light must travel from a denser medium to a rarer medium. 2. The light rays must be incident at an angle greater than the critical angle. Q.2. Give the formula for critical angle? Ans:The critical angle for medium/air interface can be calculated using the formula: \(c = \,\left( {\frac{1}{{{\mu _d}}}} \…