
What is the function of the aqueous humor in the eye?
Aqueous Humor Flow and Function. Aqueous humor is the fluid produced by the eye. It provides nutrition to the eye, as well as maintains the eye in a pressurized state. Aqueous humor flows from the ciliary body into the anterior chamber, out through a spongy tissue at the front of the eye called the trabecular meshwork and into a drainage canal ...
How does the ciliary body produce aqueous humour?
Without getting too technical, the ciliary body constantly produces aqueous humour (located in the anterior chamber near the lens of the eye). For proper functioning, the production must be balanced by drainage at an equal rate.
Where is aqueous humour secreted from?
Aqueous humour is secreted into the posterior chamber by the ciliary body, specifically the non-pigmented epithelium of the ciliary body ( pars plicata ). 5 alpha-dihydrocortisol, an enzyme inhibited by 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, may be involved in production of aqueous humour.
How does aqueous humour affect intraocular pressure?
Small variations in the production or outflow of aqueous humour will have a large influence on the intraocular pressure.
Which part of the eye produces the aqueous humour?
the ciliary bodyAqueous humor is produced by the ciliary body, in uveoscleral route, it flows from the posterior chamber through the pupil into the anterior chamber and then (shown by dashed lines and arrowheads) through the face of the ciliary body and iris root to the ciliary muscle and suprachoroidal space to either veins in the ...
How is aqueous humor formed?
The formation and chemical composition of aqueous humor is accomplished via three processes - diffusion, ultrafiltration, and active secretion by the ciliary processes - linear folds projecting from the ciliary body into the space behind the iris where the lens ligaments and ciliary muscle attach to the eyeball.
Which part of ciliary body produces aqueous humor?
ciliary epitheliumThe ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor. The aqueous humor is produced in the non-pigmented portion of the ciliary body.
What is aqueous humour in human eye?
Aqueous humor is the clear liquid inside the front part of the eye. It nourishes the eye and keeps it inflated. The eye constantly produces a small amount of aqueous humor while an equal amount flows out through the trabecular meshwork in the drainage angle.
What part of the eye produces aqueous humor quizlet?
The ciliary body is a part of the eye that includes the ciliary muscle, which controls the shape of the lens, and the ciliary epithelium, which produces the aqueous humor.
Which enzymes are involved in aqueous humor formation?
The ciliary epithelium contains enzyme systems that function in the production of aqueous humour. The enzymes sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase [(Na+:K+)ATPase] and carbonic anhydrase participate in the active transport across this epithelium.
What does the ciliary body produce?
The ciliary body produces the fluid in the eye called aqueous humor. It also contains the ciliary muscle, which changes the shape of the lens when your eyes focus on a near object. This process is called accommodation.
What's the difference between vitreous and aqueous humor?
The aqueous humour is a fluid which is between the cornea and lens that helps the eye function properly. Vitreous humour is a fluid which is between the lens and retina that keeps the eye wet.
What does the ciliary body do in the eye?
The ciliary body is found behind the iris and includes the ring-shaped muscle that changes the shape of the lens when the eye focuses. It also makes the clear fluid that fills the space between the cornea and the iris.
What drains aqueous humor from the anterior chamber?
The aqueous humor travels around the lens, through the pupil, bathes the back of the cornea, and drains into Schlemm's canal through the trabecular meshwork.
How much vitreous fluid is in the eye?
Vitreous humor is the primary fluid that makes up much of the interior volume of the eyeball – about 3 ml per eye – and is composed of 98–99% water.
What's the difference between vitreous and aqueous humor?
The aqueous humour is a fluid which is between the cornea and lens that helps the eye function properly. Vitreous humour is a fluid which is between the lens and retina that keeps the eye wet.
What are the three main functions of aqueous humor?
The major functions of aqueous humor include maintaining intraocular pressure, providing nutrients to the cornea and lens (which are avascular), and removing wastes from the cornea and lens.
What is aqueous humor quizlet?
Aqueous humor. A clear, watery fluid that fills the space between the cornea and iris (anterior cavity).
What's the function of aqueous humor?
Aqueous humor - the clear, watery fluid between the cornea and the front of the vitreous. The aqueous humor bathes and nourishes the lens and maintains pressure within the eye. Since the lens and cornea have no blood supply, the aqueous humor performs the blood's job of carrying nutrients to those structures.
How is aqueous humour produced?
Aqueous humour is continually produced by the ciliary processes and this rate of production must be balanced by an equal rate of aqueous humour drainage.Small variations in the production or outflow of aqueous humour will have a large influence on the intraocular pressure.
Which body secretes aqueous humour?
Production. Aqueous humour is secreted into the posterior chamber by the ciliary body , specifically the non-pigmented epithelium of the ciliary body ( pars plicata ). 5 alpha-dihydrocortisol, an enzyme inhibited by 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, may be involved in production of aqueous humour.
What is the effect of glaucoma on visual field?
Uncontrolled glaucoma typically leads to visual field loss and ultimately blindness . Uveoscleral outflow of aqueous humour can be increased with prostaglandin agonists, while trabecular outflow is increased by M3 agonists. Fluid production can be decreased by beta blockers, alpha2-agonists, and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
What is the aqueous humor?
Aqueous humour. Schematic diagram of the human eye. The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball.
What keeps the eyeball taut?
Maintains the intraocular pressure and inflates the globe of the eye. It is this hydrostatic pressure which keeps the eyeball in a roughly spherical shape and keeps the walls of the eyeball taut.
Where is aqueous humor located?
It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humour, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also known as the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber. Blood cannot normally enter the eyeball.
What causes a visual field defect?
Glaucoma is a progressive optic neuropathy where retinal ganglion cells and their axons die causing a corresponding visual field defect. An important risk factor is increased intraocular pressure (pressure within the eye) either through increased production or decreased outflow of aqueous humour. Increased resistance to outflow of aqueous humour may occur due to an abnormal trabecular meshwork or due to obliteration of the meshwork resulting from injury or disease of the iris. However, increased interocular pressure is neither sufficient nor necessary for development of primary open angle glaucoma, although it is a major risk factor. Uncontrolled glaucoma typically leads to visual field loss and ultimately blindness .
How Does Aqueous Humor Work?
Without getting too technical, the ciliary body constantly produces aqueous humour (located in the anterior chamber near the lens of the eye). For proper functioning, the production must be balanced by drainage at an equal rate.
Where is the aqueous humor located?
Aqueous Humor Location. The anterior and posterior chambers of the eye contain aqueous, thin, watery fluid. The anterior chamber is located between the iris (the coloured part of the eye) and the cornea's inner surface (the front of the eye). The posterior chamber is behind the iris and ahead of the lens. A large portion of the eyeball is made up ...
Why are minor changes in the production or outflow of aqueous humour significant?
Even minor changes in the production or outflow of aqueous humour are significant because they have a big impact on your intraocular pressure.
What is the fluid produced by the eye called?
The fluid produced by the eye is known as aqueous humour. It feeds the eye and keeps it under pressure. Aqueous humour flows from the ciliary body into the anterior chamber, then through the trabecular meshwork, spongy tissue at the front of the eye, and into a drainage canal (which is a dark blue region next to the trabecular meshwork.
How much humour does the ciliary body produce?
On average, the ciliary body produces aqueous humour around 2.5 μl per minute. The three processes that play a part in this production include the following:
What are the three chambers of the eye?
The anterior chamber, posterior chamber, and vitreous chamber are the three chambers of your eye. The vitreous chamber is the large chamber at the back of your eye; the anterior chamber is the space between your cornea and iris, and the posterior chamber is the space between your iris and your eye's lens. Aqueous humour fills both the anterior and ...
What happens when the fluid in the eye flows out of the eye?
When some of the fluid (aqueous humour) produced by the ciliary body of the eye flows freely out of the eye, intraocular pressure remains normal. This fluid nourishes the eye while also keeping it under pressure.
What is aqueous humor?
Aqueous Humor Flow and Function. Aqueous humor is the fluid produced by the eye. It provides nutrition to the eye, as well as maintains the eye in a pressurized state.
Which pit or depression at the center of the macula provides the greatest visual acuity?
Fovea: The pit or depression at the center of the macula that provides the greatest visual acuity. Iris: The colored ring of tissue behind the cornea that regulates the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil.
What is the tough outer coat that protects the entire eyeball?
Sclera : The tough outer coat that protects the entire eyeball. Trabecular meshwork: Spongy tissue located near the cornea through which aqueous humor flows out of the eye. Vitreous: Clear jelly-like substance that fills the eye from the lens to the back of the eye.
What is the role of pigmented epithelium in the retina?
Retinal Pigmented Epithelium (RPE): A layer of cells that protects and nourishes the retina, removes waste products , prevents new blood vessel growth into the retinal layer and absorbs light not absorbed by the photoreceptor cells ; these actions prevent the scattering of the light and enhance clarity of vision.
What is the bundle of nerve fibers at the back of the eye that carry visual messages from the retina to the brain?
Optic nerve : The bundle of nerve fibers at the back of the eye that carry visual messages from the retina to the brain. Photoreceptors: The light sensing nerve cells (rods and cones) located in the retina. Pupil: The adjustable opening at the center of the iris through which light enters the eye.
What is the effect of glaucoma on the optic nerve?
In open-angle glaucoma, fluid does not flow freely through the trabecular meshwork, causing an increase in intraocular pressure, damage to the optic nerve and vision loss.al. Most, but not all, forms of glaucoma are characterized by high eye (intraocular) pressure.
Where is Bruch's membrane located?
Bruch's membrane: Located in the retina between the choroid and the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) layer; provides support to the retina and functions as the 'basement' membrane of the RPE layer. Ciliary body: Part of the eye, above the lens, that produces the aqueous humor.
How is aqueous humor produced?
Aqueous humor is constantly produced by the ciliary processes and this rate of production need to be balanced by an equal rate of aqueous humor drainage. Small variations in the production or outflow of aqueous humor will have a large influence on the intraocular pressure.
What are the structures that are involved in aqueous humor?
The primary eye structures connected to aqueous humor dynamics are the ciliary body (the site of aqueous humor production), and the trabecular meshwork and the uveoscleral path (the principal places of aqueous humor outflow). Aqueous humor is produced into the posterior chamber by the ciliary body, particularly the non-pigmented epithelium ...
Why does aqueous humor increase resistance?
Increased resistance to outflow of aqueous humor might occur due to an unusual trabecular mesh work or to obliteration of the meshwork due to injury or disease of the iris. However, increased interocular pressure is neither enough nor necessary for advancement of main open angle glaucoma, although it is a major risk element.
What is aqueous humor?
What is an aqueous humor and what does the aqueous humor do? The aqueous humor is a transparent, watery fluid similar to plasma, however consisting of low protein concentrations. It is produced from the ciliary epithelium, a structure supporting the lens. It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humor, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also called the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber.
Where does aqueous humor flow?
From there, the aqueous humor exits the eye through the trabecular meshwork into Schlemm’s canal (a channel at the limbus, i.e., the signing up with point of the cornea and sclera, which encircles the cornea) It streams through 25-30 collector canals into the episcleral veins. The best resistance to aqueous flow is offered by the trabecular meshwork (esp. the juxtacanalicular part), and this is where most of the aqueous outflow happens. The internal wall of the canal is very delicate and allows the fluid to filter due to high pressure of the fluid within the eye. The secondary route is the uveoscleral drain, and is independent of the intraocular pressure, the aqueous circulations through here, but to a lower level than through the trabecular meshwork (approx. 10% of the total drainage whereas by trabecular meshwork 90% of the total drain).
What keeps the eyeball in a roughly round shape?
Keeps the intraocular pressure and pumps up the globe of the eye. It is this hydrostatic pressure which keeps the eyeball in a roughly round shape and keeps the walls of the eyeball tight.
Where is the vitreous humor located?
It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humor, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina , also called the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber.
What is the aqueous humor?
The aqueous humor is what fills up the eye’s anterior and posterior chamber. It is also responsible for your eye’s shape.
Where is the aqueous humor located?
The aqueous humor is a clear fluid located at the front part of the eye. Because the eye doesn’t contain blood vessels, the aqueous humor is responsible for providing nutrients to the eye. The aqueous humor also drains out any excess material and waste from the eye.
Why does my eye float?
It means that your eye is either producing excess liquid or that your aqueous humor is not properly able to drain itself through the trabecular network. The vitreous humor often becomes stringy as you get older. This may cause small parts to detach and float around your eye.
Why is vitreous humor important?
It plays a more important role in the early years of life, providing structure to the eye and protecting the retina. Anything that gets stuck in the vitreous humor must be removed using surgical procedures.
How to repair a macular hole?
It is the part of the eye that lets you see things in detail. If a part of your macula breaks, it could result in a hole that causes vision problems . Some macular holes heal on their own, while surgery is needed to repair others. Surgery involves removing the vitreous liquid and supplanting it with a mixture of gas and liquid. You will have to be face down for one to two days or even a few weeks after this surgery. You will usually not be allowed to fly for two months to prevent changes in air pressure from causing the bubble to increase in size, which could result in additional eye pressure.
How to protect the eye from dust?
Allow the cornea to expand , so it can protect the eye against dust, particles, and bacteria that can cause harm. Preserve ocular pressure. Transport nutrients, including vitamin C. The aqueous humor is produced by a part of the eye called the ciliary body, located above the eye’s lens.
What are the two substances in the eye?
The retina, pupil, iris, and cornea are well-known. The eye also consists of two water and gel-like substances called the aqueous humor ( Learn More) and vitreous humor. ( Learn More) Damage to either of these can occur because of age, injury, and other conditions. Problems with the aqueous and vitreous humor may require surgery.
Which structure in the eye focuses light rays onto the retina?
The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light rays onto the retina. Lower eyelid. Skin that covers the lower part of the eyeball, including the cornea, when closed. Macula. The central portion of the retina that allows us to see fine details. Optic nerve.
Which layer of the eye senses light?
The opening in the middle of the iris through which light passes to the back of the eye. Retina. The light-sensitive nerve layer that lines the inside of the back of the eye. The retina senses light and creates impulses that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain. Sclera.
What is the white part of the eyeball?
The white visible portion of the eyeball. The muscles that move the eyeball are attached to the sclera. Suspensory ligament of lens. A series of fibers that connects the ciliary body of the eye with the lens, holding it in place.
What is the anterior chamber of the eye?
Anterior chamber. The front section of the eye's interior where aqueous humor flows in and out, providing nourishment to the eye.
What part of the eye is covered by the skin?
Upper eyelid. Skin that covers the upper part of the eyeball, including the cornea, when closed.
What is the clear dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye?
Cornea. The clear, dome-shaped surface that covers the front of the eye.
Which membrane is responsible for supplying blood to the outer portion of the retina?
Choroid. The thin, blood-rich membrane that lies between the retina and the sclera and is responsible for supplying blood to the outer portion of the retina.
Which part of the retina has the highest density of cones?
has the highest density of cones in the retina, the center of the neural portion of the retina
Where is the membranous labyrinth found?
sections of the membranous labyrinth found within vestibule

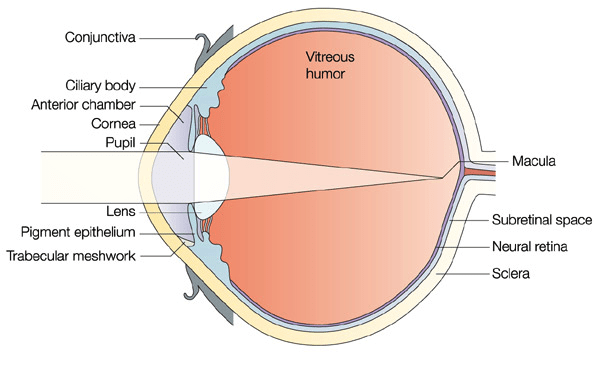
Overview
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humour, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also known as the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber. Blood cannot normally enter the eyeball.
Structure
• Amino acids: transported by ciliary muscles
• 98% water
• Electrolytes (pH = 7.4 -one source gives 7.1 )
• Ascorbic acid
Function
• Maintains the intraocular pressure and inflates the globe of the eye. It is this hydrostatic pressure that keeps the eyeball in a roughly spherical shape and keeps the walls of the eyeball taut.
• Provides nutrition (e.g. amino acids and glucose) for the avascular ocular tissues; posterior cornea, trabecular meshwork, lens, and anterior vitreous.
Clinical significance
Glaucoma is a progressive optic neuropathy where retinal ganglion cells and their axons die causing a corresponding visual field defect. An important risk factor is increased intraocular pressure (pressure within the eye) either through increased production or decreased outflow of aqueous humour. Increased resistance to outflow of aqueous humour may occur due to an abnormal trabecular meshwork or due to obliteration of the meshwork resulting from injury or di…
Additional Images
• Structures of the eye labeled
• Another labeled view of the structures of the eye
• Sectional Anatomy of the Eye in greater detail, showing Anterior and Posterior Chambers in Anterior Cavity, and Posterior Cavity; also Canal of Schlemm, Ciliary body, and Ora serrata
See also
• Vitreous Humour
External links
• "Anatomy diagram: 02566.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.
Production of Aqueous Humor
- The aqueous humor is formed and reabsorbed continually in the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye. The formation and reabsorption of this fluid are determined by the volume of aqueous humor remaining and intraocular pressure of the eye. However, the standard rate of production from the ciliary body in the anterior cavity is 2µL/min. Most of ...
The Roles of Aqueous Humor
- Key functions of the aqueous humor include; 1. It inflates the globe of the eye and maintains intraocular eye pressure. Just to mention, intraocular eye pressure is the hydrostatic pressure responsible for keeping the eyeball in a spherical shape and keeps the eyeball walls taut. 2. It nourishes the eye tissues, including the lens, trabecular meshwork, cornea, and anterior vitreous…
Drainage of Aqueous Humor
- As mentioned, aqueous humor is continually produced and secreted through the ciliary processes. However, the rate of production should be equal to the rate of drainage. Otherwise, a small variation in the rate of production and drainage will affect the intraocular pressure. That said, the aqueous humor first drains through the posterior chamber and flows through a tight space betw…
Clinical Significance of The Aqueous Humor
- Like other parts of the eye, the aqueous humor is a fundamental component, ensuring that the eyes’ health and optical physics are maintained. Continuous formation and drainage of this fluid are crucial for the eye’s size, shape, and quality of vision. That said, glaucomais a major eye condition that results from imbalanced formation and drainage of aqueous humor. Glaucoma is …
The Bottom Line
- The importance of aqueous humor in the eye shouldn’t be understated. It nourishes, supports the eye structure, and maintains intraocular pressure.